
Most Ancient Mesoamerican civilizations built pyramid-shaped structures.



Most Ancient Mesoamerican civilizations built pyramid-shaped structures.


These were usually step pyramids, with temples on top more akin to the ziggurats of Mesopotamia than the Pyramids of Ancient Egypt. Mesoamerican Pyramids served many functions from - from astronomical observatories to places of ritual worship and sacrifice, and perhaps something linked to extraterrestrial Gods.
The Ciudadela is a monumental structure in Mesoamerica that is composed of 15 pyramids and encompasses approximately 11 areas. Mesoamerican pyramids form a prominent part of ancient Mesoamerican architecture. Although similar in some ways to Egyptian pyramids, these New World structures have flat tops (many with temples on the top) and stairs ascending their faces. The largest pyramid in the world by volume is the Great Pyramid of Cholula, in the east-central Mexican state of Puebla. The builders of certain classic Mesoamerican pyramids have decorated them copiously with stories about the Hero Twins, the feathered serpent Quetzalcoatl, Mesoamerican creation myths, ritualistic sacrifice, etc. written in the form of hieroglyphs on the rises of the steps of the pyramids, on the walls, and on the sculptures contained within. Read more

Inevitably pyramids collapse, mostly due to the pressures of nature.
'Bad Omen': Ancient Pyramid in Mexico Collapsed Into Pile of Rubble Under The Pressure of Incessant Rain Science Alert - November 18, 2024

The Maya are a people of southern Mexico and northern Central America (Guatemala, Belize, western Honduras, and El Salvador) with some 3,000 years of history. Archaeological evidence shows the Maya started to build ceremonial architecture approximately 3,000 years ago. The earliest monuments consisted of simple burial mounds, the precursors to the spectacular stepped pyramids from the Terminal Pre-classic period and beyond. These pyramids relied on intricate carved stone in order to create a stair-stepped design. Many of these structures featured a top platform upon which a smaller dedicatory building was constructed, associated with a particular Maya deity. Maya pyramid-like structures were also erected to serve as a place of interment for powerful rulers. Maya pyramid structures occur in a great variety of forms and functions, bounded by regional and period differences. The complexity of their celestial alignments, structure and design baffle archaeologists to this day.
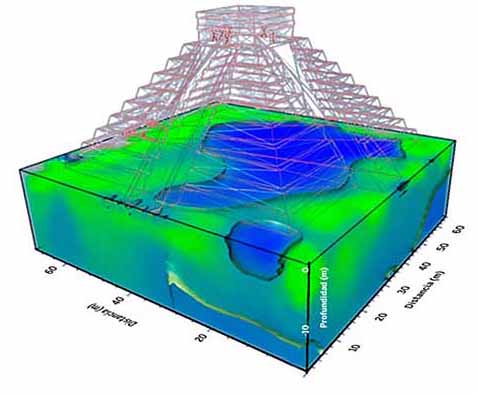
'Sacred sinkhole' discovered under 1,000-year-old Mayan temple... and it may eventually destroy the pyramid Daily Mail - August 17, 2015
It is a towering testament to a long dead civilization and has fascinated archaeologists for more than 150 years, but one of the most famous Mayan pyramids has been hiding a secret beneath its mighty steps. Researchers have discovered an enormous sinkhole beneath the 1,000-year-old Temple of Kukulkan, also known as El Castillo, which dominates the Mayan city of Chichen Itza in the northern Yucatan Peninusula of Mexico. And they fear the underground cavern, or cenote, which has a river running through it, may eventually cause the entire pyramid to collapse if its roof gives way.
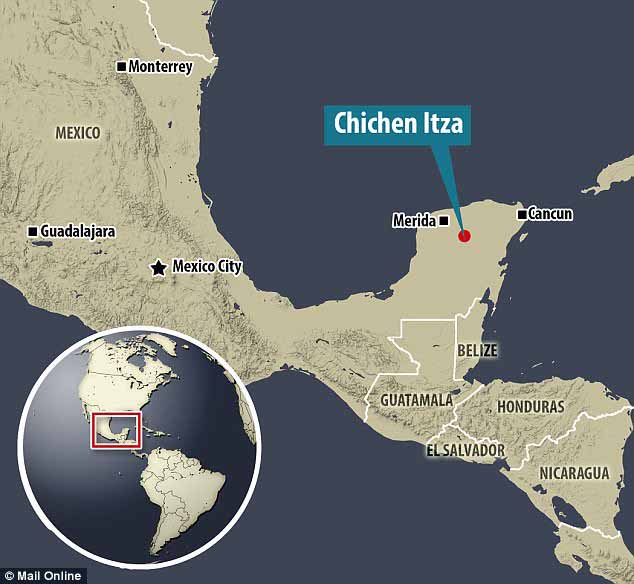
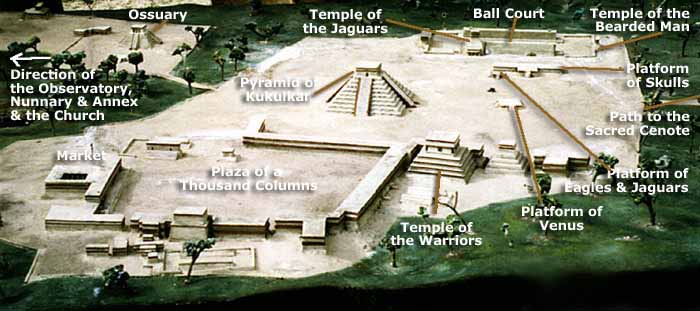
One of the most famous pyramid sites can be found at Chichen Itza, its name meaning "At the mouth of the well of the Itza (people)". Although this was the name for the site in pre-Columbian times, it is also referred to in the ancient chronicles as Uucyabnal, meaning "Seven Great Rulers". It is a large pre-Columbian archaeological site built by the Maya civilization located in the northern center of the Yucatan Peninsula, in the Yucatan state, present-day Mexico. Chichen Itza contains many fine stone buildings in various states of preservation; the buildings were formerly used as temples, palaces, stages, markets, baths, and ball courts.
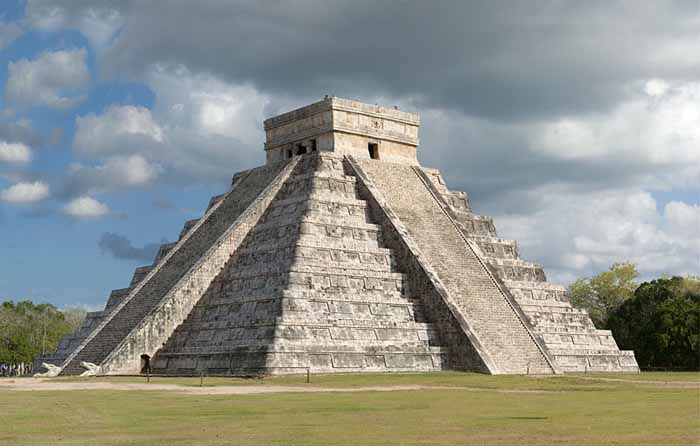

Dominating the center of Chichen is the Temple of Kukulkan (the Maya name for Quetzalcoatl), often referred to as "El Castillo" (the castle). This step pyramid has a ground plan of square terraces with stairways up each of the four sides to the temple on top.
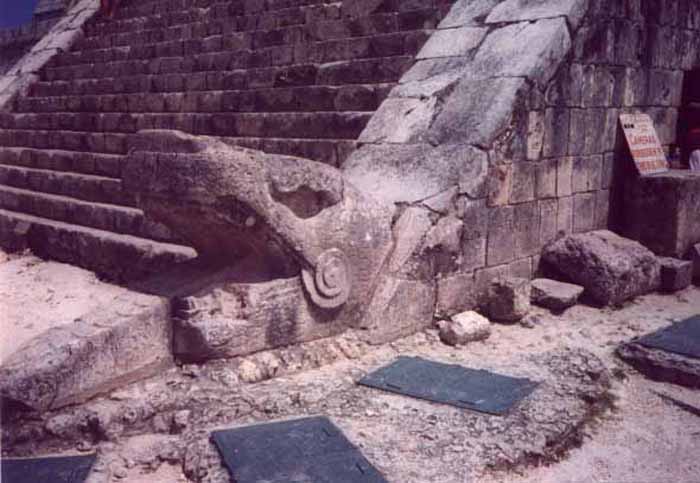

On the Spring and Autumn equinox, at the rising and setting of the sun, the corner of the structure casts a shadow in the shape of a plumed serpent - Kukulcan, or Quetzalcoatl - along the west side of the north staircase. On these two annual occasions, the shadows from the corner tiers slither down the northern side of the pyramid with the sun's movement to the serpent's head at the base.
Mesoamerican cultures periodically built larger pyramids atop older ones, and this is one such example. In the mid 1930s, the Mexican government sponsored an excavation of El Castillo. After several false starts, they discovered a staircase under the north side of the pyramid.
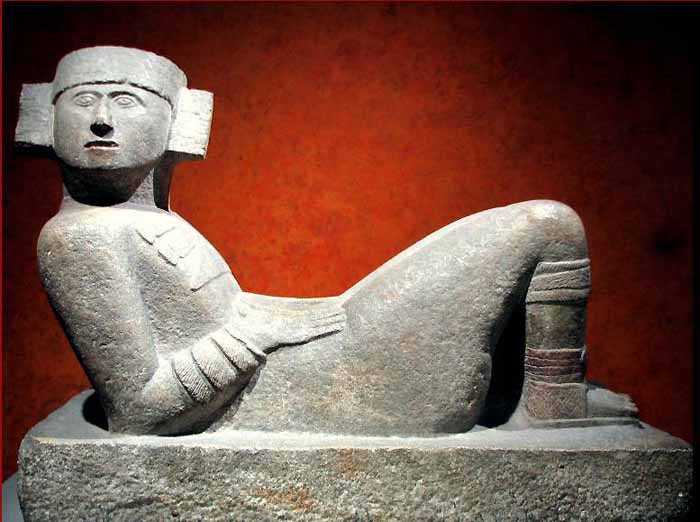

By digging from the top, they found another temple buried below the current one. Inside the temple chamber was a Chac Mool - a human figure in a position of reclining with the head up and turned to one side, holding a tray over the stomach.

A Mayan glyph shows Kukulkan/Quetzalcoatl the
plumed serpent with a gigantic Quetzal bird behind him.

Quetzalcoatl

The Quetzal has represented the Spirit of the Maya for thousands of years. Spirits, in many traditions, speak in echoes, lacking a body, just pure frequency and sound. Handclaps evoke chirped echoes from the staircases of the Pyramid of Kukulkan. The physics of the chirped echo can be explained quite simply as periodic reflections from stepfaces. The chirped-echo sounds much like the primary call of the Mayan sacred bird, the resplendent Quetzal. The sounds perhaps trigger something with the subconscious of the person listening as harmonics are linked to creation. Throughout the world, ancient cathedrals and monuments have been acoustically designed to align with the sacred geometry of human consciousness, igniting when accessed. Could the Maya have intentionally coded the sound of their sacred bird into the pyramid architecture?
The dimensions of the steps are the key to the effect. Each step is tall, but the tread, where the foot is placed, doesn't cut deeply into the pyramid. If the stairs were deeper and not so high, the effect on the echoes would not be as great, and they wouldn't sound like a chirp.
In the millennium since this pyramid was built, though the plaster has eroded from the limestone staircases, the sound is still recognizable. Today the Quetzal still plays an important role in modern Mayan culture. The Quetzal is the unit of currency in Guatemala. The Guatemalan government issues a prestigious award named "The Order of the Quetzal."
Pyramid of Kukulcan - Clap - Echo is the Rare Sacred Quetzal bird

