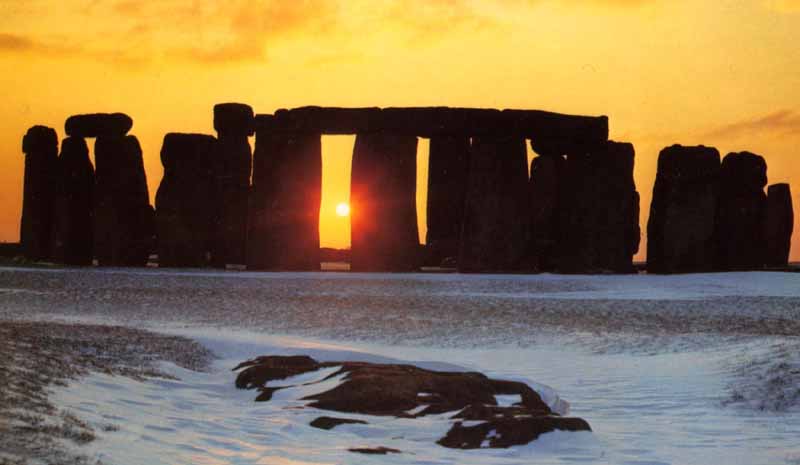


Archaeoastronomy is the study and interpretation of solar, lunar and stellar alignments found at ancient monuments such as pyramids, and other megalithic monuments like Stonehenge Carnac, Newgrange, etc. These monuments are most often on major planetary grid points.
The study of Archaeoastronomy is a cross disciplinary approach which examines the mythology, religion and world views of prehistoric and ancient civilizations through the means of their astronomical practices. It is the study of the study of contemporary native astronomies.
In examining the observations of such peoples, it is possible to gain a certain insight into the ways in which they constructed their own universes and therefore provide a more holistic understanding of the means and motivations of the culture as a whole.
The astronomical inquiry of the ancients must be looked upon as a mechanism of observation and prediction which closely tied them to their environments, depending upon various cultural, religious and mythological bases for validation in the process.
Early man was aware of the movements of celestial bodies in the heavens, especially the Sun. The ancients were also aware that everything ran in cycles of time - hence they invented celestial calendars - observatories - to mark these annual periods of time - significant horizontal astronomical events.
These ancient people were known as the Megalithic Stone Builders who lived on the planet 5,000 years ago. The remnants of their achievements can be found throughout the planet especially where the major grids points intersect.
The ancients used this knowledge to better calculate and intuit when the earth energies would be at their peak. If the energy- ley lines that run down the major axis of their observatory - or power site - is oriented to the Summer Solstice Sunrise, then that will be the day that particular site will experience a peak of power. They used this opportunity to visit these places - which became temples in many cases - to meditate - do out of body work - talk to their Gods - or try to work with interdimensional doorways.
Archaeoastronomy is the anthropology of astronomy, to distinguish it from the history of astronomy. Many of the great monuments and ceremonial constructions of early civilizations were astronomically aligned. The accurate cardinal orientation of the Great Pyramid at Giza, in Egypt, or the Venus alignment of the magnificent Maya Palace of the Governor at Uxmal in Yucatan are outstanding examples. We learn much about the development of science and cosmological thought from the study of both the ancient astronomies and surviving indigenous traditions around the world.

Archaeoastronomy and ethnoastronomy have blossomed into active interdisciplinary fields that are providing new perspectives for the history of our species' interaction with the cosmos.
One hallmark of the new research is active cooperation between professionals and amateurs from many backgrounds and cultures. The benefit of this cooperation has been that archaeoastronomy has expanded to include the interrelated interests in ancient and native calendar systems, concepts of time and space, mathematics, counting systems and geometry, surveying and navigational techniques as well as Geomancy - Dowsing - and the origins of urban planning.
Sadly, sources of such information, both archaeological and ethnographic, are vanishing rapidly in the face of technological progress, population and economic pressures.
-
Archaeoastronomy is the study of ancient or traditional astronomies in their cultural context, utilizing archaeological and anthropological evidence. The anthropological study of astronomical practices in contemporary societies is often called ethnoastronomy, although there is no consensus as to whether ethnoastronomy is a separate discipline or is a part of archaeoastronomy. Archaeoastronomy is also closely associated with historical astronomy, the use of historical records of heavenly events to answer astronomical problems and the history of astronomy, which uses written records to evaluate past astronomical traditions. It is most frequently mentioned with astronomical claims regarding Stonehenge or the pyramids of Egypt. Continued ...
Early Celtic 'Stonehenge' Discovered in Germany's Black Forest Science Daily - October 12, 2011
A huge early Celtic calendar construction has been discovered in the royal tomb of Magdalenenberg, nearby Villingen-Schwenningen in Germany's Black Forest. This discovery was made by researchers at the Romisch-Germanisches Zentralmuseum at Mainz in Germany when they evaluated old excavation plans. The order of the burials around the central royal tomb fits exactly with the sky constellations of the Northern hemisphere. Whereas Stonehenge was orientated towards the sun, the more then 100 meter width burial mound of Magdalenenberg was focused towards the moon. The builders positioned long rows of wooden posts in the burial mound to be able to focus on the Lunar Standstills. These Lunar Standstills happen every 18,6 year and were the 'corner stones' of the Celtic calendar.