

The words 'Paganism' and 'Pagan' come from the Latin 'paganus,' meaning 'country dweller. In simplest terms - Paganism is a religion of place, or a native religion, for example the Native American's religion is Pagan, Hinduism is a form of Paganism. All Pagan religions are characterized by a connection and reverence for nature, and are usually polytheistic i.e. have many Gods and/or Goddesses.
Paganism is a religion of nature, in other words Pagans revere Nature. Pagans see the divine as immanent in the whole of life and the universe; in every tree, plant, animal and object, man and woman and in the dark side of life as much as in the light. Pagans live their lives attuned to the cycles of Nature, the seasons, life and death.
Unlike the patriarchal religions (Christianity, Islam, Judaism) the divine is female as well as male and therefore there is a Goddess as well as a God. These deities are within us as well as without us (immanent); they are us.
They are not simply substitutes for the Muslim or Judeo-Christian God. This is because the Gods of the major religions tend to be super-natural i.e. above nature whereas Pagan deities are natural, symbolizing aspects of nature or human nature. Having said that God and Goddess are split from the Great Spirit or Akashka which probably equates to the God of the patriarchal religions.
The Goddess represents all that is female and the God represents all that is male. But because nature is seen as female the Goddess has a wider meaning. Often called Mother Earth or Gaia she is seen as the creatrix and sustainer of life, the mother of us all which makes all the creatures on the planet our siblings.
There are sub-groups of named Gods and Goddesses called Pantheons, drawn from the distant past, for example Isis and Osiris from Egypt or Thor, Odin, Freya et al from Norse religion and mythology.
Ancient Pagans would have worshipped one or a small number of Gods and Goddesses, while often recognizing the validity of other people's deities.
The concept of an overall, un-named Goddess and God, the sum totals of all the others, appears to be a recent one but individual named deities represent particular human qualities or archetypes and are often used as a focus for celebrations and spiritual rites.
Paganism has developed alongside mankind for thousands of years; as cultures have changed so has Paganism, yet it is grounded in deep rooted genetic memories that go back to neolithic times and before. Thus Paganism is not just a nature religion but a natural religion.
Paganism in the west takes a number of forms including Wicca - Druidism, and Shamanism.
To Pagans the four ancient elements, Earth, Air, Fire and Water have special significance. The importance of these is hard to define because they have so many correspondences, for example they are associated with the four directions, North, East, South and West.
Each element is a kind of spiritual substance from which all things are made especially ourselves and at the same time are Guardians both of ourselves and of the Goddess and God, and guarding the gateways between this world and the other world.
Many Pagans believe in reincarnation in some form. It gives Pagans a substantially different view of life. Early Christians saw Karma as a kind of treadmill, trapping people in endless reincarnations, never free. But Pagans see reincarnation as, at best, a chance to improve or to continue unfinished work, and at worst just a simple recycling of souls.
Paleo-paganism: the standard of paganism, a pagan culture which has not been disrupted by "civilization" by another culture - Bushmen modern (who are probably becoming meso-pagans), ancient Celtic religion (Druidism), the religions of the pre-patriarchal cultures of Old Europe, Norse religion, pre-Columbian Native American religions, etc.
Civilo-paganism: the religions of "civilized" communities which evolved in paleo-pagan cultures -- Classical Greco-Roman religion, Egyptian religion, Middle-Eastern paganism, Aztec religion, etc.
Meso-paganism: a group, which may or may not still constitute a separate culture, which has been influenced by a conquering culture, but has been able to maintain an independence of religious practice -- many Native American nations, etc.
Syncreto-paganism: similar to meso-pagan, but having had to submerge itself into the dominant culture, and adopt the external practices and symbols of the other religion -- the various Afro-diasporic traditions (Voudoun, Santeria, etc.), Culdee Christianity, etc.
Neopaganism: attempts of modern people to reconnect with nature, using imagery and forms from other types of pagans, but adjusting them to the needs of modern people.