Dust devil whips up Chichen Itza a day after 2019 Spring Equinox
Yucatan Life - March 23, 2019
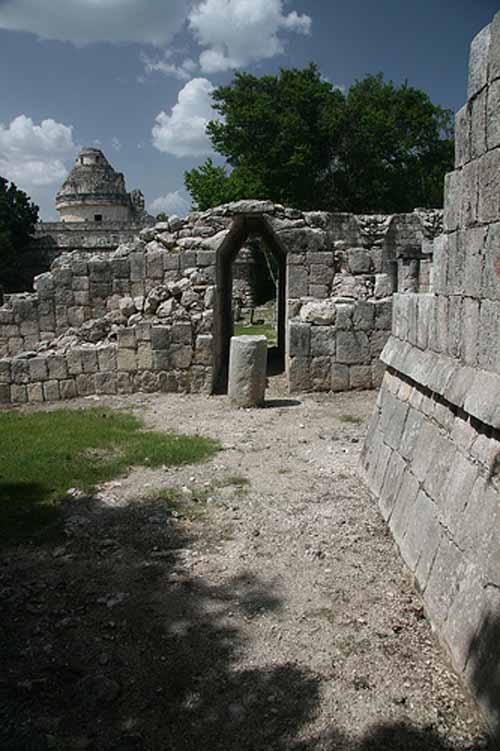

To the east of El Castillo are a series of buildings, the northernmost is the Temple of the Tables. Its name comes from a series of altars at the top of the structure that are supported by small carved figures of men with upraised arms, called Atlantes.
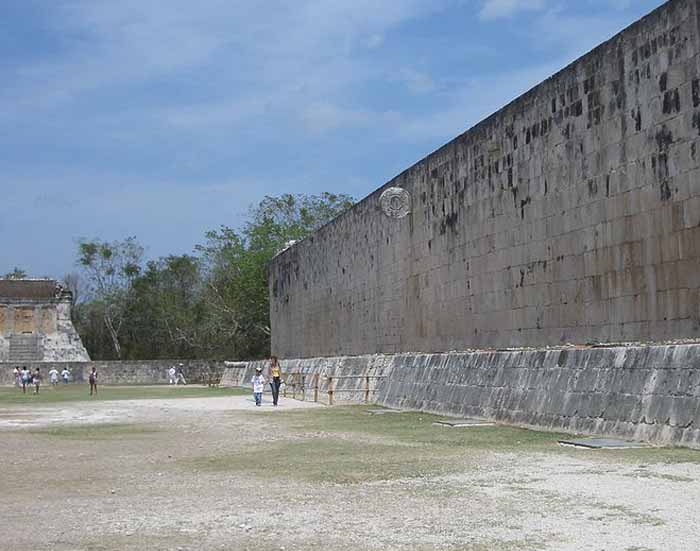
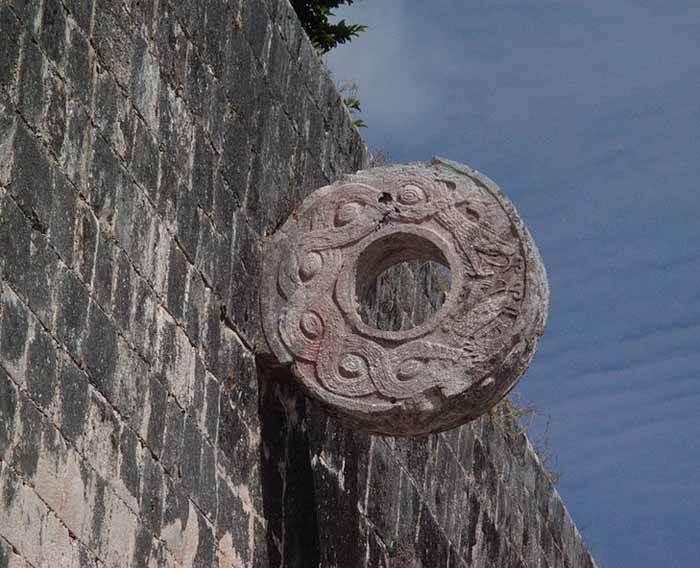


Archaeologists have identified several courts for playing the Mesoamerican ballgame in Chichen, but the Great Ball Court about 150 metres (490 ft) to the north-west of the Castillo is by far the most impressive. It is the largest ball court in ancient Mesoamerica. It measures 166 by 68 metres (540 ft x 220 ft). The imposing walls are 12 metres (39 ft) high, and in the center, high up on each of the long walls, are rings carved with intertwining serpents.
At the base of the high interior walls are slanted benches with sculpted panels of teams of ball players. In one panel, one of the players has been decapitated and from the wound emits seven streams of blood; six become wriggling serpents and the center becomes a winding plant.
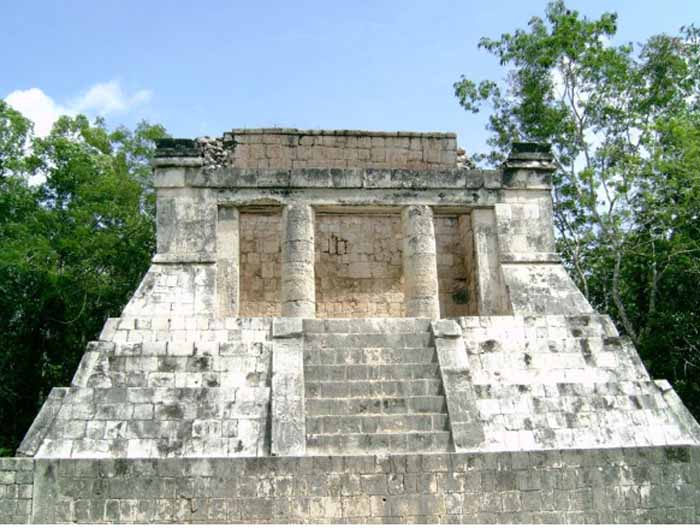

At one end of the Great Ball Court is the North Temple, popularly called the Temple of the Bearded Man. This small masonry building has detailed bas relief carving on the inner walls, including a center figure that has carving under his chin that resembles facial hair. At the south end is another, much bigger temple, but in ruins.
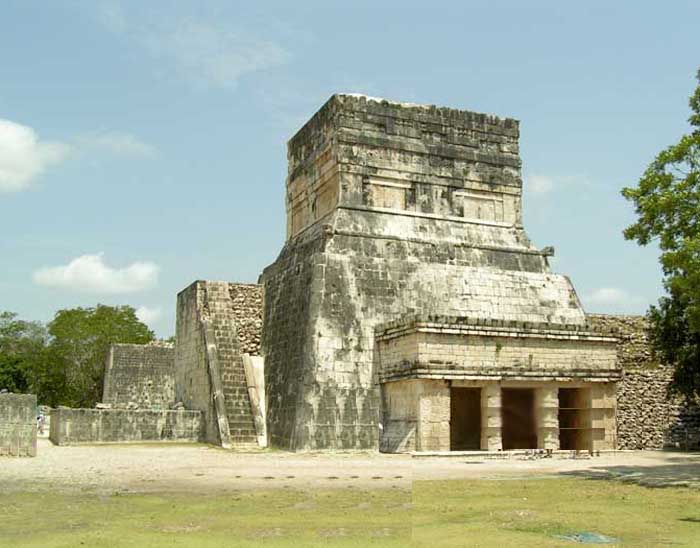

Built into the east wall are the Temple of the Jaguar. The Upper Temple of the Jaguar overlooks the ball court and has an entrance guarded by two, large columns carved in the familiar feathered serpent motif. Inside there is a large mural, much destroyed, which depicts a battle scene.
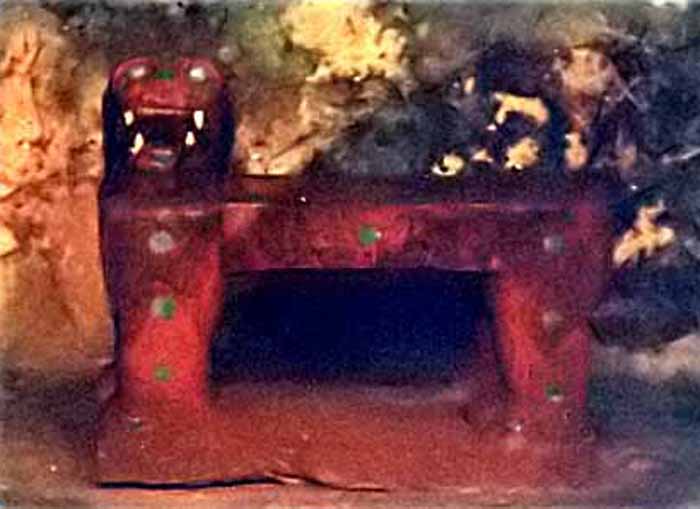

The Temple of the Jaguar features a jaguar throne with red paint and jade spots. Behind this platform is a walled inscription which depicts a relief of Tzompantli - a low, flat platform surrounded with carved depictions of human skulls. A doorway at the base of the north stairway leads to a tunnel, from which one can climb the steps of the earlier version of El Castillo inside the current one, up to the room on the top where you can see King Kukulcan's Jaguar Throne, carved of stone and painted red with spots made of inlaid jade.
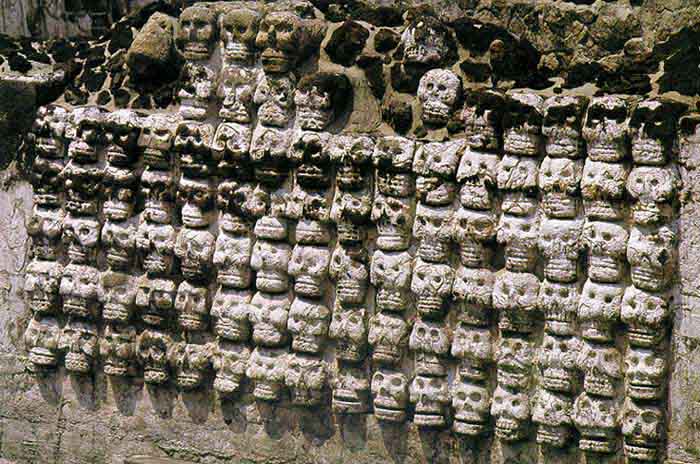

In the entrance to the Lower Temple of the Jaguar, which opens behind the ball court, is another Jaguar throne, similar to the one in the inner temple of El Castillo, except that it is well worn and missing paint or other decoration. The outer columns and the walls inside the temple are covered with elaborate bas-relief carvings.
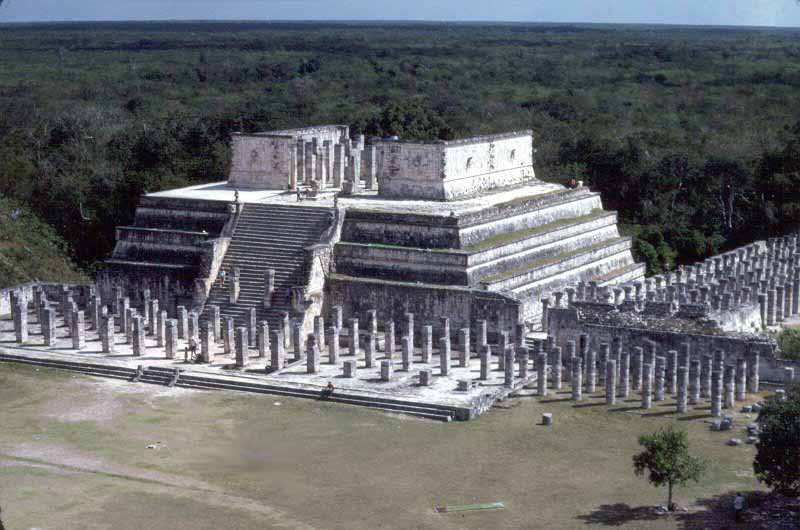


The 'Temple of the Warriors' and its adjacent 'Temple of the Jaguar' are very impressive ruins of the complex. A massive temple structure, surrounded by hundreds of columns is carved with reliefs. The columns continue on into the jungle, that part of the temple still has not been restored.
The Temple of the Warriors complex consists of a large stepped pyramid fronted and flanked by rows of carved columns depicting warriors. This complex is analogous to Temple B at the Toltec capital of Tula, and indicates some form of cultural contact between the two regions. The one at Chichen Itza, however, was constructed on a larger scale.
At the top of the stairway on the pyramid's summit (and leading towards the entrance of the pyramid's temple) is a Chac Mool. This temple encases or entombs a former structure called The Temple of the Chac Mool.
Along the south wall of the Temple of Warriors are a series of what are today exposed columns, although when the city was inhabited these would have supported an extensive roof system. The columns are in three distinct sections: an east group, that extends the lines of the front of the Temple of Warriors; a north group, which runs along the south wall of the Temple of Warriors and contains pillars with carvings of soldiers in bas-relief; and a northeast group, which was apparently formed a small temple at the southeast corner of the Temple of Warriors, which contains a rectangular decorated with carvings of people or gods, as well as animals and serpents. The northeast column temple also covers a small marvel of engineering, a channel that funnels all the rainwater from the complex some 40 metres (130 ft) away to a rejollada, a former cenote.

