
Apache is the collective name for several culturally related tribes of Native Americans, aboriginal inhabitants of North America, who speak a Southern Athabaskan language. The modern term excludes the related Navajo people.The origin of the name Apache is uncertain. It may derive from the Yavapai word epache, meaning "people". The origin has also been claimed to be the Zuni word apachu, meaning "enemy" (but this may have been the Zuni name for the Navajo people) or an unspecified Quechan word meaning "fighting-men".
The Apaches formerly ranged over southeastern Arizona and north-western Mexico. The chief divisions of the Apaches were the Arivaipa, Chiricahua, Coyotero, Faraone Gileno, Llanero, Mescalero, Mimbreno, Mogollon, Naisha, Tchikun and Tchishi. They were a powerful and warlike tribe, constantly at enmity with the whites. The final surrender of the tribe took place in 1886, when the Chiricahuas, the division involved, were deported to Florida and Alabama, where they underwent military imprisonment. The U.S. Army, in their various confrontations, found them to be fierce warriors and skillful strategists. The Apaches are now in reservations in Arizona, New Mexico and Oklahoma, and number between 5000 and 6000.
The word "Apache" comes from the Yuma word for "fighting-men". It also comes from a Zuni word meaning "enemy". The Zuni name for Navajo was called "Apachis de Nabaju" by the earliest Spaniards exploring New Mexico. They called themselves Inde, or Nide "the people".
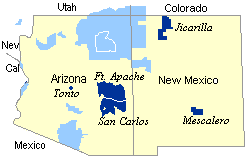
The Apache Nation is composed of six regional groups:
The Mescalero to the south were originally hunter-gatherers who developed an appetite for the roasted heads of wild mescal plants. The Mescalero band consisted of followers and a headman. They had no formal leader such as a tribal chief, or council, nor a decision making process. The core of the band was a "relative group", predominantly--but not necessarily kinsmen. They were named by the Spanish for the mescal cactus the Apaches used for food, drink, and fiber.
They moved freely, wintering on the Rio Grande or farther south, ranging the buffalo plains in the summer, always following the sun and the food supply. They owned nothing and everything. They did as they pleased and bowed to no man. Their women were chaste. Their leaders kept their promises. They were mighty warriors who depended on success in raiding for wealth and honor. To their families they were kind and gentle, but they could be unbelievably cruel to their enemies - fierce and revengeful when they felt that they had been betrayed.
Pushed southward by the invading Cheyennes and Sioux who were being pushed out of their lands in the great lake regions by the Objiwe tribes, the Kiowas moved down the Platte River basin to the Arkansas River area. There they fought with the Comanches, who already occupied the land. Around 1790, the two groups made an alliance and agreed to share the area.
From that time on, the Comanches and Kiowas formed a deep bond; the peoples hunted, travelled, and made war together. An additional group, the Plains Apache (also called Kiowa-Apache), also affiliated with the Kiowas at this time.
The Kiowas lived a not atypical Plains Indian lifestyle. Mostly nomadic, they survived on buffalo meat and gathered vegetables, living in tipis, and depended on their horses for hunting and military uses.
The Kiowa were notorious for long-distance raids as far north as Canada and south into Mexico. After 1840 the Kiowas joined forces with their former enemies, the Cheyennes, as well as the Comanches and the Apaches, to fight and raid the Eastern natives then moving into the Indian Territory.
The United States military intervened, and in the Treaty of Medicine Lodge of 1867 the Kiowa agreed to settle on a reservation in southwestern Oklahoma. Some bands of Kiowas remained at large until 1875.
On August 6, 1901 Kiowa land in Oklahoma was opened for white settlement, effectively dissolving the contiguous reservation. While each Kiowa head of household was alloted 80 acres, the only land remaining in Kiowa tribal ownership today is what was the scattered parcels of 'grass land' which had been leased to the white settlers for grazing before the reservation was opened for settlement.
The Apaches are well-known for their superior skills in warfare strategy and inexhaustible
endurance. Continuous wars among other tribes and invaders from Mexico followed the Apaches'
growing reputation of warlike character. When they confronted Coronado in 1540, they lived in
eastern New Mexico, and reached Arizona in the 1600s. The Apache are described as a gentel
people; faithful in their friendship.

