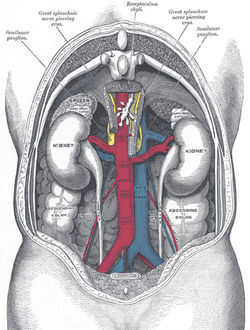

The kidneys are bean-shaped excretory organs in vertebrates. Part of the urinary system, the kidneys filter wastes (especially urea) from the blood and excrete them, along with water, as urine. The medical field that studies the kidneys and diseases affecting the kidney is called nephrology, from the Greek name for the kidney; the adjective meaning "kidney-related" is renal, from the Latin. Read more ...
Scientists Watched Kidneys Age in Months and Found a Kidney Protector SciTech Daily - February 8, 2026
A new study published in Kidney International shows that medications known as SGLT2 inhibitors helped prevent age-related damage to kidney structure and function in the African turquoise killifish. This small vertebrate lives its entire life in just a few months, giving researchers a rare chance to observe aging unfold at high speed. The results help clarify the biological processes behind the strong kidney and heart protection these drugs provide in people, effects that go beyond their original role in controlling blood sugar.
Breakthrough: Scientists Created a 'Universal' Kidney To Match Any Blood Type Science Alert - February 6, 2026
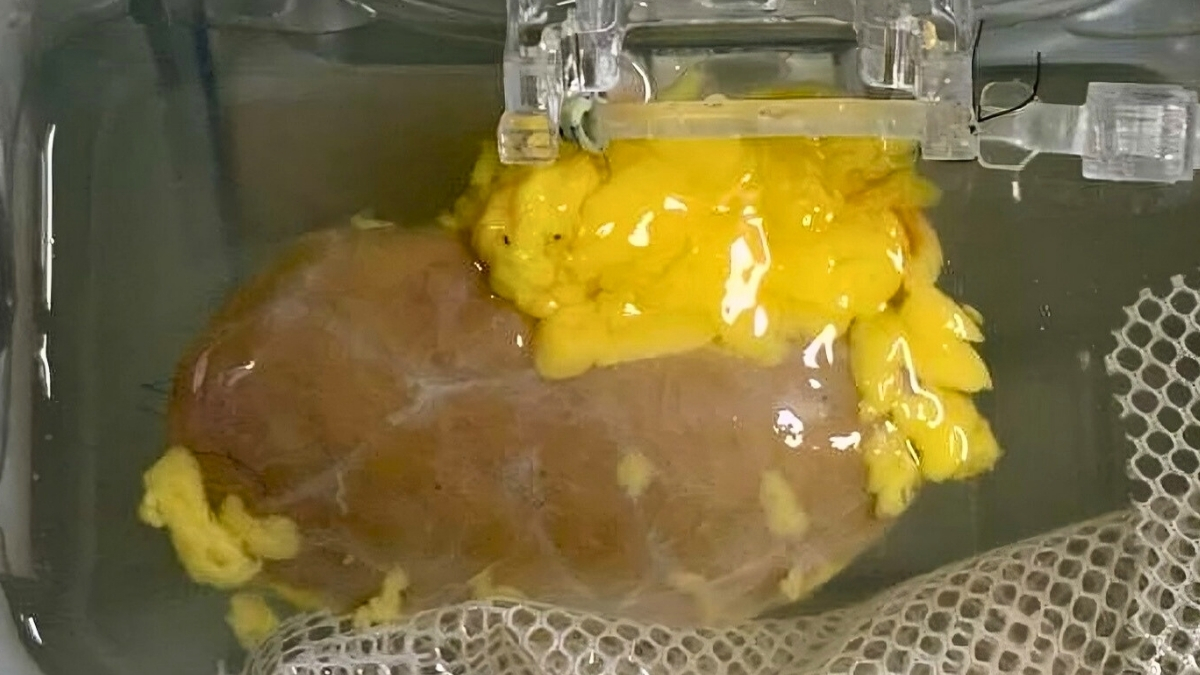
After a decade of work, researchers are closer than ever to a key breakthrough in kidney transplants: being able to transfer kidneys from donors with different blood types than the recipients, which could significantly speed up waiting times and save lives.