To the north of Las Monjas is a cockeyed, round building on a large square platform. It's nicknamed El Caracol ("the snail") because of the stone spiral staircase inside. The structure with its unusual placement on the platform and its round shape (the others are rectangular, in keeping with Maya practice), is theorized to have been a proto-observatory with doors and windows aligned to astronomical events, specifically around the path of Venus as it traverses the heavens.
Lost Cave of 'Jaguar God' Rediscovered Below Mayan Ruins - and It's Full of Treasure Live Science - March 5, 2019
Shimmying through a maze of dark tunnels below the Mayan ruins of Chichen Itza on Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula, archaeologists have rediscovered a long-sealed cave brimming with lost treasure. According to an statement from Mexico's National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH), the cave is stockpiled with more than 150 artifacts, including incense burners, vases, and decorative plates adorned with the faces of ancient gods and other religious icons. The trove is believed to be just one of seven sacred chambers in a network of tunnels known as Balamku - "Jaguar God" - that sits below Chichen Itza, a city that accommodated millions of people at its peak during the 13th century. The artifacts have likely been untouched by human hands for more than 1,000 years, according to the INAH.
Though the treasures were probably deliberately sealed off, the ritual cave, rediscovered in 2018 by archaeologists hunting for a sacred well below the city, has had at least one human visitor in the past millennium, National Geographic reported. The cave was initially discovered in 1966 by archaeologist Víctor Segovia Pinto, who wrote a report about the find, but never excavated before directing local farmers to seal the cavern's entrance for reasons that are still unknown. Segovia's records of the discovery went missing, leaving behind a mystery that would take five decades to solve.

Teotihuacan was, at its height in the first half of the 1st millennium BCE, the largest pre-Columbian city in the Americas. The city during its existence was larger than any European city of the same era, possibly including Rome. The civilization and cultural complex associated with the site is also referred to as Teotihuacan. Its influence spread throughout Mesoamerica; evidence of Teotihuacano presence, if not outright political and economic control, can be seen at numerous sites in Veracruz and the Maya region. The city was located in what is now the San Juan Teotihuacan municipality in the State of Mexico, Mexico, approximately 40 km (24.8 mi) northeast of Mexico City. It covers a total surface area of 83 kms and was made a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1987.
The early history of Teotihuacan is quite mysterious, and the origin of its founders is debated. For many years, archaeologists believed it was built by the Toltec. This belief was based on colonial period texts such as the Florentine Codex which attributed the site to the Toltecs. However, the Nahuatl word "Toltec" generally means "craftsman of the highest level" and may not always refer to the archaeological Toltec civilization centered at Tula, Hidalgo. Since Toltec civilization flourished centuries after Teotihuacan, they cannot be understood as the city's founders.
In the Late Formative period, a number of urban centers arose in central Mexico. The most prominent of these appears to have been Cuicuilco, on the southern shore of Lake Texcoco. Scholars have speculated that the eruption of the Xitle volcano may have prompted a mass emigration out of the central valley and into the Teotihuacan valley. These settlers may have founded and/or accelerated the growth of Teotihuacan.
Other scholars have put forth the Totonac people as the founders of Teotihuacan, and the debate continues to this day. There is evidence that at least some of the people living in Teotihuacan came from areas influenced by the Tiwanaku Civilization, including the Zapotec, Mixtec and Maya peoples.
The culture and architecture of Teotihuacan was influenced by the Olmec Civilization who are considered to be the Mother Civilization of Mesoamerica.
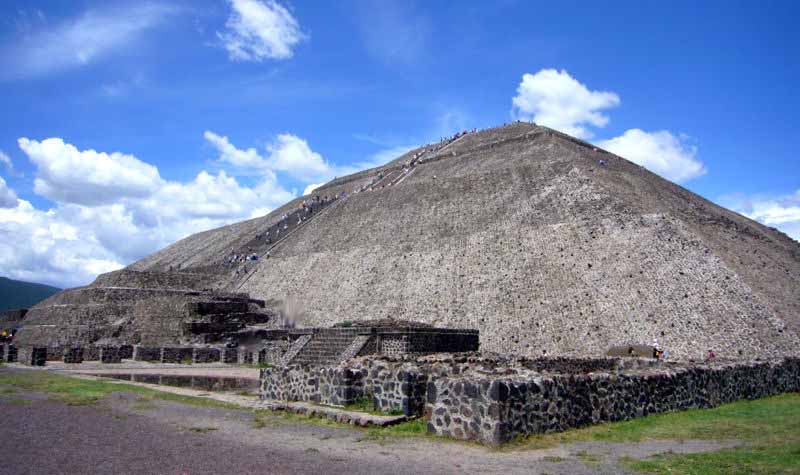


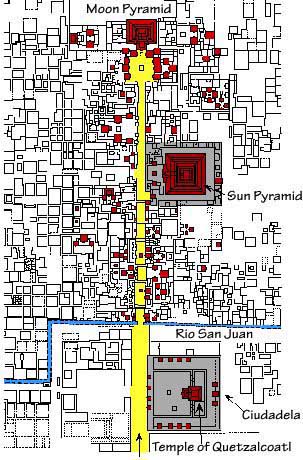
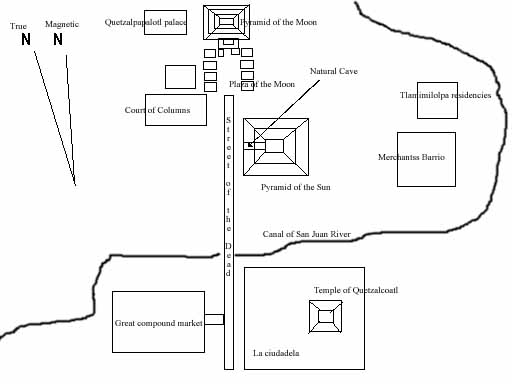
The earliest buildings at Teotihuacan date to about 200 BCE. The Pyramid of the Sun, was completed by 100 BCE. It is the largest building in Teotihuacan and one of the largest in Mesoamerica. Found along the Avenue of the Dead, in between the Pyramid of the Moon and the Ciudadela, and in the shadow of the massive mountain Cerro Gordo, the pyramid is part of a large complex in the heart of the city.
The name "Pyramid of the Sun" comes from the Aztecs, who visited the city of Teotihuacan centuries after it was abandoned; the name given to the pyramid by the Teotihuacanos. It was constructed in two phases. The first construction stage, around 100 A.D., brought the pyramid to nearly the size it is today.
The second round of construction resulted in its completed size of 738 feet (225 meters) across and 246 feet (75 meters) high, making it the third largest pyramid in the world behind the Great Pyramid of Cholula and The Great Pyramid.
The second phase also saw the construction of an altar atop of the pyramid, which has not survived into modern times. The Adosada platform was added to the pyramid in the early third century, at around the same time that the Ciudadela and Temple of the Feathered Serpent, (see below) Teotihuacan Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent were constructed.
Over the structure the ancient Teotihuacanos finished their pyramid with lime plaster imported from surrounding areas, on which they painted brilliantly colored murals. While the pyramid has endured for centuries, the paint and plaster have not and are no longer visible. Few images are thought to have been included in the mural decorations on the sides of the pyramid. Jaguar heads and paws, stars, and snake rattles are among the few images associated with the pyramids.
It is thought that the pyramid venerated a deity within Teotihuacan society but the destruction of the temple on top of the pyramid, by both deliberate and natural forces prior to the archaeological study of the site, has so far prevented identification of the pyramid with any particular deity. Some scholars have suggested that the deity of the pyramid was the Great Goddess, one of two major Teotihuacan deities and one of the few goddesses in ancient Mesoamerica. However, little evidence exists to support this theory.
Modern investigations
The first major archaeological excavation of the site was done by Leopoldo Batres in 1906. Batres supervised restoration of the Pyramid for the 1910 centennial of Mexican independence. Some aspects of Batres' reconstruction of the pyramid have been questioned by later archaeologists. Subsequent excavations of Teotihuacan have continued to the present. In 1925 Pedro Dosal discovered skeletons at the 4 corners of the foundations of the temple, which he interpreted as human sacrifices at the dedication of the temple.
Structure location and orientation
The orientation of the structure may hold some anthropological significance. The pyramid is oriented slightly northwest of the horizon point of the setting sun on two days a year, August 12 and April 29, which are about one divinatory calendar year apart for the Teotihuacanos. The day of August 12 is significant because it would have marked the date of the beginning of the present era and the initial day of the Maya long count calendar. In addition, many important astrological events can be viewed from the location of the pyramid that are important in terms of both agriculture and belief systems of the ancient society.
The pyramid was built over a man-made tunnel leading to a "cave" located six meters down beneath the center of the structure. Originally this was believed to be a naturally formed lava tube cave and interpreted as possibly the place of Chicomoztoc, the place of human origin according to Nahua legends. More recent excavations have suggested that the space is man-made instead, and could have served as a royal tomb. In 2008 scientists used muon detectors to try to find other chambers within the interior of the pyramid, but substantial looting has prevented the discovery of a function for the chambers in Teotihuacan society.
Recovered artifacts
Only a few caches of artifacts have been found in and around the pyramid. Obsidian arrowheads and human figurines have been discovered inside the pyramid and similar objects have been found at the nearby Pyramid of the Moon and Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent in the Ciudadela. These objects may have represented sacrificial victims. In addition, burial sites of children have been found in excavations at the corners of the pyramid. It is believed that these burials were part of a sacrificial ritual dedicating the building of the pyramid.
Ancient Offering Discovered Beneath Pyramid of the Sun Live Science - December 15, 2011

Ornaments

Archaeologists in Mexico have uncovered a small treasure trove of items that may have been placed as offerings to mark the start of construction on the Teotihuacan Pyramid of the Sun almost 2,000 years ago. The offerings include pieces of obsidian and pottery as well as animal remains. Perhaps most striking are three human figurines made out of a green stone, one of which is a serpentine mask that researchers think may have been a portrait.

The location of the excavation site between the Feathered Serpent Temple and the platform in front of it (Structure IC).

