Leonardo da Vinci




Leonardo da Vinci (April 15, 1452 - May 2, 1519) was a celebrated Italian Renaissance architect, inventor, engineer, sculptor and painter. He has been described as the archetype of the Renaissance Man and as a universal genius.
Leonardo is well known for his masterful paintings, such as "The Last Supper" and "Mona Lisa". He is also known for his many inventions that were made well before their time but were never published in his lifetime. In addition, he helped advance the study of anatomy, astronomy, and civil engineering.
Life
His life was described in Giorgio Vasari's biography Vite.
Leonardo was born in Vinci, Italy. His father Ser Piero da Vinci was a well-off landowner or craftsman and his mother, Caterina, a peasant girl. It has been suggested that Caterina was a slave of middle eastern origin owned by Piero, but the evidence is scant.
This was before modern naming conventions developed in Europe. Therefore, his full name was "Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci", which means "Leonardo, son of Piero, from Vinci". Leonardo himself simply signed his works "Leonardo" or "Io, Leonardo" ("I, Leonardo"). Most authorities therefore refer to his works as "Leonardos," not "da Vincis." Presumably he did not use his father's name because he was an illegitimate child.
Leonardo grew up with his father in Florence. He was a vegetarian throughout his life. He became an apprentice to painter Andrea del Verrocchio about 1466. Later, he became an independent painter in Florence.
From 1482 to 1499 he worked for Ludovico Sforza, Duke of Milan and maintained his own workshop with apprentices there. Seventy tons of bronze that had been set aside for Leonardo's "Gran Cavallo" horse statue was cast into weapons for the Duke to save Milan from the French under Charles VIII in 1495 - see also Italian Wars.
When the French returned under Louis XIII in 1498, Milan fell without a fight, overthrowing Sforza. Leonardo stayed in Milan for a time, until one morning he found French archers using his life-size clay model for the "Gran Cavallo" for target practice. He left with Salai and his friend (and inventor of double-entry bookkeeping) Luca Pacioli for Mantua, moving on after 2 months for Venice, then moving again to Florence at the end of April 1500.
In Florence he entered the services of Cesare Borgia (also called "Duca Valentino" and son of Pope Alexander VI) as military architect and engineer. In 1506 he returned to Milan, now in the hands of Maximilian Sforza after Swiss mercenaries drove out the French. There he met Francesco Melzi, who would become a close friend and companion until Leonardo's death, and later his heir.
From 1513 to 1516 he lived in Rome, where painters like Raphael and Michelangelo were active at the time; he did not have much contact with these artists, however.
In 1515 Francis I of France retook Milan, and Leonardo was commissioned to make a centrepiece (of a mechanical lion) for the peace talks in Bologna between the French king and Pope Leo X, where he must have first met the king. In 1516, he entered Francis' service, being given the use of the manor house Clos LucÚ next to the king's residence at the Royal Chateau at Amboise, and receiving a generous pension. The king became a close friend.
He died in Cloux, France in 1519. According to his wish, 60 beggars followed his casket. He was buried in the Chapel of Saint-Hubert in the castle of Amboise.
Leonardo appears to never have had intimate relations with women. In 1476 he was anonymously accused of homosexual contact with a 17-year-old model, Jacopo Saltarelli, a notorious prostitute. He was, together with three other young men, charged with homosexual conduct and acquitted because of lack of evidence. For a time Leonardo and the others were under the watchful eye of Florence's "Officers of the Night" - a kind of Renaissance vice squad.
According to Robert Payne, a biographer of Leonardo, believes that he loved women and men equally. Most modern scholars believe that one of Leonardo's lovers was Salai, A.K.A., Gian Giacomo Caprotti. Salai was Leonardo's servant and assistant.


