




Original name: The Persistent Pyramid
Original height: 93.5 m / 312 ft
Base length: 147 m / 490 ft
Angle of inclination: 51° 50' 35'
Date of construction: 3rd and 4th dynasty
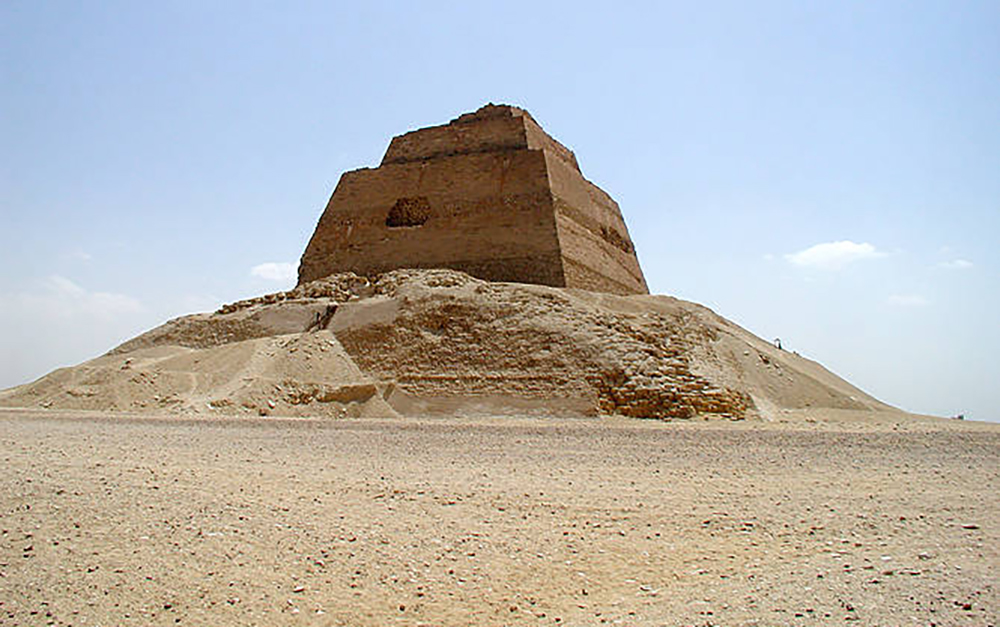
Meidum, Maydum or Maidum is an archaeological site in Upper Egypt. It contains a large pyramid and several mudbrick mastabas. The pyramid was Egypt's first straight-sided one, but it partially collapsed in ancient times.The area is located around 62 miles (100 km) south of modern Cairo.
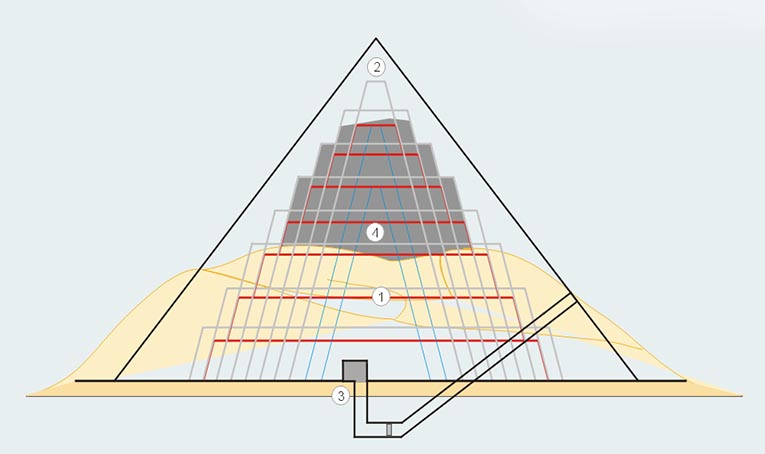
The pyramid of Maidum was originally a seven-stepped pyramid. It was enlarged to an eight-stepped pyramid. Eventually the steps were filled in and a smooth outer facing turned it into a true pyramid. It stands on the desert's edge and is the only structure in the vicinity. It is a huge structure that is surrounded by the debris from the casing that collapsed. When the casing collapsed is uncertain.
