
DEATH:
Death was always a time of sorrow and supernatural fear among traditional ATSI people. Wailing or crying was a common occurrence among the mourners who often painted their bodies with pipe clay, red ochre, or charcoal when a relative or friend died. In some districts people wore a head covering made of feathers. Others beat their bodies with sticks or clubs, or cut themselves with shells or stone knives to cause bleeding. In these instances the period of sorrow or mourning, was considered to be at an end when their wounds were healed.
Relatives and close friends often sat beside a grave of a deceased person, but this was related to their superstitious beliefs. Sitting beside a grave - sometimes shaded with a hut or covering to provide shelter for the mourner or mourners - involved ensuring that the deceased person's spirit had gone to the 'sky camp' or to its spirit-place. Obviously it is impossible to say 'how' they knew or considered when this happened. However after the mourning period was completed, a deceased person's name was never mentioned again. This often involved inventing new words for totems but was based on their superstitious beliefs in a personal spirit and ghosts.
The belief in a personal spirit was based on the Dreamtime stories that told the people that birth was the result of a spirit-child entering a woman's body. Or in some parts of the country, birth had been an act of the creators. For example in Arnham Land the Djanggau Sisters (who were considered to be daughters of the Sun and arrived in the area in a bark canoe with their brother Bralgu)created the land and gave birth to the first-people to live there. In other words birth and death were great mysteries involving supernatural beings.
The people also believed that a person's spirit could visit living people to harm or warn them of danger. This usually resulted in a 'inquiry' about the death of a person who was considered to have died prematurely or in unusual circumstances. The inquiry - usually undertaken in consultation with an Elder or a Clever Man - looked for actions undertaken by some person that had caused the death of an individual. Any culprit was severely punished. The belief in a person spirit also led the people to take great precautions in the burial or cremation of the deceased.
REINCARNATION:
A number of difference 'races' of people believe or have believed that when a person dies, their soul (or inner spirit) is born again - in the form of an animal, bird, reptile, fish or as another human being. The Eora / Dharawal Aborigines believed in transmigration also known as transmutation or metephsychosis. For example during the 1830s Quaker James Backhouse toured the Illawarra district and recorded that some Aboriginal men were mortified when some Europeans shot and killed some dolphins. The Aborigines of the area believed that after death, their warriors became dolphins. This belief was bolstered by the habit of dolphins to herd fish and to protect people from shark attacks.
Another example of the belief in reincarnation was given by David Collins who noted that when a European was about to shoot a raven, an Aborigine stepped into the firing line to stop him from doing this because 'him brother'. In other words the bird was the man's totem and he was compelled to do everything possible to make sure that the raven wasn't killed.
SPIRITUAL:
Aborigial people are spiritual though they had no formal religion.
The word spirit has many different meanings. For example it can be used to refer to the immaterial part of a human being often called his or her soul or to the personality of people when they are said to have a courageous or cowardly spirit. Or to describe qualities of people or (other) animals when they are said to be high spirited. Spirit can also refer to supernatural beings such as a deity (god) or to evil manifestation such as ghosts.
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians believed in a number of spirits. In particular to ancestral spirits; a personal spirit; animal spirits, deceased spirits or ghosts and evil spirits. Their beliefs were founded - like every other aspect of their life - on Dreamtime myths which informed them that their world had been created by was filled with the supernatural. This was something to be taken notice of and was the basis of them being very superstitious people.
Animal Spirits: During the Dreamtime the creators made spirits of every living creature including that of every animal, bird, reptile, insect and form of marine life (etc). Wherever they rested the creators left the spirits of living creatures behind them. This was the origin of life. The Aborigines believed they were intrinsically linked to every other 'species' because of the actions of the creators. They also believed that it was their personal responsibility to ensure the continuation of 'animal' life through the concept of taking care. This involved the singing of songs and performing of ceremonies which were believed to ensure the continuation of the birth of each species.
During the Dreamtime the creators had metamorphosed into various forms of animals, birds and other species. Individuals were linked to the creators through totemic relationships and did not eat their personal totem. To do so would be a form of cannibalism. The practice had the effect of providing a safe sanctuary for different species.
