

Snoring is the vibration of respiratory structures and the resulting sound, due to obstructed air movement during breathing while sleeping. In some cases the sound may be soft, but in other cases, it can be loud and unpleasant. Snoring during sleep may be a sign, or first alarm, of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Breathing through the open mouth in such a way as to cause a vibration of the uvula and soft palate, thus giving rise to a sound which may vary from a soft noise to a loud unpleasant sound. This most commonly occurs during sleep, or immediately after death.
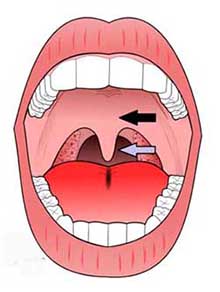
Generally speaking the structures involved are the uvula and soft palate. The irregular airflow is caused by a passageway blockage and is usually due to one of the following:
Mispositioned jaw, often caused by tension in the muscles.
Fat gathering in and around the throat.
Obstruction in the nasal passageway.
Obstructive sleep apnea.
The tissues at the top of airways touching each other, causing vibrations.
Relaxants such as alcohol or drugs relaxing throat muscles.
Sleeping on one's back, which may result in the tongue dropping to the back of the mouth.
Snoring is known to cause sleep deprivation to snorers and those around them, as well as daytime drowsiness, irritability, lack of focus and decreased libido. It has also been suggested that it can cause significant psychological and social damage to sufferers. Multiple studies reveal a positive correlation between loud snoring and risk of heart attack (about +34% chance) and stroke (about +67% chance).
Though snoring is often considered a minor affliction, snorers can sometimes suffer severe impairment of lifestyle. The between-subjects trial by Armstrong et al. discovered a statistically significant improvement in marital relations after snoring was surgically corrected.
New studies associate loud "snoring" with the development of carotid artery atherosclerosis, the risk of brain damage and of stroke. Researchers hypothesize that loud snoring creates turbulence in carotid artery blood flow closest to the airway. Generally speaking, increased turbulence irritates blood cells and has previously been implicated as a cause of atherosclerosis. A U.S. study estimates that roughly one in every 15 Americans is affected by at least a moderate degree of sleep apnea.
Statistics on snoring are often contradictory, but at least 30% of adults and perhaps as many as 50% of people in some demographics snore. One survey of 5,713 Italian residents identified habitual snoring in 24% of men and 13.8% of women, rising to 60% of men and 40% of women aged 60 to 65 years; this suggests an increased susceptibility to snoring as age increases.
Almost all treatments for snoring revolve around clearing the blockage in the breathing passage. This is the reason snorers are advised to lose weight (to stop fat from pressing on the throat), stop smoking (smoking weakens and clogs the throat) and sleep on their side (to prevent the tongue from blocking the throat).[11] A number of other treatment options are also available, ranging from over-the-counter aids such as nasal sprays, nasal strips or nose clips, lubricating sprays, oral appliances and "anti-snore" clothing and pillows, to such unusual activities as playing the didgeridoo.[
Snoring cures almost all revolve around clearing the blockage in the breathing passage. This is the reason snorers are advised to lose weight (to stop fat from pressing on the throat), to stop smoking (smoking weakens and clogs the throat), and to sleep on their side (to prevent the tongue from blocking the throat).
But for many snorers those pieces of advice are not enough.Surgery is one option to cure snoring (for example a uvulopalatopharyngoplasty); dental appliances such as a mandibular advancement splint are another.
There are many devices such as nose clips to keep the nose open and jaw mechanics to keep the jaw in the right position.
Specially made dental appliances called mandibular advancement splints, which advance the lower jaw slightly and thereby pull the tongue forward, are a common mode of treatment for snoring. Such appliances have been proven to be effective in reducing snoring and sleep apnea in cases where the apnea is mild to moderate. Mandibular advancement splints are often tolerated much better than CPAP machines.
Surgery is also available as a method of correcting social snoring. Some procedures, such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, attempt to widen the airway by removing tissues in the back of the throat, including the uvula and pharynx. These surgeries are quite invasive, however, and there are risks of adverse side effects. The most dangerous risk is that enough scar tissue could form within the throat as a result of the incisions to make the airway more narrow than it was prior to surgery, diminishing the airspace in the velopharynx. Scarring is an individual trait, so it is difficult for a surgeon to predict how much a person might be predisposed to scarring. Currently, the American Medical Association does not approve of the use of lasers to perform operations on the pharynx or uvula.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a relatively new surgical treatment for snoring. This treatment applies radiofrequency energy and heat (between 77°C and 85°C) to the soft tissue at the back of the throat, such as the soft palate and uvula, causing scarring of the tissue beneath the skin. After healing, this results in stiffening of the treated area. The procedure takes less than one hour, is usually performed on an outpatient basis, and usually requires several treatment sessions. Radiofrequency ablation is frequently effective in reducing the severity of snoring, but, often does not completely eliminate snoring.
Bipolar radiofrequency ablation, a technique used for coblation tonsillectomy, is also used for the treatment of snoring.
The Cure For Snoring Is...Singing? Smithsonian - January 21, 2014
While there are a number of sophisticated medical treatments available, such as nasal and oral devices as well as surgery, Ojay's solution is more akin to a natural home remedy. The British choir director claims that a series of routine vocalizations, performed 20 minutes a day over the course of less than a month, can reduce snoring significantly.