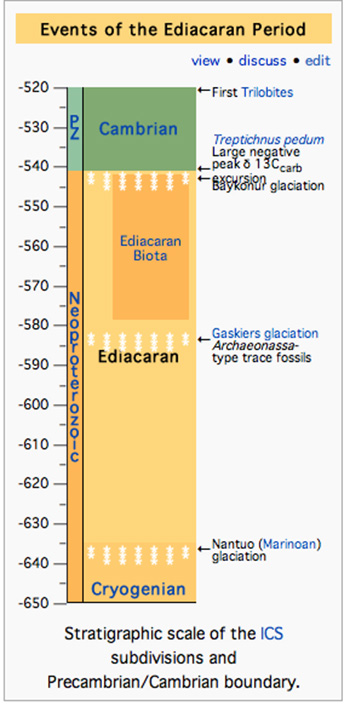

The Ediacaran Period named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia, is the last geological period of the Neoproterozoic Era and of the Proterozoic Eon, immediately preceding the Cambrian Period, the first period of the Paleozoic Era and of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The Ediacaran Period's status as an official geological period was ratified in 2004 by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), making it the first new geological period declared in 120 years. Although the Period takes its name from the Ediacara Hills where geologist Reg Sprigg first discovered fossils of the eponymous biota in 1946, the type section is located in the bed of the Enorama Creek within Brachina Gorge in the Flinders Ranges of South Australia. Read more ...
Fossils on the Edge of Forever PhysOrg - December 14, 2009
Astrobiologists have not yet found alien life on other planets. But the fossil record has evidence of aliens of another sort: the Ediacarans that lived on Earth millions of years ago.
Fractal patterns of early life revealed New Scientist - 15 July 2004

The creatures, which were neither animals or plants, are called "rangeomorphs". They first appeared on the ocean floor 575 million years ago, after the last global glaciation, and were among the first of the soft-bodied creatures in the Ediacaran period. This biota survived until 542 million years ago, when modern animals diversified rapidly in the Cambrian explosion and most Ediacaran species vanished.
Until now, almost all Ediacaran fossils were squashed flat, and the few that were not were poorly preserved. This led to debate over whether the poor preservation obscured links to later life, or if the Ediacaran organisms were in fact a failed experiment in evolution that simply became extinct.
The newly unearthed fossils, from Newfoundland, Canada, were preserved three-dimensionally in fine-grained mud by a "one-in-a-million" streak of luck, says Guy Narbonne of Queen's University in Kingston, Ontario.
Just after a mud flow entombed the organisms, a nearby volcano erupted, covering it with a thick ash protective ash deposit. Later, the bed escaped the strain that altered most of the rock in the region. Now weathering is exposing them so they basically pop out of the rock.
That exceptional preservation is cracking the mystery of Ediacara. In some spots the surface has eroded and we see for the first time what was inside an Ediacaran fossil. Each frond element, a few centimetres long, was made of many tubes held up by a semi-rigid organic skeleton. The frond elements had branches which themselves had branches, a classic fractal structure. Frondlets assembled themselves like building blocks to make larger living structures attached to the sea floor. Narbonne found rangeomorphs assembled in several different shapes, which he believes filtered food from different levels of the water column, as well as isolated free-living frondlets.
The fractal patterns look complex, but Narbonne says their self-similarity means that very simple genomes - expected in early organisms - would suffice both to assemble individual frondlets and to control their assembly into larger structures. That would explain why the rangeomorphs evolved first.
They accounted for over 80% of fossils early in the Ediacara period, when there were no mobile animals or traces of burrows. But they declined as more mobile animals evolved, apparently unable to compete, or perhaps being eaten themselves.

May 2004 - BBC
Geologists have added a new period to their official calendar of Earth's history - the first in 120 years.
The Ediacaran Period covers some 50 million years of ancient time on our planet from 600 million years ago to about 542 million years ago.
It officially becomes part of the Neoproterozoic, when multi-celled life forms started to take hold on Earth.
However, Russian geologists are unhappy their own title - the Vendian - which was coined in 1952, was not chosen.
The decision was taken after a fifteen-year long period of consideration by expert geologists.
"There's always been a recognition that the last part of the Precambrian is a special time before the first shelled animals, when there are these weird, mesh-like creatures of uncertain affinity," Professor Jim Ogg, secretary-general of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), told BBC News Online.
"Now it's an official part of the timescale."
'Snowball' Earth
The Ediacaran begins at the end of the last ice age of the Snowball Earth, or Cryogenian Period, a term given to a series of glaciations that covered most of our planet between 850-630 or 600 million years ago.
One theory proposes that these climate shocks triggered the evolution of complex, multi-celled life.
Professor Ogg said many of the new life forms that appeared in the Ediacaran seem to be simple organisms, probably related to present-day sponges.
"They appear to be lying flat on the seafloor and people think they may have had photosynthetic symbiosis much like corals do today," he explained.
"These organisms were probably ripped to shreds when the first predators came along. That probably happened in the Cambrian Period."
The proposal had to pass three balloting stages, first by the members of the ICS's Terminal Proterozoic Period subcommission (which was set up specifically to consider the Ediacaran question), then by the ICS itself and finally by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) which ratified the definition in March.
At each stage, the vote had to be passed by two-thirds of the voting members.
However, Russian geologists are likely to continue to call the period by its alternative name: the Vendian.
In 1952, the Russian geologist Boris Sokolov coined the term Vendian for a system of sedimentary rocks in the former Soviet Union.
The two Russian members of the Terminal Proterozoic Period subcommission and Dr Sokolov submitted a formal comment expressing their disappointment at the decision to choose the Ediacaran over the Vendian.
"This decision ignores both the priority of the name Vendian and a long tradition to use this term in the international geological literature," Sokolov, Mikhail Semikhatov and Mikhail Fedonkin wrote in their comment.
The name Ediacaran takes its name from the Ediacara Hills in the Flinders mountain range of south Australia. The name is of Australian Aboriginal origin and refers to a place where water is present.
The Enorama Creek section of Flinders was designated the "boundary stratotype" for the Ediacaran by the Terminal Proterozoic Period subcommission.
A boundary stratotype is a rock sequence and level that is defined and used as the standard comparison for all other rock sequences of its age.
ANCIENT AND LOST CIVILIZATIONS
ALPHABETICAL INDEX OF ALL FILES