Vertical shaft in front of the Feathered Serpent Temple.
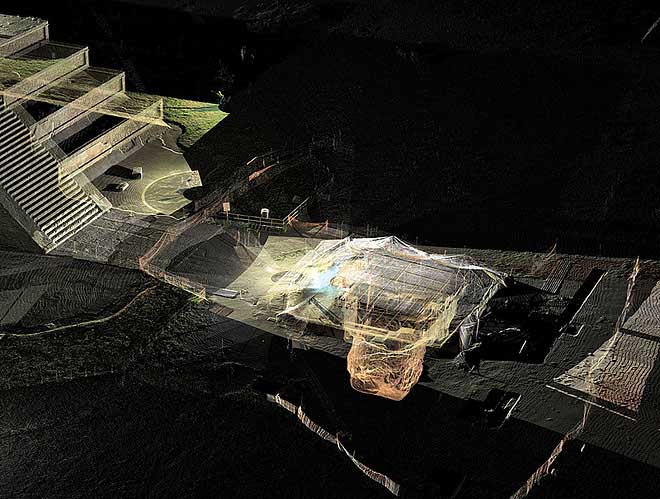
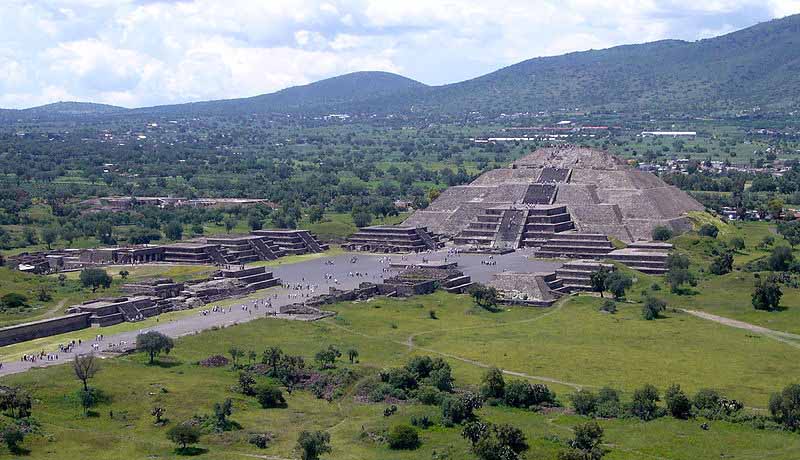


The Pyramid of the Moon is the second largest building in Teotihuacan after the Pyramid of the Sun. The Pyramid of the Moon is located in the northern part of Teotihuacan and it mimics the contours of Cerro Gordo. Some have called it Tenan which in Nahuatl means "mother or protective stone." The Pyramid of the Moon covers a structure older than the Pyramid of the Sun which existed prior to 200 A. D.
The Pyramid's construction between 200 and 450 A.D. completed the bilateral symmetry of the temple complex. A slope in front of the staircase gives access to the Avenue of the Dead, a platform atop the pyramid was used to conduct ceremonies in honor of Chalchiuhtlicue, the goddess of water and of the moon. This platform and the sculpture found at the pyramid's bottom are thus dedicated to Chalchiuhtlicue.
Opposite Chalchiuhtlicue's altar is the Plaza of the Moon. The Plaza contains a central altar and an original construction with internal divisions, consisting of four rectangular and diagonal bodies that formed what is known as the "Teotihuacan Cross."
Between 100 and 500 A.D, an ancient people built a flourishing metropolis called Teotihuacan on a plateau about 25 miles (40 km) from present-day Mexico City. With its accurately aligned avenues and a huge plaza surrounded by 15 monumental pyramids. It was said by the Aztecs to have been surmounted by a huge stone figure related to the moon but this figure was uncovered (weighing 22 tonnes and was somehow lifted to the top of the pyramid) and it is thought more likely that it represents a water deity.
Recently, archaeologists have excavated beneath the Pyramid of the Moon. The archaeologists are looking for clues to the history of this mysterious culture. Tunnels dug into the structure have revealed that the Teotihuacan's citizens did not remain pleased with their architectural feats for very long.
Over a period of several hundred years, the pyramid underwent at least six facelifts and each new addition was larger and covered the previous structure. As the archeologists burrowed through the layers of the pyramid, they discovered artifacts that provide the beginning of a timeline to the history of Teotihuacan. The latest find, made by a team led by Saburo Sugiyama, associate professor at Aichi Prefectural University in Japan and adjunct faculty at Arizona State University, and Ruben Cabrera of Mexico's National Institute of Anthropology and History, is a tomb apparently made to dedicate the fifth phase of construction. It contains four human skeletons, animal bones, jewelry, obsidian blades, and a wide variety of other offerings. Archeologists estimated that the burial occurred between 100 and 200 A.D.
Another tomb dedicated to Chalchiuhtlicue was discovered in 2007. It is dated to the fourth stage of construction. It contained a single human male sacrificial victim as well as a wolf, jaguar, puma, serpent, bird skeletons, and more than 400 other relics which include a large greenstone and obsidian figurines, ceremonial knives, and spear points.
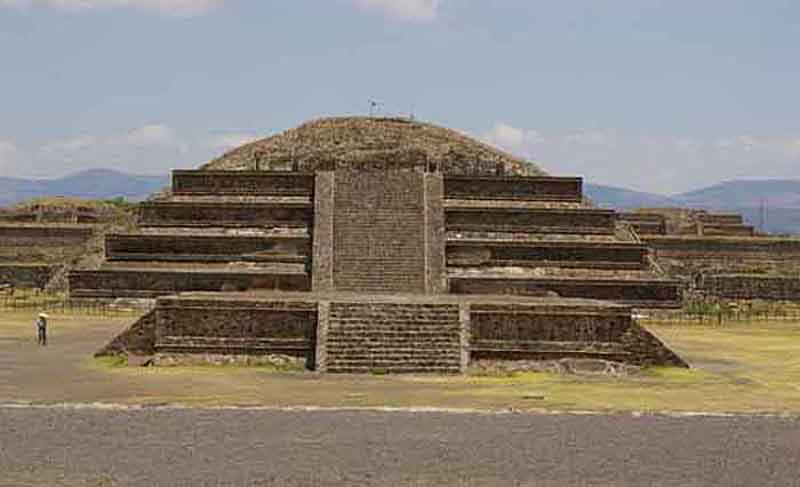
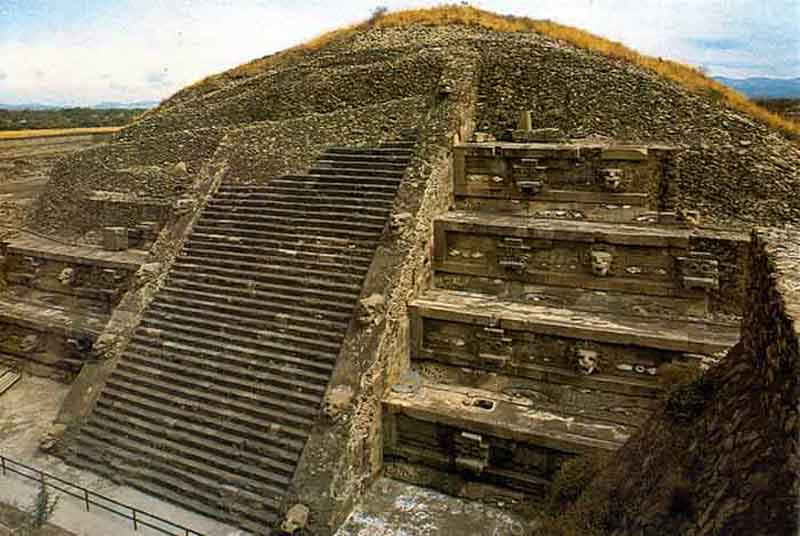
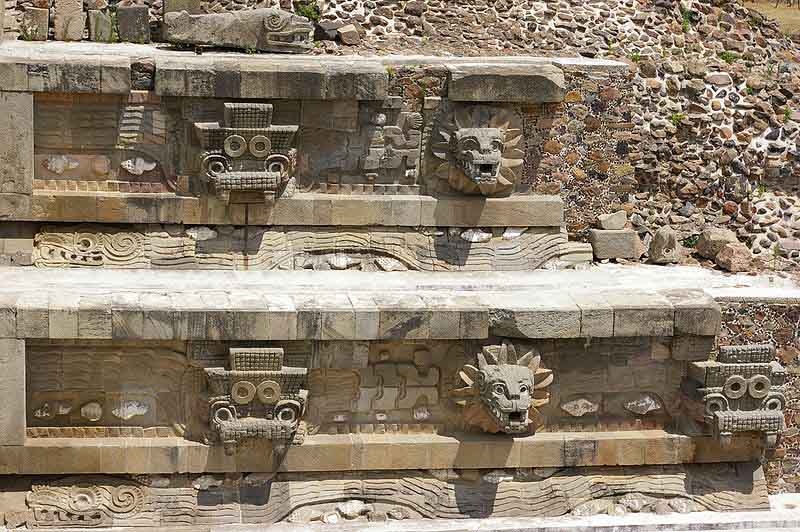




The Temple of the Feathered Serpent of Teotihuacan is an important religious and political center of the city. The Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent has revealed a great deal about religious ceremonies, burials, and politics in ancient Mesoamerica for the site of Teotihuacan. The structure contains some of the earliest-known representations of the Mesoamerican "plumed serpent" deity figure, most generally known by the term Quetzalcoatl, from the Nahuatl language of the much-later Aztec peoples.
The Feathered Serpent Pyramid is located at the Pre-Columbian site of Teotihuacan, which was at one time the largest city in the western hemisphere. The Feathered Serpent Pyramid is located in the Ciudadela at the South end of the Avenue of the Dead, a long avenue which is surrounded by platforms displaying the talud-tablero architectural style.
The Ciudadela is a Spanish term first used when the Spanish conquistadors arrived at Teotihuacan. It is a structure with high walls and a large courtyard that surrounds the Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent. The Ciudadela's courtyard is massive enough that it could house the entire adult population of Teotihuacan within its walls, which was estimated to be one hundred to two hundred thousand people during its peak. Within the Ciudadela there are several monumental structures, including the Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent, two mansions on the North and South side of the pyramid and the Adosada platform. The Adosada platform is located on the front, West side of the Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent, blocking its front view.
The Feathered Serpent Pyramid is built in the talud-tablero style, with several platforms forming the pyramid. In between every platform there is a wall where a feathered serpent's head sticks outward. Its body wraps around the entire pyramid. Along with the feathered serpent there is also another figure that some believe is a representation of a crocodile or a representation of the deity Tlaloc. These figures alternate around the pyramid. In the eyes of these figures there is a spot for obsidian glass to be put in, so when the light hits, its eyes would glimmer. In between the heads a row of three shells can be found, showing that the people of Teotihuacan were trading with people along the Mexican coast. In antiquity the entire pyramid was painted. Today it is hidden by the adosada platform built in the 4th century hinting at political restructurisation of Teotihuacan during that time.
Burials at the Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent
The people of Teotihuacan believed in ritual sacrifice to satisfy the gods. Multiple burials were found at the pyramid, and it is believed that they were sacrificed as part of the dedication of the temple. The numbers of the burials are 4, 8, 9, 13, 18, and 20; these numbers represent significant ideology in Mesoamerica. There are four directions in the world, nine layers of their underworld, thirteen layers of heaven and earth, and a ritual calendar of thirteen months of twenty days or two hundred and sixty day calendar, and a solar calendar of eighteen months of twenty days.
Relation to the Calendar
As stated above there was a correlation between the Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent and a calendar for the people of Teotihuacan. The pyramid also is thought to contain two hundred and sixty feathered serpent heads between the platforms. Each of these feathered serpents also contains an open area in its mouth. This open area is big enough to put a place holder in. Thus, it is believed that the people of Teotihuacan would move this place marker around the pyramid to represent the ritual calendar. When a spiritual day would arrive the people would gather within the walls of the Ciudadela and celebrate the ritual.
Political Influences
The Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent was not only a religious center but also a political center as well. The rulers of Teotihuacan were not only the leaders of men; they were also the spiritual leaders of the city. The two mansions near the pyramid are thought to have been occupied by powerful families. An interesting feature of the Feathered Serpent Pyramid is that there are examples of a shift in power or ideology in Teotihuacan and for the Pyramid itself. The construction of the Adosada platform came much later than the Feathered Serpent Pyramid. The Adosada platform is built directly in front of the pyramid and blocks its front view. Thus, it is thought that the political leaders lost favor or that the ideology of the Feathered Serpent Pyramid lost virtue and was covered up by the Adosada
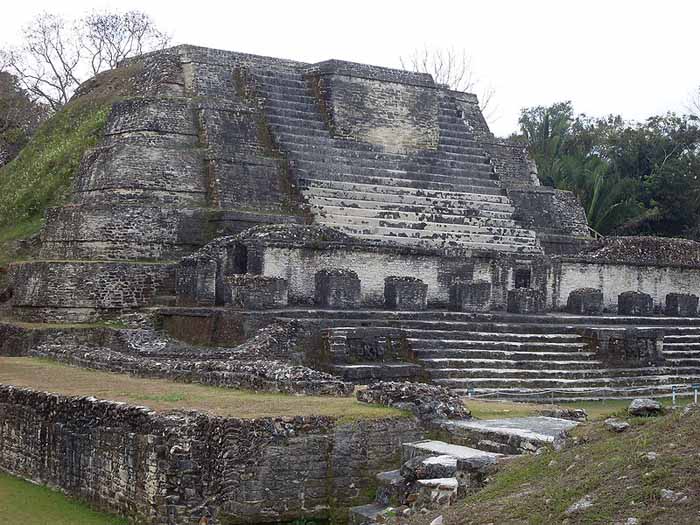