Mona Lisa - 1503-06
Leonardo often planned grand paintings with many drawings and sketches, only to leave the projects unfinished in the end.
In 1481 he was commissioned to paint the altarpiece "The Adoration of the Magi". After grand plans and many drawings, the painting was left unfinished and Leonardo left for Milan.
There he spent many years making plans and models for a monumental 7 metre (24 feet) high horse statue in bronze ("Gran Cavallo"), to be erected in Milan. Because of war with France, the project was never finished. Based on private initiative, a similar statue was completed according to some of his plans in 1999 in New York, given to Milan and erected there.
Back in Florence, he was commissioned for a large public mural Battle of Anghiari; his rival Michelangelo was to paint the opposite wall. After producing a fantastic variety of studies preparing for the work, he left town, the mural unfinished because of technical difficulties.
Maybe even more impressive than his artistic work are his studies in science and engineering, recorded in notebooks comprising some 13,000 pages of notes and drawings which combine art and science. He was left-handed and used mirror writing throughout his life.
His approach to science was an observatory one: he tried to understand a phenomenon by describing and depicting it in utmost detail and did not emphasize experiments or theoretical explanations. Throughout his life, he planned a grand encyclopedia based on detailed drawings of everything. Since he lacked formal education in Latin and mathematics, Leonardo the scientist was mostly ignored by contemporary scholars.
He participated in autopsies and produced many extremely detailed anatomical drawings, planning a comprehensive work of human and comparative anatomy. Around the year 1490, he produced a study in his sketchbook of the Canon of Proportions as described in recently rediscovered writings of the Roman architect Vitruvius. The study, called the Vitruvian Man, is one of his most well-known works.
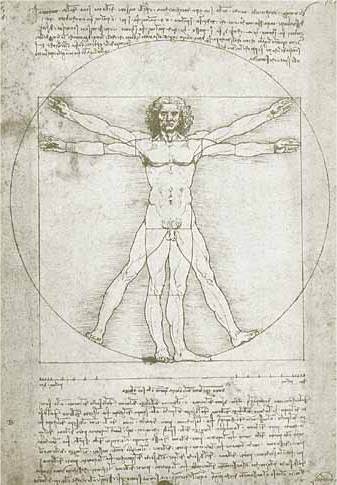
His study of human anatomy led eventually to the design of the first known robot in recorded history. The design, which has come to be called Leonardo's robot, was probably made around the year 1495.
His study of human anatomy led eventually to the design of the first known robot in recorded history. The design, which has come to be called Leonardo's robot, was probably made around the year 1495 but was rediscovered only in the 1950s. It is not known if an attempt was made to build the device.
He was always fascinated by the topic of flight, producing detailed studies of the flight of birds and plans for several flying machines, including a helicopter powered by four men (which would not have worked since it would have rotated) and a light hang-glider which could have flown. On January 3, 1496 he unsuccessfully tested a flying machine he had constructed.
In 1502 Leonardo da Vinci produced a drawing of a single span 720-foot (240 m) bridge as part of a civil engineering project for Sultan Beyazid II of Constantinople. The bridge was intended to span an inlet at the mouth of the Bosphorus known as the Golden Horn. It was never built, but Da Vinci's vision was resurrected in 2001 when a smaller bridge based on his design was constructed in Norway.
His notebook also contain several inventions in the military field: machine guns, an armored tank powered by humans or horses, cluster bombs, etc. even though he later held war to be the worst of human activities. Other inventions include a submarine, a cog-wheeled device that has been interpreted as the first mechanical calculator, and a car powered by a spring mechanism. In his years in the Vatican, he planned an industrial use of solar power, by employing concave mirrors to heat water.
In astronomy, Leonardo believed that the Sun and Moon revolve around the Earth and that the Moon reflects the sun's light because it was covered by water.
Leonardo did not publish or otherwise distribute the contents of his notebooks. They remained obscure until the 19th century, and were not directly of value to the development of science and technology until that time. On this basis, L. Sprague de Camp, in his book, The Ancient Engineers, considered Leonardo not the first modern engineer, but "the last of the ancient ones", pointing out that after Leonardo's time the practice of disseminating and publishing scientific discoveries began in earnest.
- Wikipedia Read More and Links

Discovery - April 25, 2004
A spring-propelled car conceived by Leonardo da Vinci five centuries ago could have paved the way for the Mars rovers, an eight-month study of a drawing by the Renaissance genius has revealed.
Drawn on sheet number 812r of the Atlantic Codex in 1478, when Leonardo was 24 years old, the sketch has been translated into a one-third scale model at the Institute and Museum of the History of Science in Florence.
Amazingly, the wooden 5-foot by 5-foot, 6-inch model, on display at the museum until June 5, has proved what has been doubted for centuries: the machine actually moves.
"It is the world's first self-propelled vehicle. It was designed to operate as a robot and could travel for about 40 meters. It featured a programmable steering and a brake that could be released at distance by an operator with a hidden rope," Paolo Galluzzi, director of the museum, told Discovery News.
Basically anticipating the car, the contraption was conceived as a special effect machine at Renaissance festivals. It would have worked like a child- spring propelled toy, with the springs wound up by rotating the wheels in the opposite driving direction. Leonardo probably envisaged someone hiding behind a curtain who would pull the string to release the brake.
As well as other drawings in which Leonardo (1452-1519) anticipated inventions such as the airplane, the helicopter, submarine, the steam engine, the tank, and many other devices, the sheet of Atlantic Codex do not contain a single word of explanation.
For centuries scholars puzzled over the drawing. Several attempts were made to recreate the vehicle, but none worked. "Everybody thought that Leonardo powered the car with the two big leaf springs shown in his sketch. Instead, the power is provided by coiled springs inside the tambours," Galluzzi said.
The new interpretation came from Carlo Pedretti, director of the Armand Hammer Center for Leonardo Studies in Los Angeles, who noticed a kind of squiggle in the sketch eventually identified as coiled springs.
With the help of U.S. robotics expert Mark Rosheim, the museum first created a digital model, then a fully functioning model.
The model showed that the programmable steering mechanism, consisting of wooden blocks arranged between gears, allows the spring-propelled vehicle to go straight, or turn at pre-set angles, but only to the right.
"The model has revealed a wonderful complexity that now is very clear. Looking at it carefully, it does resemble the Spirit space vehicle used on Mars," Pedretti told Discovery News.
Leonardo da Vinci Scientist - Inventor - Artist
Leonardo da Vinci BBC Homepage
The Mystery, Art, and Science of Water: Leonardo and Water
Leonardo da Vinci - Virtual Tour
Artcyclopedia
Leonardo da Vinci - Son of a slave? Discovery
Leonardo Bridge Project
Leonardo da Vinci's Horse
Fusion Anamoly - Science - Math - Metaphysics
Charles Gilchrist - Sacred Geometry

Leonardo da Vinci was like a man who awoke too early
in the darkness, while the others were all still asleep.
~ Sigmund Freud ~

