
A Wet moon (also called a Cheshire moon and in some cases a Dry moon) is a lunar phase when the "horns" of the crescent moon point up at an angle, away from the horizon. This is caused when the crescent of the moon, during its orbit around the Earth, displays the result of that orbit as well as that of Earth's orbit around the Sun.
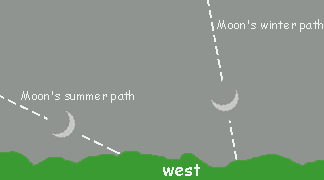
During the course of six months, the moon's path appears to move slightly southward in the sky, relative to the stars. This "movement" of the moon slowly changes its relative place to the horizon, as the motion of the Earth changes its tilt relative to the plane in which the moon orbits.
During summertime in the northern hemisphere, when the hemisphere tilts towards the Sun, the side of the Earth in nightfall is pointed away from the moon's orbit, making the lunar path appear closer to the southern horizon. This effect also causes the moon to appear lower in the night sky.
Dry moon/Cheshire moon - This process is reversed during wintertime in the northern hemisphere, causing the moon's path to appear nearly vertical to the western horizon, as well as causing the moon to appear higher in the night sky.
The terms Wet moon and Dry moon originate from Hawaiian mythology, where it was thought that the moon appeared as a bowl which would fill up with rain. The period where this is most common, January 20 - February 18, corresponds with Kaelo the Water Bearer in Hawaiian astrology and makes the moon known as the "Dripping wet moon". As the year passes into summer, the crescent shape shifts, pouring out the water and causing the summer rains. After the "bowl" empties, it dries out and rights itself, creating the "dry moon".
The term "Cheshire moon" is a reference to the smile of the Cheshire Cat of Lewis Carroll's story Alice's 'Adventures in Wonderland.'
Cheshire Moon Wikipedia