Altun Ha is the name given ruins of an ancient Maya city in Belize, located in the Belize District about 30 miles (50 km) north of Belize City and about 6 miles (10 km) west of the shore of the Caribbean Sea."Altun Ha" is a modern name in the Maya language, coined by translating the name of the nearby village of Rockstone Pond. The ancient name is at present unknown.The largest of Altun Ha's temple-pyramids, the "Temple of the Masonry Altars", is 54 feet (16 m) high. A drawing of this structure is the logo of Belize's leading brand of beer, "Belikin".
The site covers an area of about 5 miles (8 km) square. The central square mile of the site has remains of some 500 structures.Archeological investigations show that Altun Ha was occupied by 200 BC. The bulk of construction was from the Maya Classic era, c. 200 to 900 AD, when the site may have had a population of about 10,000 people. About 900 there was some looting of elite tombs of the site, which some think is suggestive of a revolt against the site's rulers.
The site remained populated for about another century after that, but with no new major ceremonial or elite architecture built during that time. After this the population dwindled, with a moderate surge of reoccupation in the 12th century before declining again to a small agricultural village.
The ruins of the ancient structures had their stones reused for residential construction of the agricultural village of Rockstone Pond in modern times, but the ancient site did not come to the attention of archeologists until 1963, when the existence of a sizable ancient site was recognized from the air by pilot and amateur Mayanist Hal Ball.
Starting in 1965 an archeological team lead by Dr. David Pendergast of the Royal Ontario Museum began extensive excavations and restorations of the site, which continued through 1970. One of the most spectacular discoveries is a large (almost 10 pounds or 5 kilograms) piece of jade elaborately carved into an image of the head of the Maya Sun God, Kinich Ahau. This jade head is considered one of the national treasures of Belize. A road connects Altun Ha to Belize's Northern Highway, and the site is accessible for tourism.
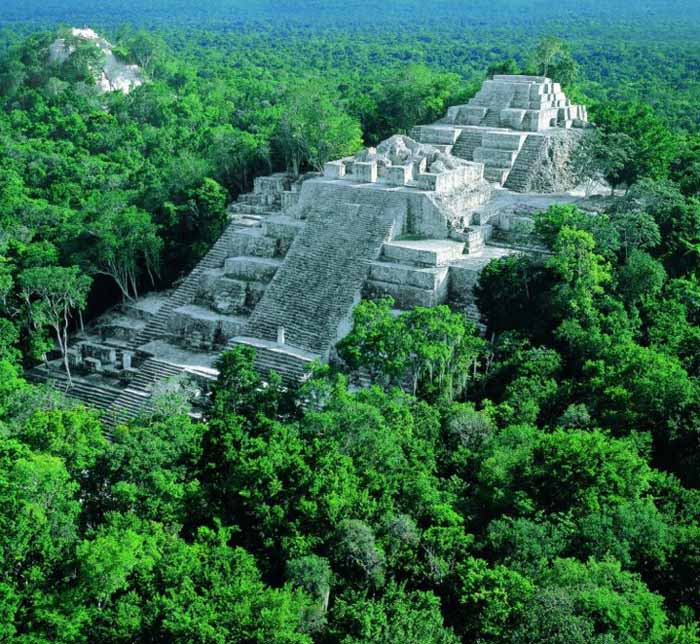

Calakmul is the name of both a municipality and a major archeological site in the Mexican state of Campeche, in the central part of the Yucatan Peninsula.
Calakmul (also Kalakmul and other less frequent variants) is also the name given to site of one of the largest ancient Maya cities ever uncovered. It is located in the 1,800,000 acre Calakmul Biosphere Reserve, deep in the jungles of the Peten, 30 km from the Guatemalan border.
First discovered from the air by biologist Cyrus L. Lundell of the Mexican Exploitation Chicle Company on December 29, 1931, the find was reported to Sylvanus G. Morley of the Carnegie Institute at Chichen Itza in March 1932. According to Lundell, who named the site, "In Maya, 'ca' means 'two', 'lak' means 'adjacent', and 'mul' signifies any artificial mound or pyramid, so 'Calakmul' is the 'City of the Two Adjacent Pyramids'."
Calakmul was the major seat of power of the Kaan or "Kingdom of the Snake", which first arose further north but built Calakmul into a Late Classic Era superpower ally of Caracol and rival to Tikal. A series of 11 painted vessels, dubbed Dynastic Vases, describe the ascensions of the Kaan rulers, including ancestral and legendary figures.
Calakmul probably supported a population of over 50,000, and so far more than 6,250 structures have been discovered in an area of up to 70 square kilometers with a substantial northern wall and a series of water management features (Calakmul's reservoirs include the largest in the Maya world) delineating a dense core of 22 square kilometers. Calakmul's 45 meter pyramid "Structure 2" is the largest Classic Era Maya temple platform known. Many of the city's monuments and structures are constructed of chalky local limestone, which has made interpretation of the site difficult.
After a long period of inactivity following Morely's 1932 expedition, the city was explored by William Folan between 1984 and 1994, and is now the subject of a large-scale project of the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) under Ramon Carrasco.
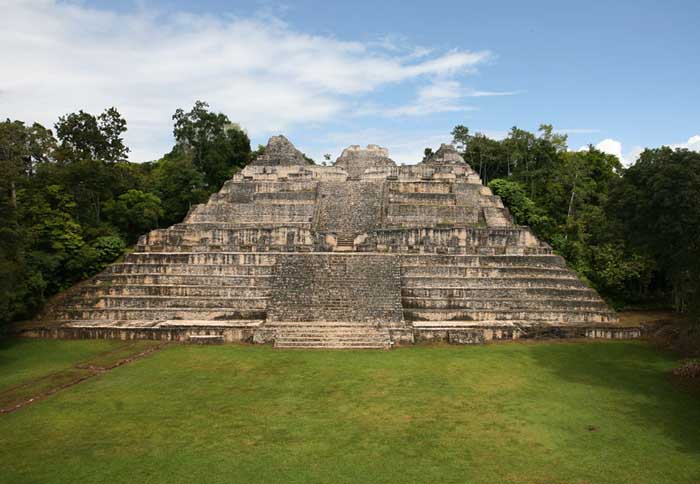
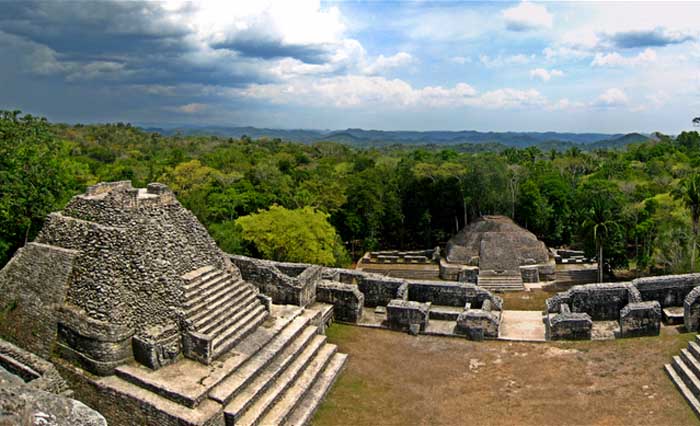


�Caracol or El Caracol is the name given to a large ancient Maya site located in the Cayo District of the nation of Belize. Caracol is about 25 miles south of Xunantunich and San Ignacio Cayo, at an elevation of 1500 feet (460 m) above sea-level, in the foothills of the Maya Mountains. The name is Spanish for "The Snail"; the ancient Maya name may have been Oxhuitza. It is known as such due to the large numbers of these creatures found at the site on its visitation by A.H. Anderson, the then chief archaeologist to British Honduras, after its discovery in 1937 by Rosa Mai, a mahogany logger. The site was occupied as early as 1200 BCE, but had its greatest period of construction in the Maya Classic period, with over 40 monuments dated between 485CE to 889CE which record the dynastic sequence of the rulers.
Ancient Caracol was one of the largest ancient Maya cities, covering some 65 square miles (168 kms) with an estimated peak population of about 120,000, or possibly as many as 180,000 people. One monument here records a military victory over the army of Tikal in 562CE, where Caracol's Lord Water is shown to have captured and sacrificed Tikal's Double Bird. This event is seemingly concurrent with archaeological and epigraphic evidence indicating the beginning of the Tikal Mid-Classic Hiatus, when a seeming decline in Tikal's population, a cessation of monument building, and the destruction of certain monuments in the Great Plaza occurred as Caracol's population and urban development seemingly skyrocketed.
The site was first noted and documented in archaeological terms in 1937. More extensive explorations and documention of the site was undertaken by the University of Pennsylvania in 1951 and 1953. A project of archaeological excavations and restorations of the ancient structures at Caracol started in 1985 and is ongoing. The project is currently directed by Drs. Arlen and Diane Chase of the University of Central Florida in Orlando. The site is maintained by residential wardens from the Belize Institute of Archaeology, a sub-division of the National Institute of Culture and History, a government-run agency.
The site currently accommodates an average of 15-20 tourists per day, with greater numbers during the peak season around Easter. A museum to hold the large monuments found at the site is currently being constructed. A visitor center is already at the site, and recent developments include new directional and informational signs and a house for the residential staff. The only road Caracol may be accessed by is paved for the last ten miles and leads to the Western Highway between San Ignacio and Belmopan and to Santa Elena.
Caana ("sky-palace") is the largest building at Caracol. It remains one of the largest man-made structures in Belize.
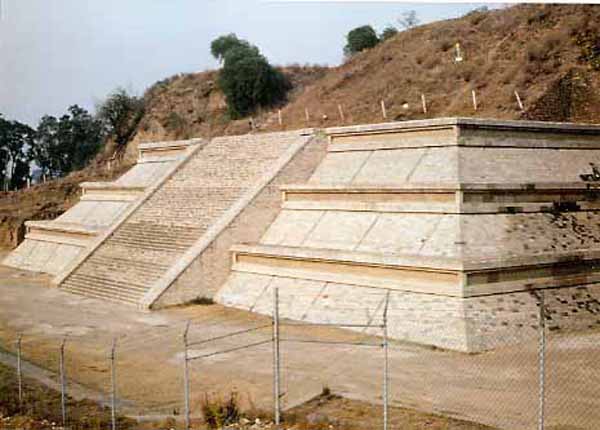


The Mesoamerican region's largest pyramid by volume, the largest in the world by volume is the Great Pyramid of Cholula in the Mexican state of Puebla. It is also known as Tlachihualtepetl - Nahuatl for "artificial mountain". The Aztecs believed that Xelhua built the pyramid.
The temple-pyramid complex was built in four stages, starting from the 3rd century BCE through the 9th century CE, and was dedicated to the deity Quetzalcoatl. It has a base of 450 by 450 m (1476x1476 ft) and a height of 66 m (217 ft). According to the Guinness Book of Records, it is in fact the largest pyramid as well as the largest monument ever constructed anywhere in the world, with a total volume estimated at over 4.45 million m, even larger than that of the Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt which is about 2.5 million m. However the Great Pyramid of Giza is higher at 138.8 m (455 feet).
Today the pyramid at first appears to be a natural hill surmounted by a church. This is the Iglesia de Nuestra Senora de los Remedios (Church of Our Lady of the Remedies), also known as the Santuario de la Virgen de los Remedios (Sanctuary of the Virgin of the Remedies), which was built by the Spanish in colonial times (1594) on the site of a pre-Hispanic temple. The church is a major Catholic pilgrimage destination, and the site is also used for the celebration of indigenous rites. Many ancient sites in Latin America are found under modern Catholic holy sites, due to the practice of the Catholic Church repurposing local religious sites.
Because of the historic and religious significance of the church, which is a designated colonial monument, the pyramid as a whole has not been excavated and restored, as have the smaller but better-known pyramids at Teotihuacan. Inside the pyramid are some five miles (8 km) of tunnels excavated by

