

Gaia theory is a class of scientific models of the biosphere in which life fosters and maintains suitable conditions for itself by affecting Earth's environment. The first such theory was created by the English atmospheric scientist, Dr. James Lovelock, who developed his theories in the 1960s before formally publishing them in 1979. He hypothesized that the living matter of the planet functioned like a single organism and named this self-regulating living system after the Greek goddess, Gaia.

Gaia theories have non-technical predecessors in the ideas of several cultures. Meanwhile today, "Gaia theory" is sometimes used among non-scientists to refer to theories of a self-regulating Earth that are non-technical but take inspiration from scientific models. Among some scientists, "Gaia" carries connotations of scientifically quasi-mystical thinking about Earth, and Lovelock's own hypothesis was received initially with much antagonism by the scientific community. No controversy exists, however, that life and the physical environment significantly influence one another.
Gaia theory today is a spectrum of hypotheses, ranging from the undeniable to the radical.
At one end is the undeniable statement that the organisms on the Earth have radically altered its composition. A stronger position is that the Earth's biosphere effectively acts as if it is a self-organizing system which works in such a way as to keep its systems in some kind of equilibrium that is conducive to life. The history of evolution, ecology and climate show that the exact characteristics of this equilibrium intermittently have undergone rapid changes, however, which are believed to have caused extinctions and felled civilizations.
Biologists and earth scientists usually view the factors that stabilize the characteristics of a period as an undirected emergent property of the system; as each individual species pursues its own self-interest, for example, their combined actions tend to have counterbalancing effects on environmental change.
Opponents of this view sometimes point to examples of life's actions that have resulted in dramatic change rather than stable equilibrium, such as the conversion of the Earth's atmosphere from a reducing environment to an oxygen-rich one. However, proponents will point out that those atmospheric composition changes created an environment much more suitable to life.
Some go a step further and hypothesize that all lifeforms are part of a single planetary being called Gaia. In this view, the atmosphere, the seas and the terrestrial crust would be results of interventions carried out by Gaia through the coevolving diversity of living organisms. While the Earth as a unit does not match the generally accepted biological criteria for life itself (Gaia does not reproduce, for instance), many scientists would be comfortable characterizing the earth as a single "system".
The most extreme form of Gaia theory is that the entire Earth is a single unified organism; in this view the Earth's biosphere is consciously manipulating the climate in order to make conditions more conducive to life. Scientists contend that there is no evidence at all to support this last point of view, and it has come about because many people do not understand the concept of homeostasis. Many non-scientists instinctively see homeostasis as an activity that requires conscious control, although this is not so.
Much more speculative versions of Gaia theory, including all versions in which it is held that the Earth is actually conscious or part of some universe-wide evolution, are currently held to be outside the bounds of science. These are discussed in the Gaia philosophy article.
James Hutton made the first scientific expression of an ancient wisdom, Gaia. He saw the Earth like an animal - a physiological system. He popularized the name and notion of 'Gaia', the self-regulating system that maintains comfortable conditions for life at the surface of the Earth.
British biochemist, James Lovelock, formulated a theory called The Gaia Hypothesis - while working with NASA's space program. He was looking for ways to detect life on Mars. The crux of his theory is that living organisms and inorganic material are part of a dynamic system that shape Earth's biosphere. The Earth is a self-regulating environment and the planet itself is the core of a single, unified, cooperating and living system - a superorganism that regulates physical conditions to keep the environment hospitable for lifeforms.
Gaia theory is about the evolution of a tightly coupled systems whose constituents are the biota and their material environment, which comprises the atmosphere, the oceans, and the surface rocks. self-regulation of important properties, such as climate and chemical composition, is seen as a consequence of this evolutionary process. Like living organisms and many closed-loop self-regulating systems, it would be expected to show emergent properties; that is, the whole will be more than the sum of its parts.
American microbiologist Lynn Margulis was Lovelock's principal collaborator for twenty-five years. She is an expert on the role that microorganisms play in evolution. Margulis contends that symbiosis, not chance mutation, is the driving force behind evolution and that the cooperation between organisms and the environment are the chief agents of natural selection -- not competition among individuals. She says that "Darwin's grand vision was not wrong, only incomplete. In accentuating the direct competition between individuals for resources as the primary selection mechanism Darwin (and especially his followers) created the impression that the environment was simply a static arena for "nature, red in tooth and claw.
