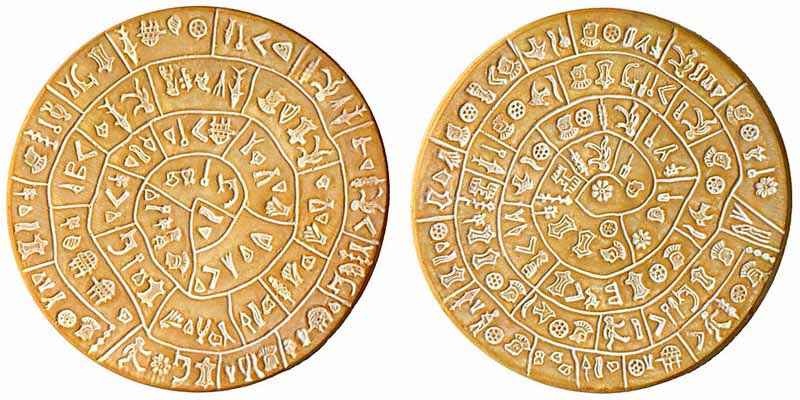



�Phaistos - also Phaestos and Phaestus - was an ancient city on the island of Crete. Map of Minoan CretePhaistos was located in the south-central portion of the island, about 3 1/2 miles from the sea. It was inhabited from about 4000 BC. A palace, dating from the Middle Bronze Age, was destroyed by an earthquake during the Late Bronze Age. Knossos and other Minoan sites were also destroyed at that time. The palace was later rebuilt toward the end of the Late Bronze Age. The area upon which Phaistos stood was the site where, in 1908, a curious clay disk, dating to about 1700 BC, and containing a sophisticated pictographic writing, was discovered. Its purpose and meaning, and even its original geographical place of manufacture, remain disputed.
The Phaistos Disk was discovered in the basement of room XL-101 of the Minoan palace-site of Phaistos, near Hagia Triada, on the south coast of Crete. Italian archaeologist Luigi Pernier recovered this remarkably intact "dish", about 15 cm in diameter and uniformly just over 1 cm thick, on July 3, 1908.
Luigi Pernier discovered the disc during his excavation of the first Minoan palace. It was found in the main cell of an underground "temple depository". These basement cells, only accessible from above, were neatly covered with a layer of fine plaster. Their context was poor in precious artifacts but rich in black earth and ashes, mixed with burnt bovine bones. In the northern part of the main cell, a few inches south-east of the disk, and about twenty inches above the floor, linear A tablet PH-1 was also found. The site apparently collapsed as a result of an earthquake, possibly linked with the explosive eruption of the Santorini volcano that affected large parts of the Mediterranean region ca. 1628 BC.
The inscription was made by pressing pre-formed hieroglyphic "seals" into the soft clay, in a clockwise sequence spiraling towards the disc's center. It was then baked at high temperature. There are a total of 241 figures on the disc. Many of the 45 different glyphs represent easily identifiable every-day things, including human figures, fish, birds, insects, plants, a boat, a shield, a staff, etc. In addition to these, there is a small diagonal line that occurs underneath the final sign in a group a total of 18 times. The disk shows traces of corrections made by the scribe in several places.
Although there is no official Unicode encoding for the symbols on the disk, the ConScript Unicode Registry has assigned a block of the Unicode Private Use Area to be used for the script. Two fonts include support for this area; Code2000 and Everson Mono Phaistos. The text on the disk is given on the second of these links; you can read that text if you have either of them installed.
Mysterious 4,000-Year-Old 'CD-ROM' Code Cracked Discovery - October 23, 2014
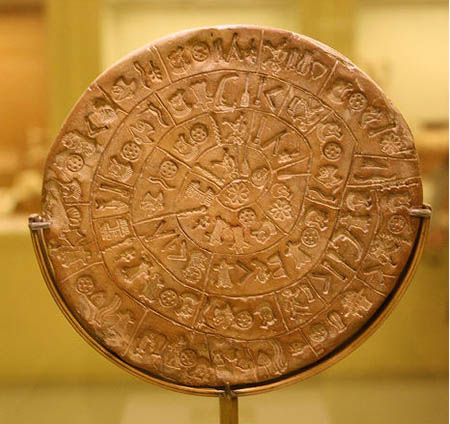

A fired-clay disk from the Second Millenium B.C. may finally have had some of its markings decoded. The mysterious "Phaistos disk," found in 1908 in a palace called Phaistos on the island of Crete, contains symbols on both sides, in a spiral configuration meant to be read from the outside toward the center. It is estimated to date from about 1,700 B.C. For better than a century, scientists have been trying to decode the meaning behind the symbols, and now Dr. Gareth Owens, of the Technological Educational Institute of Crete, says he has figured out some of its keywords and the general message it conveys. Using specific groups of symbols Owens says one side of the disk contains the translated wording "great lady of importance" while the other uses the expression "pregnant mother." One side, Owens says, is dedicated to a pregnant woman and the other to a woman giving birth.
There are a number of glyphs marked with an oblique stroke, the strokes are not imprinted but carved by hand and are attached to the first or last sign of a "word", depending on the direction of reading chosen. Their meaning is a matter of discussion. One hypothesis, supported by Evans, Duhoux, Ohlenroth and others, is that they were used to subdivide the text into paragraphs, but alternative meanings have been offered by other scholars.
