JUDAH
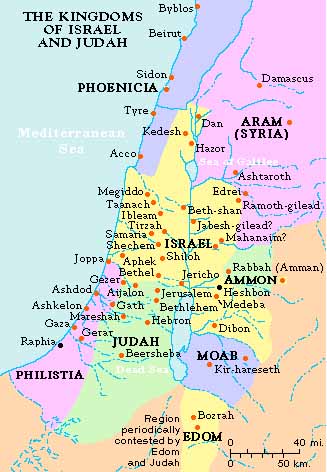

The tribe of Judah was named for Jacob's fourth son, Judah. When the Israelites entered the Promised land, the area allotted to Judah was a large area from the Mediterranean running just south of Jerusalem to the Dead Sea, as far south as Kadesh Barnea and west to the Wadi of Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea. Some of the southwest of this area was given to Simeon and the land along the Mediterranean coast was still inhabited by Philistines.
The kingdom that David united ended when Solomon's son Rehoboam vowed to rule harshly. The northern tribes established a separate government under the leadership of Jeroboam I in 922 B.C. and only the southern tribes remained loyal to Rehoboam.
The southern kingdom was known as "Judah." Judah was governed by kings from David's line for several centuries.
Some of Judah's kings were favorable toward the worship of Baal, but Hezekiah and later Josiah introduced religious reforms.
There were ongoing tensions with Israel to the north. For a time, Israel and Syria tried to pressure Judah into joining them in resisting Assyria. Judah refused.
The Assyrians captured Samaria in the north and besieged Jerusalem, but they were not able to capture the city.
The end of the kingdom of Judah came as Assyria's power waned and Egypt and Babylonia struggled for dominance.
The Babylonians prevailed and captured Jerusalem in 587 after a siege.
Many of the leading people of Judah were taken into exile in Babylonia, where they remained until some were permitted to return nearly fifty years lat
ALPHABETICAL INDEX OF ALL FILES