El Tajin is a Pre-Columbian archaeological site near the city of Papantla, in the state of Veracruz, Mexico.
Construction of ceremonial buildings at El Tajin began about the 1st century. Early classic Tajin shows influence of Teotihuacan; early postclassic shows considerable Toltec influence. Construction continued to about the start of the 13th century, at which time the city was conquered and burned by Chichimec invaders. The site continued to be occupied after this by a smaller population, but no new large construction projects were initiated. The site was completely abandoned with the arrival of the Spanish conquerors in the early 16th century.
The abandoned site was overgrown with forest. In 1785 engineer Diego Ruiz visited the site and published the first description of the site. In the early 19th century it was visited by Guillermo Dupaix, Alexander von Humboldt, and Carlos Nebel, who published additional accounts.The first archeological excavation of the site was made by Jose Garcia Payon from 1943 through 1963. The Mexican Institute of Anthropology & History has made additional restoration to buildings at the site since the 1980s.
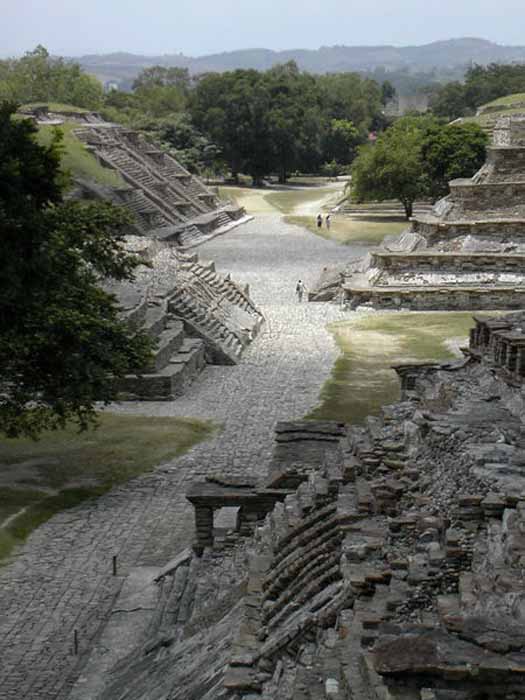

The ceremonial center of the site is covers only about 1 km square, but there are mostly nonexcavated remains of subsidiary buildings extending for a considerable distance beyond.The ceremonial center has number of temple-pyramids, palaces, and several courts for playing the Mesoamerican ballgame.
The site's most famous building is the Pyramid of the Niches. The step pyramid of 6 terraces is some 60 feet high. The size is only medium as Mesoamerican pyramids go, but the architecture creates a striking and visually pleasing effect. The terraces are of well cut stone forming a series of 365 niches. A staircase rises up the pyramid's east side. Originally the pyramid was topped by a temple, but little remains of this.
A number of the buildings have carved relief on them, and the site also has some free standing stone stelae. Many of the sculptures depict the ritual ballgame and ritual bloodletting by the elite. The site is now a tourism destination, has a moderate sized museum.
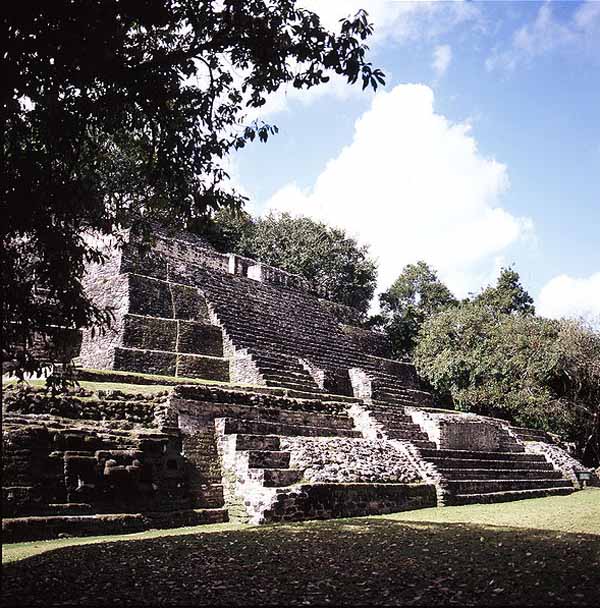

Lamanai (from Lama'anayin, "submerged crocodile" in Yucatec Maya) is a Mesoamerican archaeological site, and was once a considerably sized city of the Maya civilization, located in the north of Belize, in Orange Walk District. The site's name is pre-Columbian, recorded by early Spanish missionaries, and documented over a millennium earlier in Maya inscriptions as Lam'an'ain.
Lamanai was occupied as early as the 16th century BC. The site became a prominent centre in the Pre-Classic Period, from the 4th century BC through the 1st century CE. In 625 CE, "Stele 9" was erected there in the Yucatec language of the Maya. Lamanai continued to be occupied up to the 17th century AD. During the Spanish conquest of Yucatan Spanish friars established two Roman Catholic churches here, but a Maya revolt drove the Spanish out. The site was subsequently incorporated by the British in British Honduras, passing with that colony's independence to Belize.
The vast majority of the site remained unexcavated until the mid-1970s. Archaeological work has concentrated on the investigation and restoration of the larger structures, most notably the Mask Temple, Structure N10-9 ("Temple of the Jaguar Masks") and High Temple. The summit of this latter structure affords a view across the surrounding jungle to a nearby lagoon, part of New River.
A significant portion of the Temple of the Jaguar Masks remains under grassy earth or is covered in dense jungle growth. Unexcavated, it would be significantly taller than the High Temple.
The first detailed description of the ruins was made in 1917 by Thomas Gann. Archeological excavations at the site began in 1974 under David M. Pendergast of the Royal Ontario Museum, which continued through 1988. Further excavations and restoration work is being conducted as of 2004. The ruins are being excavated by a team from the nearby villages of Indian Church and San Carlos. The current project is co-directed by Dr. Elizabeth Graham (Institute of Archaeology, University College London) and Dr. Scott Simmons (University of North Carolina at Wilmington). Since 2006 research at the site has been directed mostly towards artifact analysis. Major excavations will resume when funding for more artifact processing, analyses and storage is acquired.

Lubaantun is a pre-Columbian ruined city of the Maya civilization in southern Belize, Central America. Lubaantun is in Belize's Toledo District, about 42 kilometres (26 mi) northwest of Punta Gorda, and approximately 3.2 kilometres (2 mi) from the village of San Pedro Columbia - at an elevation of 61 metres (200 ft) feet above mean sea level. One of the most distinguishing features of Lubaantun is the large collection of miniature ceramic objects found on site; these detailed constructs are thought to have been charmstones or ritual accompanying acoutrements.
The city dates from the Maya Classic era, flourishing from the AD 730s to the 890s, and seems to have been completely abandoned soon after. The architecture is somewhat unusual from typical Classical central lowlands Maya sites. Lubaantun's structures are mostly built of large stone blocks laid with no mortar, primarily black slate rather than the limestone typical of the region. Several structures have distinctive "in-and-out masonry"; each tier is built with a batter, every second course projecting slightly beyond the course below it. Corners of the step-pyramids are usually rounded, and lack stone structures atop the pyramids; presumably some had structures of perishable materials in ancient times.
The centre of the site is on a large artificially raised platform between two small rivers; it has often been noted that the situation is well-suited to military defense. The ancient name of the site is currently unknown; "Lubaantun" is a modern Maya name meaning "place of fallen stones".
A deluge of heavy rain near Lake Patzcuaro has triggered the collapse of an ancient pyramid in Michoacan, Mexico, just days after the iconic 'Double Arch' in Utah's Glen Canyon National Recreation Area came crashing down into Lake Powell. Both victims of an increasingly wild global climate IFL Science - August 12, 2024
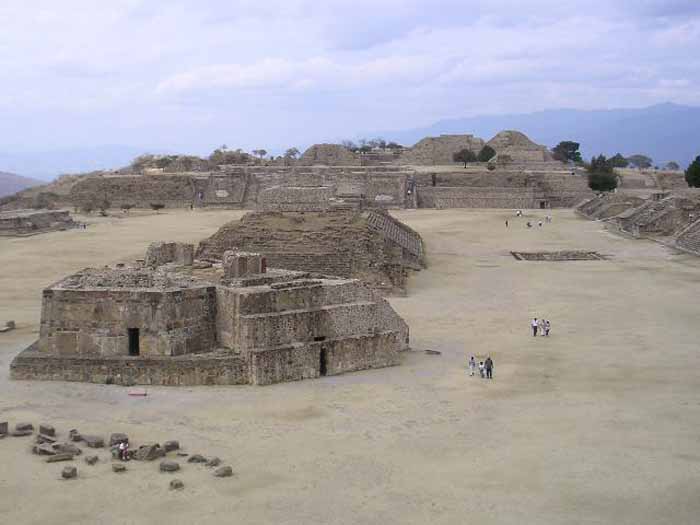

Monte Alban is a large archaeological site in the state of Oaxaca, Mexico, located at 17.02° N 96.45° W, elevation 1941 meters.The name "Monte Alban" means "White Mountain" in the Spanish language; the Zapotec name was Danipaguache, meaning "Sacred Mountain of Life".
The Aztecs knew it as Ocelotepec, or "Jaguar Mountain".
This sacred Mesoamerican city is on an artificially flattened mountain top some 400 meters above the city of Oaxaca.
Monte Alban was built over a period of over 2,000 years, starting about 900 BCE, by the Zapotec people. The early art shows Olmec influence. The most impressive building period was during the Mesoamerican Classic era, from about 550 CE to 1000 CE.
|About 1300 CE, the Zapotec were driven out of the site and surrounding area by the Mixtec people. The Mixtec made further additions to Monte Alban until they in turn were conquered by the Spanish Conquistadores in 1521, at which time Monte Alban was abandoned.
Monte Alban has many step-pyramids, temples, elite tombs, and a court for playing the Mesoamerican ballgame. There are also free-standing sculptured stelae, and large bas-relief carved panels in some of the buildings.
The oldest carved stones at the site are the so-called "Danzantes" (literally, dancers), featuring drawings of people in contorted and twisted poses. Although the notion that they depict a dance is generally discredited now, there is still little agreement on what exactly the figures represent, but many archaeologists think that the "dancers" are representations of tortured war prisoners. Some of the original stones can be viewed in the museum at the site.
Building J (the arrowhead-shaped building shown in the top picture) has also invited much speculation, due to its unusual shape and orientation. Alfonso Caso suggested it was an astrological observatory, though other theories have been offered.
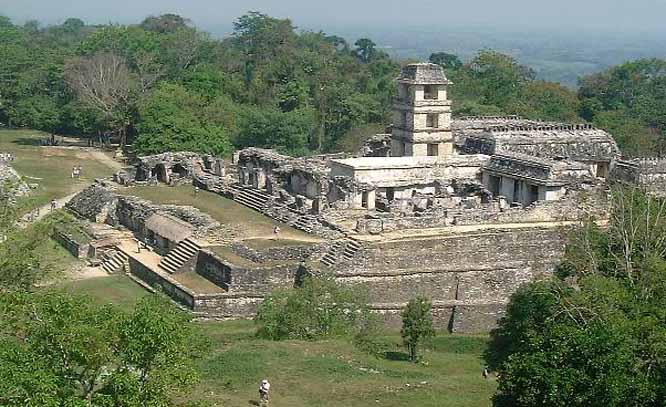

�Palenque is a Maya archeological site near the Usumacinta River in the Mexican state of Chiapas. It is a medium-sized site, much smaller than such huge sites as Tikal or Copan, but it contains some of the finest architecture, sculpture, roof comb and bas-relief carvings the Maya produced.
The site was already long abandoned when the Spanish arrived in Chiapas. The first European to visit the ruins and publish an account was Father Pedro Lorenzo de la Nada in 1567; at the time the local Chol Maya called it Otolum meaning "Land with strong houses", de la Nada roughly translated this into Spanish to give the site the name "Palenque", meaning "fortification". Palenque also became the name for the town (Santo Domingo del Palenque) which was built over some peripheral ruins down in the valley from the main ceremonial center of the ancient city.
An ancient name for the city was Lakam Ha, which translates as "Big Water" or "Wide Water", for the numerous springs and wide cascades that are found within the site. Palenque was the capital of the important classic-age Mayan city-state of B'aakal (Bone).
The Maya Classic City
While the site was occupied by the middle Pre-Classic, it did not gain importance until several hundred years later. By 600 the first of the famous structures now visible were being constructed. Situated in the western reaches of Maya territory, on the edge of the southern highlands, B'aakal was a large and vital center of Maya civilization from the 5th century AD to the 9th century.
The B'aakal state had a chequered career. Its original dynasts were perhaps Olmec. Politically, the city experienced diverse fortunes, being disastrously defeated by Kalakmul in 599 and again in 611.
Nevertheless, B'aakal produced what is arguably the best-known Maya Ajaw (king or lord), Pacal the Great, who ruled from 615 to 683, and left one of the most magnificent tomb-works of ancient Mesoamerica, beneath the Temple of Inscriptions. This is a grand temple atop a step pyramid dedicated in 692; inside is an elaborate, long hieroglyphic text carved in stone detailing the city's ruling dynasty and the exploits of Pacal the Great.
A stone slab in the floor could be lifted up, revealing a passageway (filled in shortly before the city's abandonment and reopened by archeologists) to a long interior stairway leading back down to ground level and the shrine/tomb of the semi-divine Pacal. Over his crypt is an elaborate stone showing him falling into the underworld, and taking the guise of one of the Maya Hero Twins in the Popul Vuh who defeated the lords of the underworld to achieve immortality.
Other important structures at Palenque include:
The site also has a number of other temples, tombs, and elite residences, some a good distance from the center of the site, a court for playing the Mesoamerican Ballgame, and an interesting stone bridge over the Otulum River some distance below the Aqueduct.

