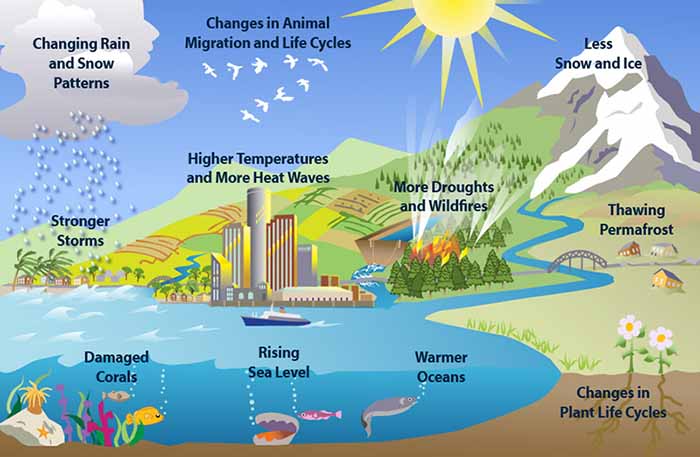

Climate is the long-term pattern of weather in a particular area. It is measured by assessing the patterns of variation in temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, precipitation, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological variables in a given region over long periods of time. Climate is different from weather, in that weather only describes the short-term conditions of these variables in a given region. Continue reading
2025 - Planet Earth is destabilizing as we move toward closure of our simulated reality. The signs are everywhere for those not stuck in their emotions. Believing that some form of climate change or natural disaster is not going to hit your area is impractical and denial. ~ Ellie
Heat Waves Can Accelerate Aging as Much as Smoking or Drinking Science Alert - August 29, 2025

As our planet steadily gets warmer, our bodies will need to cope with the stresses of higher temperatures. A new study shows that continued exposure to heat waves can age the body as much as regular drinking or smoking.

Flood Stories July 2025 - U.S. rocked by four 1-in-1,000-year storms in less than a week NBC - July 11, 2025
Climate change is making severe storms both more common and more intense. First the river rose in Texas. Then, the rains fell hard over North Carolina, New Mexico and Illinois. In less than a week, there were at least four 1-in-1,000-year rainfall events across the United States - intense deluges that are thought to have roughly a 0.1% chance of happening in any given year.
The U.S. faces more frequent extreme weather events, but attitudes and actions aren't keeping up NBC - July 10, 2025

Earth's soil is drying up. It could be irreversible. ABC - March 29, 2025

Earth may have hit a point of irreversible moisture loss in its soil as a result of climate change, according to a new study.
Scientists say sprinkling diamond dust into the sky could offset almost all of climate change so far - but it'll cost $175 trillion Live Science - December 19, 2024
The geoengineering scheme, known as stratospheric aerosol injection, would not be cheap, but scientists say it could buy us some time until we reach net-zero carbon.
Nature is adapting to climate change - why aren't humans? PhysOrg - September 26, 2024

Faced with the degradation of their habitat, the species that will survive will be those that are able to adapt.
Climate change and natural disasters are increasing exponentially within the simulation of reality.
Coastal hurricanes around the world are intensifying faster, new study finds PhysOrg - May 3, 2024

Hurricanes are among the world's most destructive natural hazards. Their ability to cause damage is shaped by their environment; conditions like warm ocean waters, guiding winds, and atmospheric moisture can all dictate storm strength.
Pivotal Moment For Humanity as Disasters Threaten to Converge Science Alert - March 3, 2024

A new review of literature on global climate change written by an international team of more than 200 researchers leaves no room for doubt: humanity is heading for disaster, unless significant steps are taken to change that course. How disastrous? The research team mentions trillions of US dollars in climate-related damage, billions of people pushed into hardship around the world, and millions of lives lost as a result of a rapidly warming planet. The report focuses specifically on tipping points - sudden, large scale shifts in ecological conditions caused by a culmination of smaller environmental changes. Those cataclysmic shifts include the widespread destruction of coral reefs and the collapse of the biggest ice sheets, each of which would in turn lead to even greater widespread disruption.

July 10, 2023
I have a male friend in Tampa who gets panic attacks before and during a storm wherein he lies in bed - immobile - until it passes. With insurance often expensive and hard to get in Florida - storms and tornados can destroy everything in one's world in a few seconds.
Anxiety comes from fear and panic disorders. Usually the person is predisposed to anxiety disorders and depression - oftentimes a drinker.
This reminds me of people who developed Covid anxiety or burnout (the mini-breakdown) - after having Covid. Most were predisposed to depression and anxiety - Covid exacerbating a pre-existing condition.
Then there's the fact that exponentially a growing number of people understand the planet will be not sustainable much longer - that we are in end times - and worry about what happens next.
Years of studies may have led you to believe that we are moving to a higher level of consciousness and light - however you envision that - but is it true or something you've read or heard about that brings comfort? You may envision gods, aliens, religious icons, deceased loved ones, other - but is that what's really in the grids (matrix) of reality?
You might be surprised at the answer.
Two Psychologists Say Your Climate Anxiety Isn't Actually About Personal Risk. Science Alert - July 10, 2023
It manifests out of concerns for global and societal consequences of climate change and impacts on animals and vulnerable populations
Eco-anxiety (short for ecological anxiety and also known as eco-distress or climate-anxiety) has been defined as "a chronic fear of environmental doom". Extensive studies have been done on ecological anxiety since 2007, and various definitions remain in use. Another widely cited definition is: "the generalized sense that the ecological foundations of existence are in the process of collapse." Continue reading
Ecological doom-loops: Why ecosystem collapses may occur much sooner than expected PhysOrg - June 25, 2023