Early Apache inhabitants of the southwestern United States were a nomadic people; some groups roamed as far south as Mexico. They were primarily hunters of buffalo but they also practiced limited farming. For centuries they were fierce warriors, adept in desert survival, who carried out raids on those who encroached on their territory.
The primitive Apache was a true nomad, a wandering child of Nature, whose birthright was a craving for the warpath with courage and endurance probably exceeded by no other people and with cunning beyond reckoning. Although his character is a strong mixture of courage and ferocity, the Apache is gentle and affectionate toward those with his own flesh and blood, particularly his children.
The Apache people (including the Navajo) came from the Far North to settle the Plains and Southwest around A.D. 850. They settled in three desert regions, the Great Basin, the Sonoran, and the Chihuachuan.
They were always known as 'wild" Indians, and indeed their early warfare with all neighboring tribes as well as their recent persistent hostility toward our Government, which precipitated a "war of extermination," bear out the appropriateness of the designation.
The first intruders were the Spanish, who penetrated Apache territory in the late 1500s. The Spanish drive northward disrupted ancient Apache trade connections with neighboring tribes.
When New Mexico became a Spanish colony in 1598, hostilities increased between Spaniards and Apaches. An influx of Comanche into traditional Apache territory in the early 1700s forced the Lipan and other Apaches to move south of their main food source, the buffalo. These displaced Apaches began raiding for food.
Apache raids on settlers accompanied the American westward movement and the United States acquisition of New Mexico in 1848. The Native Americans and the United States military authorities engaged in fierce wars until all Apache tribes were eventually placed on reservations.
Most of the tribes were subdued by 1868, except for the Chiricahua, who continued their attacks until 1872, when their chief, Cochise, signed a treaty with the U.S. government and moved with his band to an Apache reservation in Arizona. The last band of Apache raiders, led by the Chief Geronimo, was hunted down in 1886 and was confined in Florida, Alabama, and finally Oklahoma Territory.

June 16, 1829 - February 17, 1909
Geronimo was born in what is now the state of New Mexico and according to the maps of the time was part of Mexico, but which his family considered Bedonkohe Apache land. Geronimo himself was a Chiricahua Apache. He grew up to be a respected medicine man and an accomplished warrior who fought frequently with Mexican troops. Mexican bandits massacred some of his relatives in 1858, and as a result he hated all Mexicans for the rest of his life. His Mexican adversaries gave him the nickname of "Geronimo", the Spanish version of the name "Jerome".
Geronimo fought against ever increasing numbers of both Mexican and United States troops and became famous for his daring exploits and numerous escapes from capture. His forces became the last major force of independent Indian warriors who refused to acknowledge the United States Government in the American West. This came to an end on September 4, 1886, when Geronimo surrendered to United States Army General Nelson A. Miles at Skeleton Canyon, Arizona.

Geronimo was sent in as a prisoner to Fort Pickens, Florida. In 1894 he was moved to Fort Sill, Oklahoma. In his old age Geronimo became something of a celebrity, appearing at fairs and selling souvenirs and photographs of himself, but not allowed to return to the land of his birth. He rode in President Theodore Roosevelt's 1905 inaugural parade. He died of pneumonia at Fort Sill.

The Apache's gorilla war tactics came naturally and were unsurpassed. The name Apache struck fear into the hearts of Pueblo tribes, and in later years the Spanish, Mexican, and Anglo-American settlers, which they raided for food, and livestock.
The Apache and the Pueblos managed to maintain generally peaceful relations. But the arrival of the Spaniards changed everything. A source of friction was the activity of Spanish slave traders, who hunted down captives to serve as labor in the silver mines of Chihuahua in northern Mexico. The Apache, in turn, raided Spanish settlements to seize cattle, horses, firearms, and captives of their own.
The prowess of the Apache in battle became legend. It was said that an Apache warrior could run 50 miles without stopping and travel more swiftly than a troop of mounted soldiers.