Wicca - in all its many forms
Neo-Shamanism
Neo-Druidism
Asatru and other forms of Norse neopaganism
No-Native American practices
The range of things labeled 'Women's Spirituality'
The Sabaean Religious Order
Church of All Worlds
Discordianism
Radical Faeries and other "Men's Spirituality" movements
Certain people within Thelema and Hedonistic Satanism
Some of eco-feminism
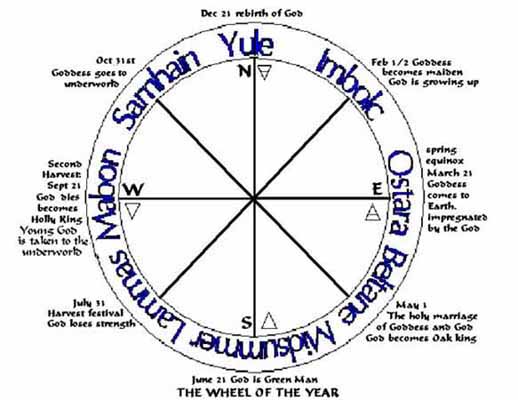
This wheel is sometimes called the Gardnerian Wheel because it is a combination of two ancient wheels (acknowledgements to Kenny Klein). The hunting wheel, the oldest, has two God births: The Oak King is born at midsummer and rules through to Yule when he dies and the Holly King is born. The agricultural wheel has the young God born at Ostara, symbolic of the sun/son rising in the East. He dies in the second harvest, Mabon, which means 'the young Lord'.
In the different traditions these holidays (holy days) may have different names, for example Imbolc is called the festival of light in the northern tradition.
Western Pagans have no fixed temples in which to worship but instead (usually) make a circle around all the celebrants (or the celebrants themselves form a circle) in a room or in a clearing or on a beach or find a naturally ocurring circle such as a grove or use one of the ancient stone circles. Pagans have no hierarchy like the established religions so Pagans are free to follow whatever spiritual path they choose.
Pagans like to celebrate more rites of passage than the prevailing culture. Most people see two rites of passage: coming of age (18 or 21) and marriage. Christians also get a first one, the Christening, though the subject is unable to experience it.
The Pagan equivalent of a Christening is a Naming ceremony. Other rites of passage may include Child - celebrating change from baby to child, Puberty and so on. Marriage is called hand-fasting and this may be arranged for eternity or just for a year-and-a-day, renewable. The latter is a great stabilizer against casual relationships and divorces, providing some level of commitment yet recognizing that some relationships will not last.
Changes it's face roughly every 28-29 days, at about the same rate that female humans menstruate, it has long been associated with the feminine and hence the Goddess - Artemis and Hecate.
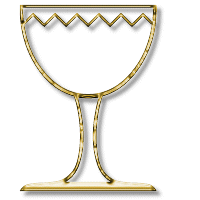
It is a container and is associated with the womb and vagina, and hence a symbol of the Goddess. Two examples of Chalices in myth are the Cup that Jesus had drunk from at the last supper, and the Holy Grail, which the knights of the round table had to search for in order for Arthur (and the land) to become whole again.
It is a dagger used in rituals, primarily to focus and concentrate power. It is a phallic symbol and as a cutting tool a divider, and thus represents The God. Magic swords are another version of the Atheme and are popular in fantasy novels and myth. One example is Excaliber, which King Arthur uses via "divine right". Another is Stormbringer, as used by Elric in the stories written by Micheal Moorcock. Note the dual imagery. Excalibre was used as a force for order, Stormbringer drank souls and was a force for Chaos. Tools are only as good as their user.
Pentangle or a Pentagram - Goddess

For neo-pagans this is symbolic of the four elements: air, water, earth, fire + spirit. Pythagoras held the number 5 to be the sum of the feminine element (2) and the masculine element (3), so it is also symbolic of a union of masculine and feminine. The symbol also has meaning in Taoism, Hinduism and Islam.