The Gaia Hypothesis is highly controversial because it intimates that individual species (e.g., ancient anaerobic bacteria) might sacrifice themselves for the benefit of all living things. Furthermore, the hypothesis has yet to be formulated quantitatively and in a scientifically testable manner. However, regardless of the eventual validity of the idea that life controls its environment for its own benefit, the recognition that the Earth's physical, chemical, and biological components interact and mutually alter their collective destiny, by accident or design, is a profound insight.
Gaia science is the study of the Earth as a system. As in physiology, the focus is on the ability of the whole to regulate significant variables, such as temperature and chemical composition. It asks how the system evolves and how it responds to stress and is an integrated approach to Earth science. Ever since we first saw the Earth from space, our view of the Earth has matured. Understanding has grown with increasing information about the trace components in the atmosphere and oceans and through the observation of trends over time. With the gathering of this new information came the predictions of numerical models and Gaia emerged as observational and theoretical science. Read more...
James Lovelock, creator of Gaia hypothesis, dies on 103rd birthday - best known for his theory that the Earth is a self-regulating community of organisms Guardian - July 28, 2022
Lovelock, who was one of the UK's most respected independent scientists, had been in good health until six months ago, when he had a bad fall. Known as something of a maverick, he had been dispensing predictions from his one-man laboratory since the mid-1960s, and in his old age he continued to work.
James Lovelock: Gaia theory creator video on coronavirus and turning 101 BBC - August 3, 2020
James Lovelock, one of BritainÕs greatest scientists, is famous for developing the Gaia hypothesis, which sees the Earth as a self-regulating system. In his long and influential career, he also revealed the chemicals that were destroying the ozone layer. HeÕs just celebrated his 101st birthday and the BBC's chief environment correspondent Justin Rowlatt visited him at his home in Dorset.
New finding may hold key to Gaia hypothesis of Earth as living organism PhysOrg - May 16, 2012
Is Earth really a sort of giant living organism as the Gaia hypothesis predicts? A new discovery made at the University of Maryland may provide a key to answering this question. This key of sulfur could allow scientists to unlock heretofore hidden interactions between ocean organisms, atmosphere, and land -- interactions that might provide evidence supporting this famous theory. The Gaia hypothesis -- first articulated by James Lovelock and Lynn Margulis in the 1970s -- holds that Earth's physical and biological processes are inextricably connected to form a self-regulating, essentially sentient, system.
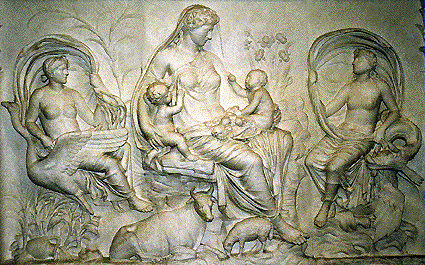
Gaia in Greek Mythology
In the theory of Hesiod, Gaia was the first being, who appeared out of the chaos together with Tartaros (underworld), Nyx (night), Erebos (darkness) und Eros (ghost of love). Without the help of a man she created her sons Uranos (heaven) and Pontos (ocean). She fused with her son Uranos and bore the titans, Kronos Rhea, also Okeanos and Tethis, gods of the great stream, which is winding around the earth. Furthermore the Kyklops and the giants with a hundred amrs. But her man and son Uranos hated these creatures so much that he pushed them back into the womb before they were born, which caused Gaia bad harm. Angry about her tyrannical man Gaia gave a sickle made from firestone to her son Kronos and ordered him to unman his father the next opportunity which was given. Kronos did what hsi mother had told him and throw detached genitals far along the sea. Out of the falling blood drops appeared the Erinnyias (furies), the giants, and also the Meliai (nymphs of the ashen). The phallus prowled on the sea and finally arrived at Paphos (Cypern) - or on the island Kythera/Lakonia. Out of the foam which was formed on the phallus the love-goddess Aphrodite came to being.
When studying metaphysics you learn to connect your consciousness to all things through frequency harmonics which create grid matrices of experience. You come to understand that all things have consciousness and are linked to One Source. Hence the Earth itself would have consciousness linked through a frequency grid system.
The Earth, as a living entity, would also have a chakra system based on 12 major grid points. They are referred to as the acupressure points on the planet. When you physically visit these grid points, your chakra system becomes activated, or heightened, bringing you to higher consciousness awareness, to remember why your soul spiraled into this experience and where it is all going.
Indigenous people, especially the Shaman, the Medicine People, the healers, those who connect with higher frequencies of thought and consciousness, understood the Human - Earth consciousness connection. They recognize the trouble the 'Earth Mother' is having at this point in history as we experience unprecedented Earth Changes.
Many Native American prophecies speak of this time in Earth's history as a shift in consciousness from one cycle to another, the move to a golden age. Gold references alchemy - the evolution of consciousness in the alchemy of time.
Gaia, as the Earth Mother, or Consciousness Creator of our Reality, is a living organism spiraling through cycles of time on all levels of consciousness, following the patterns of sacred geometry, guided from above and below.










Nature Spirits