Odd Pyramid Had Rooftop Homes, Ritual Sacrifices? National Geographic - October 22, 2010
A newly excavated platform atop a pyramid at the Huaca Colorada site looks out on the Peruvian desert. it's yielded human remains - including five females who may have been ritually sacrificed. But it's the signs of life that make a half-excavated Peruvian pyramid of the Moche culture stand out, archaeologists say.
"Often these pyramidal mounds were built as mortuaries more than anything else," said excavation co-leader Edward Swenson. (See pictures from the tomb of the Moche "king of bling.") The newly exposed 1,400-year-old flat-topped pyramid supported residences for up to a couple dozen elites, who oversaw and perhaps took part in copper production at the site, evidence suggests. The pre-Inca pyramid dwellers likely presided over important rituals, feasted on roasted llama and guinea pig, and drank corn beer, according to archaeologists working at the site.
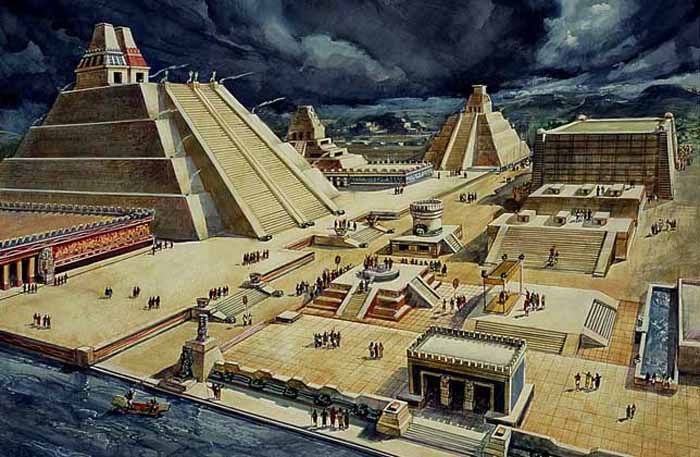

The Great Pyramid or Templo Mayor was the main temple of the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan (modern Mexico City). The temple rose 60 m (197 ft) above the city's ritual precinct, surmounted by dual shrines to the deities Huitzilopochtli (god of war and sun) and Tlaloc (god of rain and fertility). It was mostly destroyed in 1521 after the conquest of the Aztec empire by the Spanish conquistadores under the leadership of Hernan Cortes. Remains of the lower portions of the temple complex have been discovered by modern archaeologists buried under a portion of modern Mexico City.
Numerous smaller buildings and platforms associated with the temple formed a closely-situated complex around its base. A stucco relief depicting a tzompantli, or "skull rack", decorated one platform leading to the temple. The temple was enlarged several times, and for the last time in 1487. The Great Temple was excavated between 1978 and 1987 in a major project directed by Eduardo Matos Moctezuma.
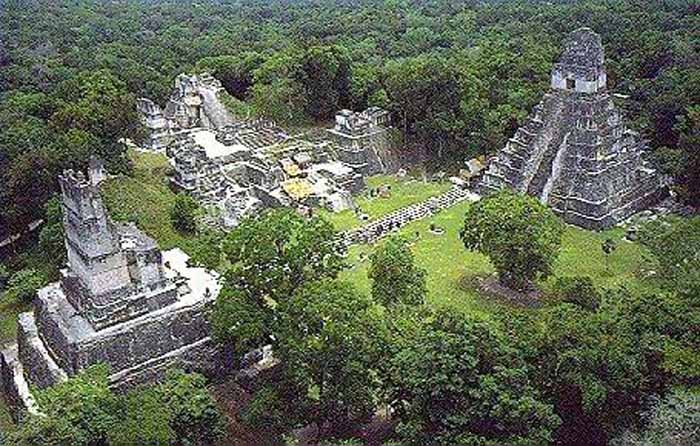


Tikal is the largest of the ancient ruined cities of the Maya civilization. It is located in the El Peten department of Guatemala. The ruins lay on lowland rainforest. Conspicuous trees at the Tikal park include gigantic ceiba (Ceiba pentandra) the sacred tree of the Maya; tropical cedar (Cedrela odorata), and mahogany (Swietenia). Regarding the fauna, agouti, spider monkeys, howler monkeys, ocellated turkeys, guans, toucans, green parrots and leaf-cutting ants can be seen there regularly. Jaguars and coatis are said to roam in the park.
Tikal was one of the major cultural and population centers of the Maya civilization. Monumental architecture was built here as early as the 4th century BC. The city was at its height in the Maya Classic Period, approximately 200 AD to 850 AD, after which no new major monuments were built, some of the palaces of the elite were burned, and the population gradually declined until the site was abandoned by the end of the 10th century.
The name "Tikal" means "Place of Voices" or "Place of Tongues" in Maya, which may be an ancient name for the city, although the ancient hieroglyphs usually refer to it as Mutal or Yax Mutal, meaning "Green Bundle", and perhaps metaphorically "First Prophecy".
Scholars estimate that at its peak its population was between 100,000 -- 200,000.
The site presents hundreds of significant ancient buildings, only a fraction of which have been excavated in the decades of archeological work.
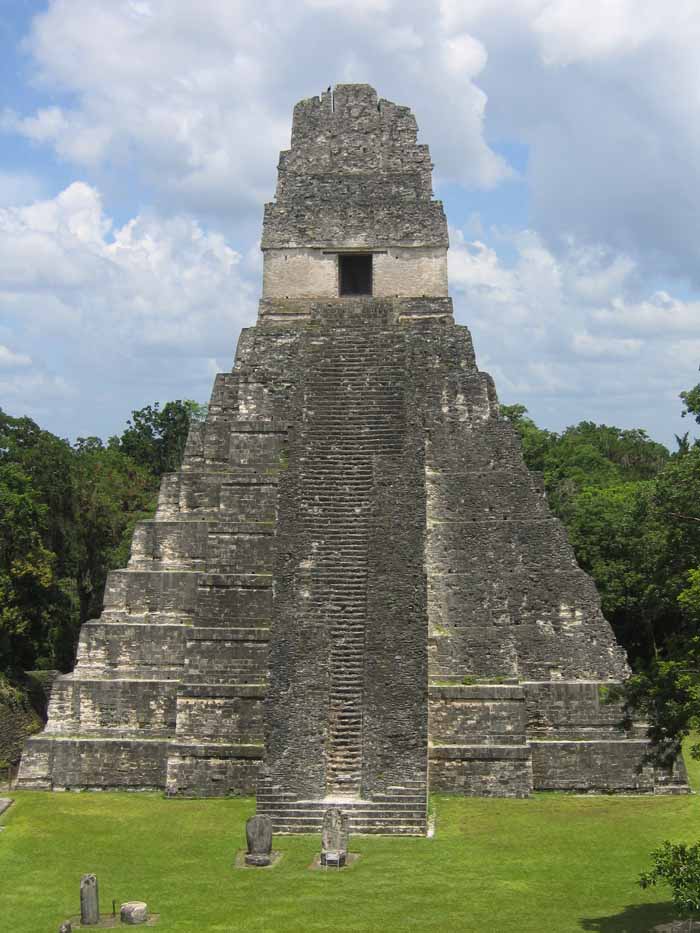
The most prominent surviving buildings include six very large step pyramids supporting temples on their tops. They were numbered geographically by early explorers. They were built during the city's height from the late 7th and early 9th century. Temple I was built around 695; Temple III in 810; The largest, Temple-pyramid IV, some 72 meters (230 feet) high, was dedicated in 720. Temple V is from about 750.
Temple VI was dedicated in 766.The ancient city also has the remains of royal palaces, in addition to a number of smaller pyramids, palaces, residences, and inscribed stone monuments. There is even a building which seemed to have been a jail, originally with wooden bars across the windows and doors. There are also several courts for playing the Mesoamerican ballgame.
The residential area of Tikal covers an estimated 60 square km (23 square miles), much of which has not yet been cleared or excavated.
Some of the pyramids of Tikal are over 60 meters high (200 feet).A huge set of earthworks has been discovered ringing Tikal with a 6 meter wide trench behind a rampart. Only some 9km of it has been mapped; it may have enclosed an area of some 125 km square.
Recently, a project exploring the earthworks has shown that the scale of the earthworks is highly variable and that in many places it is inconsequential as a defensive feature. In addition, some parts of the earthwork were integrated into a canal system. The earthwork of Tikal varies significantly in coverage from what was originally proposed and it is much more complex and multifaceted than originally thought.
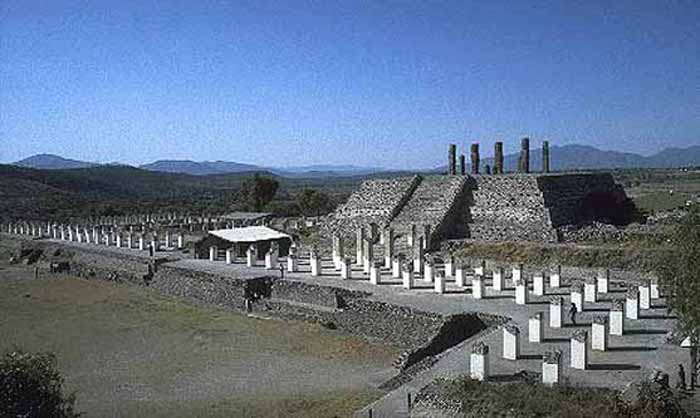
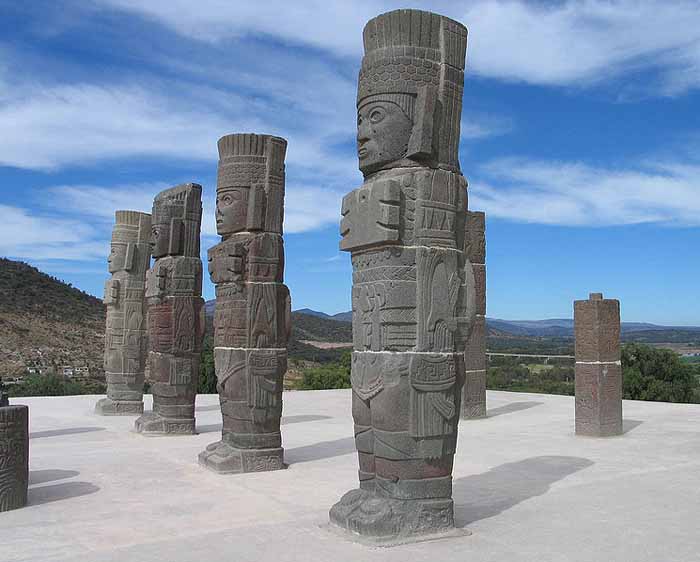


Tula is a town of 28,432 (2005 census) in the southwestern part of the state of Hidalgo in central Mexico, some 100 km to the north-northwest of Mexico City. The modern town is known as Tula de Allende; also a state municipality that covers part of the southeastern portion of the Pre-Columbian city. The present-day municipality has a population of 93,296 and an areal extent of 305.8 kms (118.07 sq mi), which includes numerous smaller outlying towns, the largest of which are El Llano, San Marcos, and San Miguel Vindho.
Nearby are the remains of the ancient capital city of the Toltecs, also known as "Tula" or as "Tollan". Usually identified as the Toltec capital around 980 CE, the city was destroyed at some time between 1168 or 1179.
The site is at and around the junction of two rivers, the Rio Rosas and the Rio Tula. The two largest clusters of grand ceremonial architecture are nicknamed "Tula Grande" (the most visited by tourists) and "Tula Chico". Remains of other buildings extend for some distance in all directions. In the residential areas streets were laid out in a grid pattern.
The city was the largest in central Mexico in the 9th and 10th centuries, covering an area of some 12 kms with a population of at least some 30,000, possibly significantly more. While it might have been the largest city in Mesoamerica at the time, some Maya sites in the Yucatan may have rivaled its population during this period.
Distinctive Toltec features here include terraced pyramids, colonnaded buildings, and relief sculptures, including the characteristic chacmools, reclining figures that may have been avatars of the rain god, Tlaloc. There are two large courts for playing the Mesoamerican ballgame. Some of the architecture is similar to that at Chichen Itza.
The site was extensively looted in Aztec times, with much of the artwork and sculpture carted off. The first scholarly description of the ruins was made by Antonio Garcia Cubas of the Mexican Society of Geography and History in 1873. The first archaeological excavations were conducted in the 1880s by French antiquarian Desire Charnay. A twenty year archaeological project under Jorge Acosta of Mexico's National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) began in 1940. In the 1970s further excavations and restorations of some structures were conducted by INAH and the University of Missouri Columbia.
Parts of the site are open for tourist visits, and Tula has a small museum.