ATSI people also believed that particular animal spirits could harm living people. For example they believed that killing a willy-wagtail would result in the spirit of this bird becoming angry and to the creation of storms of violence which could destroy others.
Evil Spirits: A number of Dreamtime stories related stories of evil spirits. One Queensland story recorded by A.W. Howitt told of a group who went to hunt and fish leaving behind two boys in camp, with instructions not to leave the camp: The boys played about for a time in the camp, and then getting tired of it, went down to the beach where a Thugine came out of the sea, and being always on the watch for unprotected children, caught the two boys and turned them into rocks that now stand between Double Island Point and Inskip Point and have deep water close to them. 'Here you see', the old men used to say, 'the result of not paying attention to what you are told by your elders'."
The Thugine mentioned in this story is one of hundreds of evil spirits whose evil deeds were recorded in stories and songs. Along the south-east coast of New South Wales evil spirits were and are known as Goonges. Generally speaking contemporary Aboriginal people still believe in these spirits. For example if they go to a particular area they believe they must be invited to stay there; if they are not welcome they will feel this and to remain there under these circumstances will result in being punished. Punishment may mean death or injury and this may extend to other members of a family. Some areas are forbidden to women because the male spirits that are believed to live there will punish them if they disobey the trespassing laws.
Beliefs in spirits and ghosts among Aboriginal Australians was common to all tribes throughout the continent, although there were a number of variations in the actual names that were used to describe them. Contextually the beliefs were one aspect of Aboriginal culture and need to be understood from their perspective. Modern day Western understanding tends to 'see' body, mind and spirit as separate entities, which we somehow or other manage to unite into concepts of person or oneness. This understanding can lead to skepticism about spirit as this has largely become associated with religious beliefs. Traditional Aborigines did not think this way. They certainly understood the separate concepts of body and spirit, but in such a way that they seen as being united with other people and every other living creature, in a unique oneness. This applied to the past, present and future in an ontology (philosophy) that humanism, rationalism and science cannot understand.
The Australian Aborigines believed that the land they lived in (and owned) along with all it contained (every rock, tree, waterhole and cave), was created for them during the Dreamtime.
In some areas of the continent the creators were all-powerful figures such as Biami. In other areas creation was the result of the actions of ancestral heroes and heroines. In Central Australia the Tnatantja Pole was responsible for forming mountain ranges and valleys.
MAGIC:
Because Aboriginal society was very spiritual (in the sense that spirits were thought to have made the land and were responsible for birth and sometimes death),it is not surprising that Aboriginal people 'believed' in magic.
It was practiced in a number of ways. For example through the pointing of the bone (sometimes called singing someone) which was believed to cause death. People who had been 'pointed' often died, not as a result of the magic itself, but because of their belief that they would die ie., death through superstition or imagination. In the same way, people were 'cured' of sickness / illness through the use of magic stones and crystals.
INITIATION:
Boys began a period of initiation from when they were 7 or 8 years of age. The first initiation ceremonies they attended were designed to make them independent on their mothers and other females. At other ceremonies and meetings with older males they were informed about the history and customs of the tribe and were taught how to survive and to be dependent on other males. Initiation continued over a number of years and boys gradually acquired knowledge through learning stories, attending ceremonies and through education by initiated males.
Pain endurance was an important part of initiation of males and was considered to be manly. In theEora / Dharawal tribe teenage boys attended a tooth evulsion ceremony when a front tooth was knocked out during the ceremony. In some tribes boys were circumcised at puberty as a pain endurance test.
Initiation was also a time of obedience as boys were expected to comply with food and other taboos during this time. For example Louisa Atkinson reported in her reminiscences of knowing the Aborigines of the south coast of New South Wales (published as A Voice in the Country: Sydney Mail 19th September 1863), that two boys of the Picton area disobeyed a food taboo and were punished by death.
'For some time the lads are not permitted to mingle with the tribe, or eat particular food. The tooth is knocked out by the point of a boomerang...should they disobey the regulations deadly consequences ensue. This report goes on to report that two initiates killed and ate a duck. Mullich (a Koradji or Clever Man of the area)discovered what they had done: in consequence the lads were surprised when asleep, stunned by a blow of a club, and an insidious poison, administered to them, under which they sank in about three months.