Cochise (c. 1812đJune 9, 1874) was a chief of one of the bands of the Chiricahua Apache and the leader of an uprising that began in 1861. Cochise was a chief of central Chiricahua in the southwestern United States. Cochise was the most famous Apache leader to resist intrusions by whites during the 19th century.Cochise was born in the area that now contains the border between Mexico, New Mexico and Arizona. That area had experienced significant tension between the Apache and European settlers from about 1831 until the greater part of the area was annexed by the United States in 1850, which ushered in a time of relative peace. Cochise worked as a woodcutter at the stagecoach station in Apache Pass for the Butterfield Overland line.
The peace was shattered in 1861 when an Apache raiding party drove away a local rancher's cattle and kidnapped his 12-year-old son. Cochise and five others of his band were falsely accused of the incident (which had actually been done by the Coyotero band of Apaches), and were ordered by an inexperienced Army officer (Lt. George Bascom) to report to the fort for questioning. When they went there and maintained their innocence the group was arrested and imprisoned.
The five soon mounted an escape attempt; one was killed and Cochise was shot three times but managed to slip away. He quickly took hostages to use in negotiations to free the other four Chiricahua. However, the plan backfired and both sides killed all their hostages in what was later known as "The Bascom Affair."
Cochise then joined with his father-in-law Mangas Coloradas (Colorado), a Mimbreľo Apache chief, in a long series of retaliatory skirmishes and raids among the settlements. Many were killed on both sides, but the Apaches began to achieve the upper hand, which prompted the United States Army to send an expedition (led by General James Carleton).
At Apache Pass in 1862, Cochise and Colorado, with 500 fighters, held their ground against a force of 3000 California volunteers under Carleton until artillery fire was brought to bear on their position. Colorado was later captured and subsequently killed while imprisoned leaving Cochise in sole command of the insurrection.
He and his men were gradually driven into the Dragoon Mountains but were nevertheless able to use the mountains as cover and as a base to continue significant skirmishes against white settlements from. This was the situation until 1871 when General George Crook assumed command and used other Apaches as scouts and informants and was thereby able to force Cochise's men to surrender. Cochise was taken into custody in September of that year.
The next year the Chiricahua were ordered to Tularosa Reservation in New Mexico but refused to leave their ancestral lands, which were guaranteed to them under treaty. Cochise managed to escape again and renewed raids and skirmishes against settlements through most of 1872. A new treaty was later negotiated by General Oliver O. Howard and Cochise retired to an Arizona reservation where he died of natural causes.

The Apache and Navajo (Dine) tribal groups of the American Southwest speak related languages of the language family referred to as 'Athabaskan.' Southern Athabaskan peoples in North America fan out from west-central Canada where some Southern Athabaskan-speaking groups still reside. Linguistic similarities indicate the Navajo and Apache were once a single ethnic group. Archaeological and historical evidence suggests a recent entry of these people into the American Southwest, with substantial numbers not present until the early 1500s.


The primitive dress of the men was deerskin shirt, leggings, and moccasins. They were never without a loin-cloth. A deerskin cap with attractive symbolic ornamentation was worn. The women wore short deerskin skirts and high boot top moccasins.


The Apache dwellings consisted of a dome shaped frame of cottonwood or other poles, thatched with grass. The house itself was termed, "Kowa" and the grass thatch, "Pi".

They pitched tentlike dwellings made of brush or hide, called 'wikiups'. The wickiup was the most common shelter of the Apache. The dome shaped lodge was constructed of wood poles covered with brush, grass, or reed mats. It contained a fire pit and a smoke hole for a chimney. The Jicarillas and Kiowa-Apaches, which roamed the Plains, used buffalo hide tepees. The basic shelter of the Chiricahua was the domeshaped wickiup made of brush.

The ceremonies are invariably called "dances. Among these are the rain dance, a puberty right, a harvest and good crop dance, and a spirit dance.
The Apache are devoutly religious and pray on many occasions and in various ways. Recreated in the human form, Apache spirits are supposed to dwell in a land of peace and plenty, where there is neither disease or death.
To celebrate each noted event a feast and dance is given. The music for our dance is sung by the warriors, and accompanied by beating the esadadedne (buck-skin-on-a-hoop). No words are sung - only the tones. When the feasting and dancing are over they have horse races, foot races, wrestling, jumping, and all sorts of games (gambling),
There are no formal churches, no religious organizations, no sabbath day, no holidays, and yet they worship. Sometimes the whole tribe assembles to sing and pray; sometimes a smaller number, perhaps only two or three. The songs have a few words, but are not formal. The singer will occasionally put in such words as he wished instead of the usual tone sound. Sometimes they prayed in silence; sometimes each one prays aloud; sometimes an aged person prays for all of us. At other times they rise and speak to us of our duties to each other and to Usen. The services are short.
When disease or pestilence abound we assemble and are questioned by our leaders to ascertain what evil we had done, and how Usen - a god - could be satisfied. Sometimes sacrifice is deemed necessary. Sometimes the offending one is punished.
If an Apache has allowed his aged parents to suffer for food or shelter, if he has neglected or abused the sick, if he has profaned our religion, or has been unfaithful, he can be banished from the tribe.
The Apaches have no prisons as white men have. Instead of sending their criminals into prison they send them out of their tribe. These faithless, cruel, lazy, or cowardly members of the tribe are excluded in such a manner that they cannot join any other tribe. Neither can they have any protection from our unwritten tribal laws.
Frequently these outlaw Indians band together and commit depredations which were charged against the regular tribe. However, the life of an outlaw Indian is a hard lot, and their bands never become very large; besides, these bands frequently provoke the wrath of the tribe and secured their own destruction.