The overlapping arms (which does not appear in all versions) shows how each part is interconnected with the others. The circle around the star represents unity, the self, and wholeness.
One mode of understanding is that the pentagram shown as above (with one point at the top) represents the Goddess, and inverted (with two points at top) the God. Of course the inverted pentagram in Christian belief represents the Devil -- not surprising since the versions of Pan and The God were used to represent such.
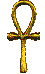
This is an ancient Egyptian symbol representing eternal life. It is said to be taken from a simple sandal strap. Regardless of that, it is also a symbol representing the Goddess and the God and this a Neo-Pagan symbol.
This is an ancient Egyptian symbol. It has three elements. The circle represents the Goddess; the vertical line represents the God, and the horizontal bar is the "scroll of knowledge". Join them together and you get an ankh.
"Neo-Pagan" means "new pagan" (derived from the Latin paganus, "country-dweller") and hearkens back to times before the spread of today's major monotheistic (one god) religions. A good general rule is that most Wiccans are Neo-Pagans but not all Pagans are Wiccans.
Neopagans hold a reverence for the Earth and all its creatures, generally see all life as interconnected, and tend to strive to attune one's self to the manifestation of this belief as seen in the cycles of nature.
Pagans are usually polytheistic (believing in more than one god), and they usually believe in imanance, or the concept of divinity residing in all things. Many pagans, though polytheistic, see all things as being part of one Great Mystery. The apparent contradiction of being both polytheistic and monotheistic can be resolved by seeing the God/desses as masks worn by the Great Mystery. Other pagans are simply monotheistic or polytheistic, and still others are atheistic.
Some people believe paganism to be a religion within itself; others see it as a belief system (such as monotheism) that can be incorporated into religions like Wicca or Druidism; others see it as a broad category including many religions. The fact that we are re-creating religion for ourselves after centuries of suppression makes us very eclectic and very concerned with the "rightness" of a particular thing for the individual. So when you see some people calling it a religion and others not, when you see it capitalized in some instances and not in others, don't be confused - we're all still basically talking about the same thing.
Neo-Paganism is any of several spiritual movements that attempt to revive the ancient polytheistic religions of Europe and the Middle East. These movements have a close relationship to ritual magic and modern witchcraft. Neo-Paganism differs from them, however, in striving to revive authentic pantheons and rituals of ancient cultures, though often in deliberately eclectic and reconstructionist ways, and by a particularly contemplative and celebrative attitude.
Typically people with romantic feelings toward nature and deep ecological concerns, Neo-Pagans centre their dramatic and colourful rituals around the changes of the seasons and the personification of nature as full of divine life, as well as the holy days and motifs of the religions by which their own groups are inspired.
Modern Neo-Paganism has roots in 19th-century Romanticism and activities inspired by it, such as the British Order of Druids (which, however, claims an older lineage). Sometimes associated with extreme nationalism, Neo-Pagan groups and sentiments were known in Europe before World War II, but contemporary Neo-Paganism is for the most part a product of the 1960s. Influenced by the works of the psychiatrist Carl Jung and the writer Robert Graves, Neo-Paganists are more interested in nature and archetypal psychology than in nationalism.
Neo-Paganism in the postwar decades has flourished particularly in the United States and the United Kingdom and in Scandinavia. Some of the major Neo-Pagan groups are the Church of All Worlds, the largest of all the pagan movements, which centres on worship of the earth-mother goddess; Feraferia, based on ancient Greek religion and also centred on goddess worship; Pagan Way, a nature religion centred on goddess worship and the seasons; the Reformed Druids of North America; the Church of the Eternal Source, which has revived ancient Egyptian religion; and the Viking Brotherhood, which celebrates Norse rites. Beginning in the late 1970s, some feminists, open to feminine personifications of the deity, became interested in witchcraft and Neo-Paganism.