Girls did not participate in initiation ceremonies. At puberty they were married and went to live with their husband. However, their mothers and other women prepared them in knowledge about their bodies and sexual intercourse. Ceremonies included ritual bathing, separation from the main tribal group for varying periods of time and food taboos.
CULTURE:
Culture is a celebration of beliefs and usually (if not always) includes rites of passage from one stage of life to another. Culture is stories and songs.
Particularly because their stories and songs informed them about creation, the relationship between mankind and nature and were the source of their tribal laws. The tradition of initiation was an expression of Aboriginal culture and was carried out for thousands of years in exactly the way that had been ordered by the ancestors in the Dreamtime. On another level the stories and songs were believed to be important for the preservation and conservation of their land and all it contained. This involved singing Songlines that had been sung by the ancestors and the concept of taking care.
Until 1788 the Aborigines of Australia lived and celebrated a culture that was basically unchanged for thousands of years. Each tribe had their own beliefs - their own songs and stories, but until colonization, they were the oldest surviving race in the entire world. They existed as a race of people well before the Egyptians were building the pyramids, while the Greeks were constructing the Pantheon and while Britain was ruled by the Roman Empire. However the first Europeans to arrive in the continent considered the 'natives' to be primitives. This was largely due to a lack of understanding about the culture of the Aborigines.
A cultural group was comprised of two or more tribes that associated with each other for cultural purposes. For example to celebrate corroborees, barter or exchange goods, conduct initiation ceremonies or intermarry.
On the Far South Coast of New South Wales early records show that members of the Yuin tribe often associated with those from the Canberra area. These tribes did not associate with the Dharawal tribe of the Shoalhaven, Illawarra and Sydney districts, who gathered from time to time with the Gundungurra of the Goulburn and Camden area.
Modern day scientists and others often say that the Australian Aborigines arrived in the continent of Australia, by crossing land bridges or landing on the northern shores by canoes.
ELDERS:
Traditional Aboriginal people had great respect for older people such as Grandfathers and Grandmothers. However old age, seniority or maturity were not sufficient for a person to be considered an Elder.
Elders (who were usually males), were people who were considered to be wise in tribal knowledge and worldly matters. They were leaders of family or kinship groups who made decisions about moving camp, when boys would be initiated, when girls would be married and settled disputes among other members of the social unit.
Senior females were not considered to be Elders in traditional Aboriginal society. However they did play important roles in tribal matters. For example they decided when girls would undergo rituals in preparation for marriage, conducted or organized ceremonies including those that males and children participated in (but not initiation ceremonies). They also acted as midwives and story-tellers.
Today some Aboriginal people call themselves Elders but are not recognized by traditional people. Sometimes because they are too young to be Elders or live in areas that is not their traditional land. There are also a number of female Elders in society today, but this seems to be an adaptation of the traditional leadership laws. However Aboriginal laws are not and probably never have been static and there is a great need today, for female Aborigines to be involved in achieving rights, recognition and reforms for all ATSI people.
One important aspect of traditional Aboriginal life was the custom of being led by Elders (see Elders). However, Governor Lachlan Macquarie set about changing Aboriginal society by awarding some Aboriginal people with a Brass plates and calling them Kings. This was a breach of traditional tribal laws, but the people who accepted these titles were those 1) who were considered by the authorities to have shown an inclination to accept the new way of life under British Law or 2) to those who had led exploration parties.
Britain was of course based on a monarchy and various Governors and settlers such as Alexander Berry in the Shoalhaven district also rewarded some Aborigines with the title of King. Females were not awarded brass plates as Queens. But the men who accepted the title of King were eager to have it known that their wives were Queens and their children Princes and Princesses. Circa 1810 to 1820 (the period when Governor Macquarie was in charge of the colony), there were many inter-tribal disputes over the awarding of brass plates. In other words the traditional people of various areas resented those Aborigines who did not belong to their tribe, or who had not become Elders, accepting European titles and being styled as Kings over their traditional lands.(also see Brass Plates on our Historical Pages which includes a photograph).