The Apaches were nomadic hunter-gatherers - hunting of wild game and gathering of cactus fruits and other wild plant foods. . They chased any wild game located within their territory, especially deer and rabbits. When necessary, they lived off the land by gathering wild berries, roots, cactus fruit and seeds of the mesquite tree. They planted some corn, beans, and squash as crops. They were extremely hardy prior to the arrival of European diseases, and could live practically naked in zero temperature.
Hunting is a part of daily life - for food, clothing, shelter, blankets. Apache hunted deer, wild turkeys, rabbits, buffalo, bears, mountain lions. There was no fishing. Eagles were hunted for their feathers.
They exchanged buffalo hides, tallow and meat, bones that could be worked into needles and scrapers for hides, and salt from the desert with the Pueblos for pottery, cotton, blankets, turquoise, corn and other goods. But at times they simply saw what they wanted and took it. They became known among the Pueblo villages by another name, Apachu, "the enemy".


All Apachean peoples lived in extended family units (or family clusters); they usually lived close together, with each nuclear family in separate dwellings. An extended family generally consisted of a husband and wife, their unmarried children, their married daughters, their married daughters' husbands, and their married daughters' children.
Thus, the extended family is connected through a lineage of women who live together (that is, matrilocal residence), into which men may enter upon marriage (leaving behind his parents' family). When a daughter was married, a new dwelling was built nearby for her and her husband. Among the Navajo, residence rights are ultimately derived from a head mother. Although the Western Apache usually practiced matrilocal residence, sometimes the eldest son chose to bring his wife to live with his parents after marriage. All tribes practiced sororate and levirate marriages.
All Apachean men practiced varying degrees of "avoidance" of his wife's close relatives, a practice often most strictly observed by distance between mother-in-law and son-in-law. The degree of avoidance differed in different Apachean groups.
The most elaborate system was among the Chiricahua, where men had to use indirect polite speech toward and were not allowed to be within visual sight of the wife's female relatives, whom he had to avoid. His female Chiricahua relatives through marriage also avoided him.
Several extended families worked together as a "local group", which carried out certain ceremonies, and economic and military activities. Political control was mostly present at the local group level. Local groups were headed by a chief, a male who had considerable influence over others in the group due to his effectiveness and reputation.
The chief was the closest societal role to a leader in Apachean cultures. The office was not hereditary, and the position was often filled by members of different extended families. The chief's leadership was only as strong as he was evaluated to be no group member was ever obliged to follow the chief. The Western Apache criteria for evaluating a good chief included: industriousness, generosity, impartiality, forbearance, conscientiousness, and eloquence in language.
Many Apachean peoples joined together several local groups into "bands". Band organization was strongest among the Chiricahua and Western Apache, while among the Lipan and Mescalero, it was weak. The Navajo did not organize local groups into bands, perhaps because of the requirements of the sheepherding economy. However, the Navajo did have "the outfit", a group of relatives that was larger than the extended family, but not as large as a local group community or a band.
On the larger level, the Western Apache organized bands into what Grenville Goodwin called "groups". He reported five groups for the Western Apache: Northern Tonto, Southern Tonto, Cibecue, San Carlos, and White Mountain. The Jicarilla grouped their bands into "moieties", perhaps influenced by the example of the northeastern Pueblo. The Western Apache and Navajo also had a system of matrilineal "clans" that were organized further into phratries (perhaps influenced by the western Pueblo).
The notion of "tribe" in Apachean cultures is very weakly developed; essentially it was only a recognition "that one owed a modicum of hospitality to those of the same speech, dress, and customs." The seven Apachean tribes had no political unity (despite such portrayals in common perception) and often were enemies of each other - for example, the Lipan fought against the Mescalero just as they did against the Comanche.