From the diverse epigraphical facts (overcuts, angulous points of the spirals, corrections, etc.), it can be shown that the text has been written from the exterior to the center. The fact that most of the corrections were done on the spot, and other epigraphical facts, are showing that the scribe was "composing" his text in proportion as he was printing it. There is therefore no way to dissociate the direction of printing from the direction of reading.
A great deal of speculation developed around the disc during the 20th century. The Phaistos Disc captured the imagination of amateur archeologists. Alas, some of the more fanciful interpretations of its meaning are living classics of pseudoarchaeology.
Many attempts have been made to decipher the code behind the disc's glyphs. Historically, almost anything has been proposed, including prayers, a narrative or an adventure story, a "psalterion", a call to arms, a board game, and a geometric theorem. While many enthusiasts still believe the mystery can be solved, scholarly attempts at decipherment are thought to be unlikely to succeed unless more examples of the glyphs turn up somewhere, as it is generally thought that there isn't enough context available for meaningful analysis.
This general opinion is nevertheless disputed by several scholars on the basis of the work of the mathematician Claude Shannon. Shannon theory about the Unicity distance states that, in theory, the text's length is sufficient for reaching only one decipherment that makes sense. The problem is, however, that once there are reasons to think that a valid solution has been found, it is necessary to verify this solution by all means possible (generally by deciphering another text written in the same script), to be sure about it. Unfortunately until today no second disc was found, what makes the verification difficult.
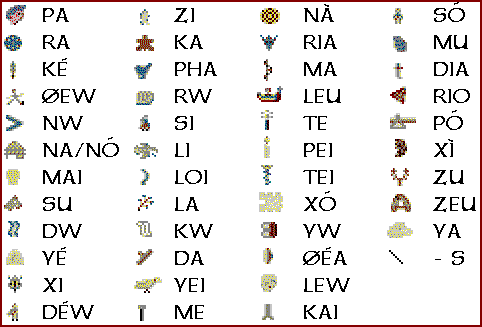
Some of the symbols were pictographs which means they represented the object depicted. Others functioned as ideograms in which the picture of, say, a boat, no longer means "boat" but expresses an idea like "travel". However, such associations of the object with its main qualities, uses, or features were usually direct, quite obvious, and widely recognized. Pictographs and ideograms are also usually much easier to understand intuitively than the syllabic and/or phonetic systems of writing which evolve from them as a means of expressing more abstract ideas in a particular language.
The uniqueness of this archaeological object is contested by at least two other apparently related specimens - a votive double axe found by Spyridon Marinatos in the Arkalohori Cave, Crete, and a fragment of a smaller clay disk, found at Vladikavkaz, North Ossetia. But both inscriptions were engraved, not made with stamps. Moreover, the first contains only superficially similar hieroglyphics, and the second, interesting as it might prove, disappeared mysteriously. So far, the Phaistos Disc remains a hapax.
This unique object is now on display at the archaeological museum of Heraklion in Crete, Greece.
Reference: Thomas Balistier The Phaistos Disc - An Account of its Unsolved Mystery
Token
Used in healing rituals or other ceremonies in ancient times
Legal document
Farmer's almanac
Schedule for palace activities as well as a site plan description for the palace of Phaistos
Story of the journey of humanity
The repeated combination of the Rosette with the bald head functions here like the cartouches on the Rosetta Stone that gave Thomas Young and Jean-Francois Champollion the first clues for their decipherment of the Egyptian hieroglyphs.
Symbols or messages from extraterrestrials who visited Earth thousands of years ago - stamping their imprint for future generations to find as they move through time
A Calendar System - Astronomical Calendarium in Harmony with the Mechanic of the Cosmos from a geocentrical view. Side B explains on 30 fields, including 12 peripheral fields and 5 completing-points (called Epagomenen by the ancient Egyptians) a year divided into 12 month x 30 days +5 days = 365 days. The 'Invisible Hand' of God directed the Sun-Path and the mechanic of the Cosmos. A 'Great Goddess' and a 'Highest Goddess' are connected with this Calender-Calculation of the mankind and the position of the sacrifice days. The relevant 'Great Year' shown on the Disk was July -2776 to July -1321. This is the beginning of the Time Calculation Method (Fish with two legs).
Crossword Puzzle or Game Board - There are those who feel the signs on the disc's fields were the markings for the fields of a board game which illustrated along its track the journeys of the sun god and the moon goddess, both in astronomical and mythological terms. That game had close parallels in ancient Egypt which allow the reconstruction of its main features and event fields. These fields coincide with many virtually identical fields in the still popular "Game of the Goose" and are often still in the same locations along the track of this "modern" game as on its direct predecessor from at least three dozen centuries ago. Continued
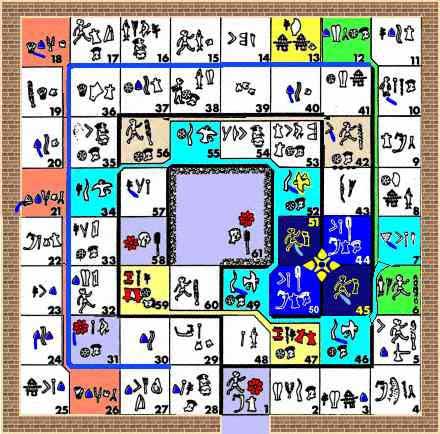
Portal or Stargate