LANGUAGES:
Before colonization there were between 200 and 250 Aboriginal languages spoken throughout the continent of Australia. In other words the Aborigines did not speak the same or 'one' language. It has also been estimated that there were as many as 600 languages spoken at the time of colonization. However, it has also been said, that there was one language and several dialects.
The 'one language' theory fits with the theory of the migratory origins of the people in the continent. In other words that all Aborigines belong to the one race as descendants of people who came from Asia, Africa and other places across land bridges. Whether this happened or not is speculative. What is certain, is that the Aborigines who belonged to a particular tribe spoke a language that was different to their neighbors. This fact has led to scientists identifying Language or Cultural groups which were comprised of a number of tribes who spoke the same language. It is also certain that some Aboriginal people spoke more than one language and it is interesting to note, that when the Europeans arrived in this country some Aborigines quickly learned to speak English while the Europeans themselves often struggled to speak even a few Aboriginal words.
In 1888 it was said that the language of the Australian Aborigines was "in fullness of tone, variety of sound, and easy flow, is not to be surpassed. In proof of this it is only necessary to refer to the Aboriginal names of the various locations throughout the colonies.
Some Aboriginal words are still used today. For example the word Bundi is the basis for the name Bondi n Sydney's eastern suburbs which has become the most famous beach in the world. Bennelong Point (the site of the Sydney Opera House) is named after Bennelong an Aborigine of the Manly area who was kidnapped by Governor Arthur Philip); Botany Bay was known as Kamay to the Aborigines of the area; Cronulla is based on the word Kurranulla meaning 'pink shell'; Dapto in the Illawarra district is a corruption of the word Dappeto; Dhurawal Bay on the George's River near Liverpool is named after the traditional tribe of the Sydney district the Dharawal also called the Eora.
Aboriginal language had ice age origins News in Science - December 13, 2006
Clendon says the continent, known as Sahul, was relatively densely populated on the land bridge connecting northern Australia to New Guinea, now separated by the Arafura Sea. The other populated area was along what is now Australia's eastern seaboard. The two population groups were separated by a vast, cold, windswept, arid stretch of land that covered most of the continent, says Clendon, who was with the Batchelor Institute of Indigenous Tertiary Education when he published the research. The eastern group spoke a tongue that became what is known today as Pama Nyungan and includes languages like Pitjantjatjara, Yolngu and Warlpiri. And the Arafurans spoke another family of languages used in northern Australia today. "What I'm suggesting is that Pama Nyungan and non-Pama Nyungan languages go back about 13,000 years to when there was a land bridge between New Guinea and Australia," he says.
Until now, the reason why these two Aboriginal language groups are so different, each with a distinct grammar and vocabulary, has been a mystery. Climate change - Around 11,000 years ago what was the Arafura plain was flooded by rising seas as the ice age ended. This caused the northern people to migrate into either New Guinea or to northern parts of Australia. Meanwhile, increased rainfall and warmer temperatures made inland parts of the continent more habitable and sparked a westward migration of eastern dwellers. This introduced their language group to more central areas of Australia. Both groups maintained their distinct languages, Clendon says. His hypothesis provides an alternative picture to the traditional view that 6000 years ago a single proto-language spread from the Gulf of Carpentaria around Australia, eventually giving rise to existing Aboriginal languages. "We know about changes in climate and sea levels at the end of the Pleistocene era," Clendon says. "I'm suggesting the way languages are configured in Australia today are a result of those changes that happened at the end of the ice age."
Provocative but unconvincing - Writing in a reply to Clendon's article, Professor Nicholas Evans, an expert in Aboriginal languages from the University of Melbourne, describes Clendon's hypothesis as "fresh and provocative". However, he says there are flaws in the argument, including that there is only weak evidence of similarities between southern New Guinea and northern Aboriginal languages. Evans says he remains to be convinced about Clendon's proposal. "[But] it adds a welcome alternative to a field in which we are still a long way from having any clear picture of the unimaginably long human occupation of Sahul," he says.
LORE:
Aboriginal lore was an important and vital aspect of community life. Lore means 'the facts and stories about a particular subject or topic'. For example Aboriginal people learned their 'laws' from those Dreamtime stories that informed the listeners about acceptable and unacceptable behavior together with the punishment offenders received.