Some believe that the collapse was the cause for the change in the angle of the Bent Pyramid. Others believe it did not happen until the Roman times or possibly the Middle Ages. The theory as to the reason for the collapse is that the distribution for the stresses was calculated incorrectly. The stress was outward instead of inward such as in the pyramids at Giza. Another belief is that the smooth outer casing did not provide good bonding for the fill that was placed on there later. The foundation was not sound enough for this change and the way the blocks were laid was not well chosen. The four outer buttress walls gave way and the walls collapsed.
The Maidum Pyramid is thought to have been started by Huni, the last ruler of the 3rd Dynasty, and then completed by his son, Sneferu (Snofru). Sneferu was the first 4th Dynasty pharaoh (2613 - 2494 BC).
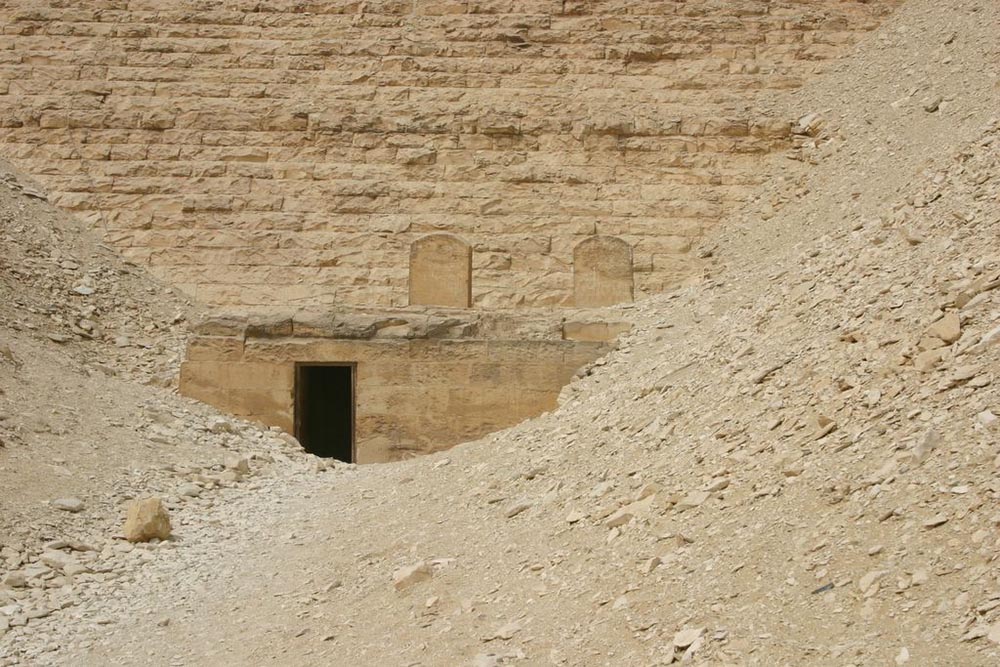
The original size of the pyramid was 144m square and 42m high. The entrance into the pyramid is on the north side up a 30m stairway. A passageway descends down 57m to a level that is below the pyramid's foundation. The passageway levels out and comes to a vertical shaft that leads up to the burial chamber. This chamber has a corbelled roof and the walls are lined in limestone. The construction timbers are still visible in this room. The chamber is on the same level as the pyramid's foundation.
Near the pyramid is a cemetery which contains some important and quite large mastabas. The most noted of these are the twin mastabas of Neferma'at and his wife Itet and Re'hotpe (Rahotep) and his wife Nofret. In the mastaba of Re'hotpe (Rahotep) were the found the statues of Re'hotpe and his wife.
These statues are now in the Egyptian Museum. There is also a mastaba in the cemetery in which the entrance is the robbers' passage. This chamber is not decorated and is a little difficult to get through. Inside the huge blocks of stone that sealed the original entrance are still in place. A little north of the Maidum Pyramid is the remains of the Seila (Silah) step pyramid. It is made of limestone and is thought to be from the 2nd Dynasty.

Snefru - Snofru