

The origins and evolutionary relationships between the three main groups of amphibians are hotly debated. A molecular phylogeny based on rDNA analysis dating from 2005 suggests salamanders and caecilians are more closely related to each other than they are to frogs and the divergence of the three groups took place in the Paleozoic or early Mesozoic before the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea and soon after their divergence from the lobe-finned fishes. This would help account for the relative scarcity of amphibian fossils from the period before the groups split. Read more ...
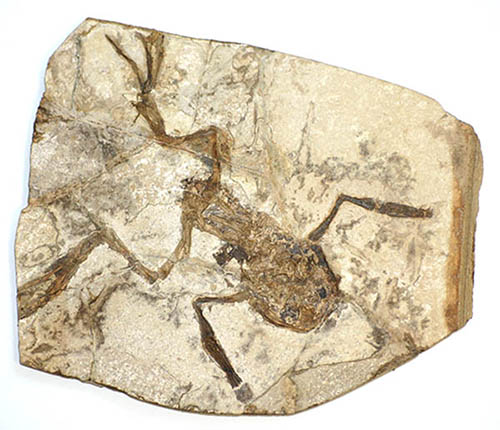
Massive Fossil Breaks Record as The World's Oldest Tadpole
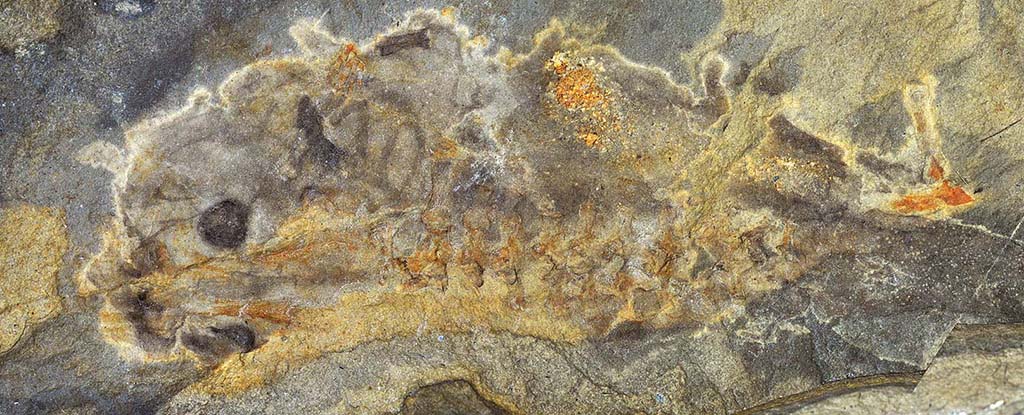
At more than 160 million years old, a recently discovered amphibian fossil has set a new record for the earliest known tadpole. And it's a doozy, stretching almost 16 centimeters (or 6 inches) in length. The impression represents the only known example of a larva from an ancient frog called Notobatrachus degiustoi . Since adults of the species have been found at a similar size, it's hypothesized the chunky pollywog could have been close to its metamorphosis phase. Scientists suspected key characteristics of tadpole evolution arose during a period of time when stem anurans - the evolutionary ancestors of modern frogs and toads - diversified rapidly, at around the cusp of the Triassic and Jurassic periods.
Paleontologists have identified fossil fragments of what are thought to be the oldest known frogs in North America. Science Daily - February 27, 2019
The fossils are comprised of several small pieces of hip bone, called an ilium, from Chinle frogs, a distant long-extinct branch of, but not a direct ancestor of, modern frogs. The fragments are packed into rock and are smaller than a pinky nail. They represent the first known and earliest equatorial remains of a salientian - the group containing living frogs, and their most-closely related fossil relatives - from the Late Triassic, roughly 216 million years ago.
Prehistoric frogs in amber surface after 99 million years BBC - June 15, 2018
Frogs trapped in amber for 99 million years are giving a glimpse of a lost world. The tiny creatures have been preserved in sticky tree resin since the end of the Age of the Dinosaurs. The four fossils give a window into a world when frogs and toads were evolving in the rainforests. Amber from Myanmar, containing skin, scales, fur, feathers or even whole creatures, is regarded as a treasure trove by paleontologists.
'Frog-amander' Fossil Fills Evolutionary Gap Live Science - May 21, 2008
A frog-like creature with a stubby tail once paddled through a quiet pond in what is now Texas, snapping up mayflies while keeping an ear out for bellowing mates, new fossil evidence suggests. That was about 290 million years ago. This amphibian is from near to the point where frogs and salamanders first split.
70-million-year-old fossil of a giant frog has been unearthed in Madagascar BBC - February 19, 2008
A 70-million-year-old fossil of a giant frog has been unearthed in Madagascar by a team of UK and US scientists. The creature would have been the size of a "squashed beach ball" and weighed about 4kg (9lb), the researchers said. They added that the fossil, nicknamed Beelzebufo or "frog from hell", was "strikingly different" from present-day frogs found on the island nation.
Fossil frogs yield 'soft tissues' BBC - July 26, 2006
Scientists have extracted marrow from the bones of frogs and salamanders that died 10 million years ago in the muddy swamps of north-eastern Spain. The first fossilized bone marrow known to science provides a rare insight into the make-up of prehistoric animals. It is preserved in remarkable detail; usually only hard tissue such as bone survives in the fossil record. The soft tissue may yield traces of protein and DNA, researchers report in the journal Geology. Bone marrow is the tissue that fills the centre of large bones, acting as a factory for producing new platelets and red and white blood cells.

Frogs
ANCIENT AND LOST CIVILIZATIONS