The lore's / laws were serious as they were considered to have originated from the ancestors and therefore were considered to be the law-givers or law-makers and law was an important aspect of Aboriginal life. On the other hand there were those early colonists who believed that the Aborigines were a lawless race of people. They accused them (as some do today), of having a genetic 'fault' as natural thieves and murderers.
It is certainly true that the Aborigines of the Sydney district stole axes and other weapons from the colonists. But history records this as happening after their own weapons and tools were stolen by the convicts (who sold them to sailors who took them back to England to sell them). This is not a justification. It is a simple fact that the Aborigines considered it quid pro quo ie., good enough to steal from those who stole from them.
They also stole corn, potatoes and other food from the early settlers. Perhaps they were starving. On the other hand the early colonists were struggling to survive in the colony and the Aborigines may have stolen their food as a strategy to drive them out of their land. Murder was also exacted by the Aborigines. They believed that anyone who shot one of them should be punished and exacted this on the Europeans.
Aboriginal lore (in songs and stories about a particular topic) also taught and guided the people to survive. Some stories informed them about the life cycle of birds, animals and insects. Others (often called Songlines) were like oral road maps and identified tracks that the people followed when moving around their tribal territory or when visiting other tribes.
MESSAGE STICKS:
Aboriginal lore / law required a person who did not 'belong' to a particular area, to be invited or granted permission, to enter into the territory of a tribe. In other words, he or she could not simply wander into the land of another tribe. To do so invited hostility that could result in the death of the individual(for trespassing).
When someone wanted to visit another tribe, they carried a message stick - a piece of bark or timber that was decorated with symbols. These symbols have sometimes been said to have been a written form of language. This is not correct. But they were a form of passport that identified the intent or authority of the bearer and 'communication' took place verbally (or by sign language), between the 'stranger' and those whom s/he wanted to visit. "The passing of a boundary line by the blacks of another territory was considered as an act of hostility against the denizens of the invaded grounds, and wars were frequently the sequence of such transgressions." (The Aborigines of Australia, Roderick J Flanagan, 1888, pp 46)
When the first European or white explorers entered the territory of a tribe, they were considered by the people to be trespassing. This was an offense to the Aborigines who bitterly resented the intrusion and particularly the felling of trees, the shooting and scaring away of animals and birds and the attitude of disrespect that was shown to the people who considered that they owned their land
CAVES:
To protect themselves from the weather, the Aborigines of Australia often used caves or overhanging rocks, as dwelling places and as burial sites. They often decorated rock with paintings, drawings and etchings using white, red and other colored earth, clay or charcoal.
In the Kurnell area (where James Cook and the First Fleet first landed at Botany Bay) there is a cave that has become known as Skeleton Cave. This was used during the smallpox outbreak in 1789 to house victims of the disease. Many died there and the name given to the area is literally true. There are also other cave in the Sutherland Shire that contain skeletons. In the Royal National Park some of the caves are burial sites. In other parts of the Shire, people were buried while sheltering in them from heavy rain. Cave-ins trapped an unknown number of people. One of these sites is Turriel Point.
Aboriginals, the keepers of this land which we know call Australia, were living in Australia thousands of years before the first white settlers, so it is natural to assume that this race of people would have recorded a history as diverse as any other. The new sacred site which was discovered only a short time ago, in an unrevealed location contains some of the oldest rock art known to man. Carbon dating has now proven that this site is older than the caves discovered, in France which were, the oldest known to man.
One of the greatest gists mankind possesses is his ability to express himself, by art. and some of this expression finds itself on "cave walls" dotted around the globe. Take the time to look at this art and reflect back to what the person, who made this was trying to describe. Cave art can be found all around the world. visit back often to be kept up to date.

This particular figure was discovered in Victoria Australia and depicts a "human" like figure. Notice the "helmet", "gloves", "boots", and body attire.

Rock Art of Ancestral figures note: the "antennas" on the 2 figures behind.

These 2 figures represent the "spirit beings" called the Lightning Brothers Tjabuinji and Jagtjadbulla
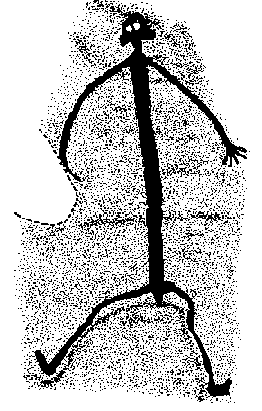
A picture of a spirit being, called a Quinkan a being which lured men to it, a trickster being which as Aboriginal lore goes would dehumanise you.