Around the world, rainforests are becoming savanna or farmland, savanna is drying out and turning into desert, and icy tundra is thawing. Indeed, scientific studies have now recorded "regime shifts" like these in more than 20 different types of ecosystem where tipping points have been passed. Around the world, more than 20% of ecosystems are in danger of shifting or collapsing into something different. These collapses might happen sooner than you'd think. Humans are already putting ecosystems under pressure in many different ways - what we refer to as stresses. And when you combine these stresses with an increase in climate-driven extreme weather, the date these tipping points are crossed could be brought forward by as much as 80%. This means an ecosystem collapse that we might previously have expected to avoid until late this century could happen as soon as in the next few decades.
Earth Could Feasibly Descend Into Chaos, Physicists Warn Science Alert - June 19, 2023
The impact of human activity on the Earth system could result in unpredictable chaos from which there is no return, physicists have calculated. Using a theory conceived to model superconductivity, a team of physicists showed that, after a certain point, we will not be able to restore equilibrium to Earth's climate. A finite amount of human activity could result in a Hothouse Earth from which there is no return.
Ice Sheet Collapse at Both Poles to Start Sooner Than Expected, Study Warns Science Alert - February 27, 2023
Even if we manage to stabilize Earth's temperatures by peaking at 2°C, Greenland's and Antarctica's vast ice sheets are on track for irreversible melting, a new study warns.
Current Siberian warming is the most powerful of the last 7,000 years PhysOrg - August 25, 2022
The north of Western Siberia is recording the warmest summers of the last 7,000 years. While for several millennia the temperature of the region was following a general cooling, in the 19th century there has been an abrupt change with rapidly rising temperature that has reached its highest value in the recent decades.
A Whole Lot of Southwest Europe Is on Fire Right Now, And It's Only Getting Hotter
Europe heatwave: Deadly wildfires spread in Mediterranean.
Mexico declares drought emergency
Private, public effort contains one million gallons of oil at longest US spill
Researchers use lasers to get a new view on Oregon's glaciers
Impact of changing climate on Andean glaciers in sync with polar ice
Tropical storms trigger Antarctic ice melt
Ten Largest Supervolcanoes include three in the Continental United States
A Supervolcano in New Zealand Is Rumbling So Much It's Shifting The Ground Above It
Scientists suggest naming heatwaves as part of early warning system to save lives
Austria and Hungary fight nature to stop lake vanishing
Climate Change Has Been Killing Rainforest Trees For Longer Than We Realized Science Alert - May 21, 2022
Scientists have documented a worrying trend in the rainforests of Australia: Tree lifespans have halved in the last 35 years, and it appears to be due to the effects of climate change on the ecosystems. With these forests acting as significant carbon sinks, the consequences for the planet could be devastating, creating a feedback loop that's both caused by global warming and which then contributes to it
Climate has shifted the axis of the Earth PhysOrg - April 23, 2021
Glacial melting due to global warming is likely the cause of a shift in the movement of the poles that occurred in the 1990s.
Earth barreling toward 'Hothouse' state not seen in 50 million years, epic new climate record shows Live Science - September 11, 2020
Sixty-six million years ago, after a massive asteroid hit Earth with the explosive energy of roughly 1 billion nuclear bombs, a shroud of ash, dust and vaporized rock covered the sky and slowly rained down on the planet. As plant and animal species died en masse, tiny undersea amoebas called foreams continued to reproduce, building sturdy shells out of calcium and other deep-sea minerals, just as they had for hundreds of millions of years. When each foream inevitably died - pulverized into seabed sediment - they kept a little piece of Earth's ancient history alive in their fossilized shells.
New mathematical method shows how climate change led to fall of ancient civilization PhysOrg - September 4, 2020
Shifting monsoon patterns led to the demise of the Indus Valley Civilization, a Bronze Age civilization contemporary to Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt.
Climate is warming faster than it has in the last 2,000 years Science Daily - July 24, 2019
Two new studies show that the 20th century was the Earth's warmest period recorded in 2,000 years of the planet's record.The studies further indicate that global warming was manmade because the warming trend began after the industrial revolution, according to climate scientist Julien Emile-Geay, associate professor of Earth sciences at USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences and a co-author of one of the studies.
America colonization ‘cooled Earth's climate’ BBC - January 31, 2019
Colonization of the Americas at the end of the 15th Century killed so many people, it disturbed Earth's climate. The disruption that followed European settlement led to a huge swathe of abandoned agricultural land being reclaimed by fast-growing trees and other vegetation. This pulled down enough carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to eventually chill the planet. It's a cooling period often referred to in the history books as the "Little Ice Age" - a time when winters in Europe would see the Thames in London regularly freeze over. The Great Dying of the Indigenous Peoples of the Americas led to the abandonment of enough cleared land that the resulting terrestrial carbon uptake had a detectable impact on both atmospheric carbon dioxide and global surface air temperatures.
Get Used to Nor'easters - Arctic Warming May Mean More Severe Winters in the Northeast Live Science - March 16, 2018
As average temperatures rise across the planet, the frozen Arctic is heating up faster than anywhere else. With that warmth comes a surprising twist: Unusually warm Arctic winter temperatures are linked to bitter cold and snow in other parts of the Northern Hemisphere, such as the northeastern U.S., parts of northern Europe and northern Asia, according to an analysis of 66 years worth of climate data.
And the relationship between Arctic warmth and severe winter weather was strongest in in the northeastern U.S. - in fact, a temperature spike in the Arctic meant that the U.S. Northeast was two to four times more likely than usual to experience a bout of extreme winter weather, the scientists reported in a new study.