Tzintzuntzan is a city in the state of Michoacan, Mexico. It stands on the eastern shore of Lake Patzcuaro, about 15 km north of the city of Patzcuaro and about 60 km west of state capital Morelia, and at some 2050 m above sea level. It serves as the administrative seat for the surrounding municipality of the same name and, in the 2000 census, reported a population of 3,610 people.
The city was founded in the 13th century by the Native American Tarascan or Purepecha nation, in whose language the name means "Place of the Hummingbirds".
The Pre-Columbian city of Tzintzuntzan covered an area of about 7 kms. The site, which stands on a hillside above the modern town, has the remains of many step pyramids of a design typically used by the P'urepecha in their ritual buildings, known locally as yacatas (by extension, the present-day archaeological site is also known as "Las Yacatas"). The Tzintzuntzan yacatas are of several different shapes, some rectangular, some oval or circular, and others in the distinctive Tarascan "T" shape. The population of the ancient city is estimated to have peaked at somewhere between 25,000 to 35,000 people.
The population of the entire Lake Patzcuaro basin was between 60,000 to 100,000, spread among 91 settlements of which Tzintzuntzan was the largest.
Tzintzuntzan was still the P'urhepecha capital when the Spaniards arrived in 1522. First contact, led by Nuno de Guzman arrived in 1529, Chieftain Tangaxuan II was burned alive and the city largely dismantled to provide stones for Roman Catholic temples and civic buildings, most notably the large 16th century Franciscan Monastery of Santa Ana. Following the disgrace and recall of Nuno de Guzman, Vasco de Quiroga was sent to the region, and Tzintzuntzan served as the headquarters of Spanish power in the area until the bishopric was relocated to Patzcuaro in 1540.
The modern town of Tzintzuntzan is known for the basketry and weaving produced there. The Monastery of Santa Ana is also still standing. It is home to several allegedly miraculous relics and icons and is reputed to have growing on its grounds what were the first olive trees to be planted in America.
Tzintzuntzan municipality covers a total of 165 kms. In addition to the municipal seat, the other main settlements are Ihuatzio, Cucuchuchu, and Los Corrales. In 1995, the municipality's total population numbered some 12,500, of whom 2550 spoke a Native American language (principally Purepecha and Ixcatec).
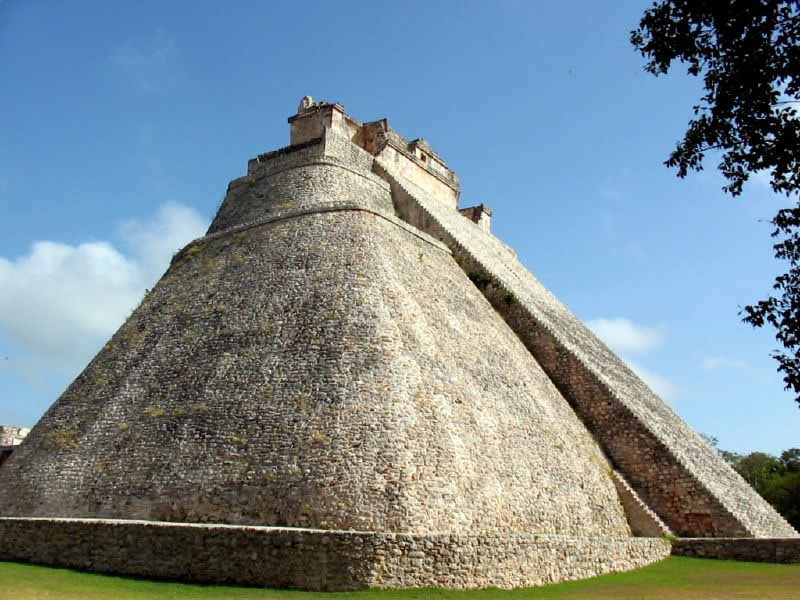

Uxmal is a large Pre-Columbian ruined city of the Maya civilization in the state of Yucatan, Mexico. Uxmal is pronounced "Oosh-mahl". The place name is Pre-Columbian and it is usually assumed to be an archaic Maya language phrase meaning "Built Three Times", although some scholars of the Maya language dispute this derivation.
Even before the restoration work Uxmal was in better condition than many other Maya sites thanks to being unusually well built. Much was built with well cut stones not relying on plaster to hold the building together. The Maya architecture here is considered matched only by that of Palenque in elegance and beauty. The Puuc style of Maya architecture predominates. Thanks to its good state of preservation, it is one of the few Maya cities where the casual visitor can get a good idea of how the entire ceremonial center looked in ancient times.
A number of temple-pyramids, quadrangles, and other monuments, some of significant size, and in varying states of preservation, are also at Uxmal. The majority of hieroglyphic inscriptions were on a series of stone stelae unusually grouped together on a single platform. The stelae depict the ancient rulers of the city, and they show signs that they were deliberately broken and toppled in antiquity; some were re-erected and repaired.A further suggestion of possible war or battle is found in the remains of a wall which encircled most of the central ceremonial center. A large raised stone pedestrian causeway links Uxmal with the site of Kabah, some 18 km to the south.
The site, located not far from Merida beside a road to Campeche, has attracted many visitors since the time of Mexico's independence. The first detailed account of the ruins was published by Jean Frederic Waldeck in 1838. John Lloyd Stephens and Frederick Catherwood made two extended visits to Uxmal in the early 1840s, with architect/draftsman Catherwood reportedly making so many plans and drawings that they could be used to construct a duplicate of the ancient city (unfortunately most of the drawings are lost).
Desire Charnay took a series of photographs of Uxmal in 1860. Some three years later Empress Carlota of Mexico visited Uxmal; in preparation for her visit local authorities had some statues and architectural elements depicting phallic themes removed from the ancient facades.
Sylvanus G. Morley made a map of the site in 1909 which included some previously overlooked buildings. The Mexican' governments first project to consolidate some of the structures from risk of collapse or further decay came in 1927.
In 1930 Frans Blom led a Tulane University expedition to the site which included making plaster casts of the facades of the "Nunnery Quadrangle"; using these casts a replica of the Quadrangle was constructed and displayed at the 1933 World's Fair in Chicago, Illinois.
In 1936 a further Mexican government repair and consolidation program was begun under Jose Erosa Peniche.
Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom visited on February 27, 1975 for the inauguration of the site's sound & light show; when the presentation reached the point where the sound system played the Maya prayer to Chaac, a sudden torrential downpour fell upon the gathered dignitaries, despite the fact that it was the middle of the dry season. Two hotels and a small museum have been built within the remains of the ancient city.

�Xochicalco is a pre-Columbian archaeological site in the western part of the Mexican state of Morelos. The name Xochicalco may be translated from Nahuatl as "in the (place of the) house of Flowers". The site is located 38 km southwest of Cuernavaca, about 76 miles by road from Mexico City. The apogee of Xochicalco came after the fall of Teotihuacan and it has been speculated that Xochicalco may have played a part in the fall of the Teotihuacan empire.
The architecture and iconography of Xochicalco show affinities with Teotihuacan, the Maya area, and the Matlatzinca culture of the Toluca Valley. Today some residents of the nearby village of Cuentepec speak Nahuatl. The main ceremonial center is atop an artificially leveled hill, with remains of residential structures, mostly unexcavated, on long terraces covering the slopes. The site was first occupied by 200 BC, but did not develop into an urban center until the Epiclassic period (A.D. 700 - 900). Nearly all the standing architecture at the site was built at this time. At its peak, the city may have had a population of up to 20,000 people.
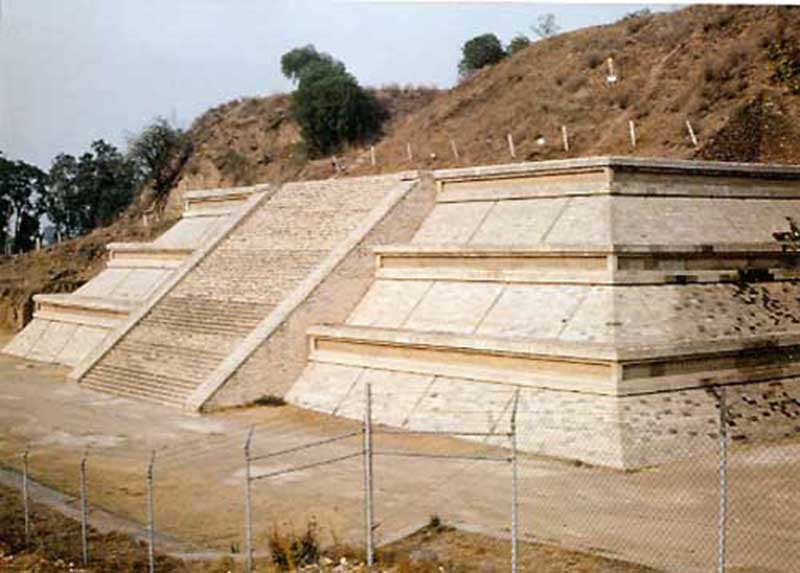

The Great Pyramid of Cholula, also known as Tlachihualtepetl (Nahuatl for "artificial mountain"), is a huge complex located in Cholula, Puebla, Mexico, and is the world's largest monument as well as the largest pyramid by volume.
The temple-pyramid complex was built in four stages, starting from the 3rd century BCE through the 9th century CE, and was dedicated to the deity Quetzalcoatl. It has a base of 450 by 450 m (1476x1476 ft) and a height of 66 m (217 ft). According to the Guinness Book of Records, it is in fact the largest pyramid as well as the largest monument ever constructed anywhere in the world, with a total volume estimated at over 4.45 million m3, even larger than that of the Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt which is about 2.5 million m3. However the Great Pyramid of Giza is higher at 138.8 m (455 feet). The Aztecs believed that Xelhua built the Great Pyramid of Cholula.
Today the pyramid at first appears to be a natural hill surmounted by a church. This is the Iglesia de Nuestra SeĖora de los Remedios (Church of Our Lady of the Remedies), also known as the Santuario de la Virgen de los Remedios (Sanctuary of the Virgin of the Remedies), which was built by the Spanish in colonial times (1594) on the site of a pre-Hispanic temple. The church is a major Catholic pilgrimage destination, and the site is also used for the celebration of indigenous rites. Many ancient sites in Latin America are found under modern Catholic holy sites, due to the practice of the Catholic Church repurposing local religious sites.
Because of the historic and religious significance of the church, which is a designated colonial monument, the pyramid as a whole has not been excavated and restored, as have the smaller but better-known pyramids at Teotihuacan. Inside the pyramid are some five miles (8 km) of tunnels excavated by archaeologists.