These figures are named the Wandjina they are always represented by a large band around the head as well as large eyes etc. They are the most popular figures to be drawn by the Aboriginals.
The Aborigines 'decorated' their bodies with personal decorations that included pipe-clay and other e symbols that conveyed messages designs or patterns on their arms, legs and upper body - particularly at ceremonial times. The patters were not random. In other words they were symbols that conveyed messages e.g., they represented the totems of individuals or denoted information about the tribe itself. The Aborigines often used the fat of animals to cover their bodies to protect them from insects such as mosquitoes. Some of the early Europeans considered that this practice 'gave them a most unpleasant odor'. No doubt it did, but it also provided effective protection against insect stings. Throughout the country various tribes used animal bones, fish bones and feathers in their hair and in the Sydney, Illawarra and Shoalhaven district the men wore a bone or piece of wood through their nose. A hole was cut through their nose during initiation and distinguished the members of the tribe from other tribes.
Bora Ground: The Aborigines considered some places to be sacred. In some parts of Australia the tribes called the places where initiation ceremonies were held, bora grounds. They were called Buna grounds in other parts of the country, but the sites were not randomly chosen and were used for thousands of years by the tribe. The bora ground itself was identified by two circles that were drawn on the ground or were formed by rocks or pebbles. The circles were connected by a path and other symbols were drawn into the earth or carved into trees near the grounds. These symbols were highly significant in ceremonies and also warned people (women and uninitiated youths and strangers), to stay away from the area.
Almost all of the Koori (preferred name of Australian aboriginies) shaman are initiated within one large group, called "The Dreamers". This is due to the fact that Australia has some of the strongest, and chaotic magic, around. All of the shaman are needed to put a check on that chaos. A Koori shaman takes only a small penalty for some tasks when astrally perceiving. As a trade off they are unable to mask. Any magician (full or adept) will notice this, whether or not he can assence. Mundanes even can tell when one of The Dreamers has entered the room. A Koori shaman will rarely travel outside of Australia, the need is too great in the outback for that.
White Australian shamans cannot join the dreamers, but some are associated with the koori group.
The Australian aboriginal shamans - "clever men" or "men of high degree" - described "celestial ascents" to meet with the "sky gods" such as Baiame, Biral, Goin and Bundjil. Many of the accounts of ritualistic initiation bare striking parallels to modern day UFO contactee and abduction lore. The aboriginal shamanic "experience of death and rising again" in the initiation of tribal "men of high degree" finds some fascinating parallels with modern day UFO abduction lore. The "chosen one" (either voluntarily or spontaneously) is set upon by "spirits", ritualistically "killed", and then experiences a wondrous journey (generally an aerial ascent to a strange realm) to met the "sky god." He is restored to life -- a new life as the tribal shaman.
Ritual death and resurrection, abduction by powerful beings, ritual removal or rearrangement of body parts, symbolic disembowelment, implanting of artifacts, aerial ascents and journeys into strange realms, alien tutelage and enlightenment, personal empowerment, and transformation - these and many other phenomena are recurring elements of the extraordinary shamanic tradition.
GAMES:
Aboriginal boys and girls played a number of games such as running, wrestling, climbing, throwing and ball games. No doubt they were fun to play but they all had a serious purpose. They were not simply for amusement.
Kicking balls made from grass or fur bound with vines taught people agility, but they also had to effect of forming individuals into teams which taught them cooperation and working with others.
Throwing sticks was a form of preparation for spear throwing. Drawing animal tracks in the earth trained children to observe their environment and provided them with the skills necessary to catch food.
Adult Aborigines were often used by Europeans to track runaway convicts and criminals.
Digging games trained people to collect food such as yams; climbing games enabled people to develop other survival skills - the main purpose behind all the games that Aboriginal children played.
ANCIENT AND LOST CIVILIZATIONS INDEX
ALPHABETICAL INDEX OF ALL FILES