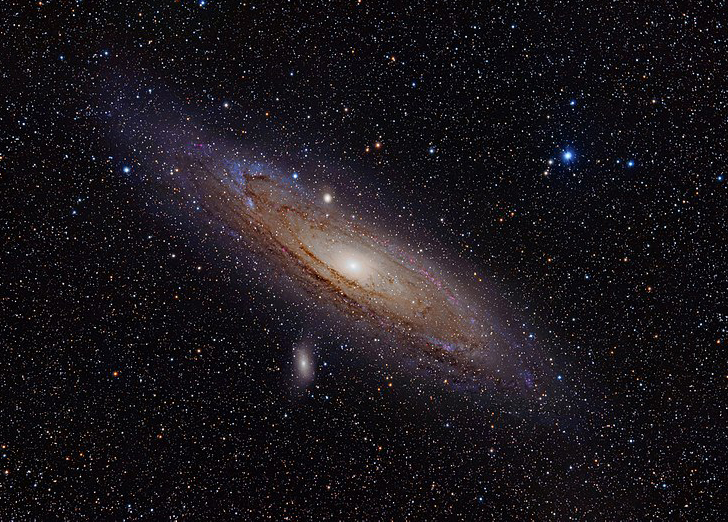


The Andromeda Galaxy also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 780 kiloparsecs (2.5 million light-years) from Earth, and the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way. Its name stems from the area of the Earth's sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda. The 2006 observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope revealed that the Andromeda Galaxy contains approximately one trillion stars, more than twice the number of the Milky Way's estimated 200 to 400 billion stars. The Andromeda Galaxy's mass is estimated to be around 1.76 times that of the Milky Way Galaxy though a 2018 study found that the Andromeda Galaxy's mass is roughly the same as that of the Milky Way.
The Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies are expected to collide in ~4.5 billion years, merging to form a giant elliptical galaxy or a large disc galaxy. With an apparent magnitude of 3.4, the Andromeda Galaxy is among the brightest of the Messier objects making it visible to the naked eye from Earth on moonless nights, even when viewed from areas with moderate light pollution. Read more
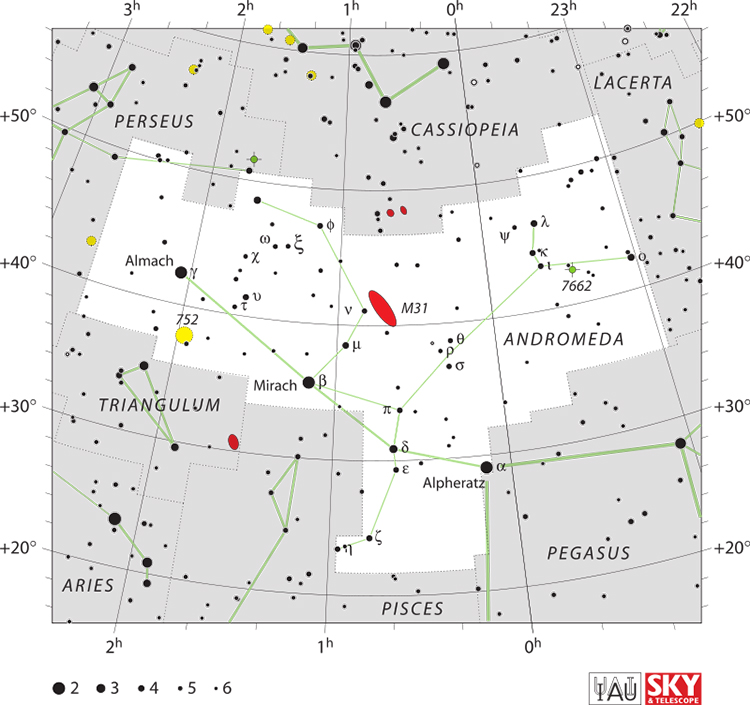
Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40¡ south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux.
Its brightest star, Alpha Andromedae, is a binary star that has also been counted as a part of Pegasus, while Gamma Andromedae is a colorful binary and a popular target for amateur astronomers. Only marginally dimmer than Alpha, Beta Andromedae is a red giant, its color visible to the naked eye. The constellation's most obvious deep-sky object is the naked-eye Andromeda Galaxy (M31, also called the Great Galaxy of Andromeda), the closest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way and one of the brightest Messier objects. Several fainter galaxies, including M31's companions M110 and M32, as well as the more distant NGC 891, lie within Andromeda. The Blue Snowball Nebula, a planetary nebula, is visible in a telescope as a blue circular object.
In Chinese astronomy, the stars that make up Andromeda were members of four different constellations that had astrological and mythological significance; a constellation related to Andromeda also exists in Hindu mythology. Andromeda is the location of the radiant for the Andromedids, a weak meteor shower that occurs in November. Read more
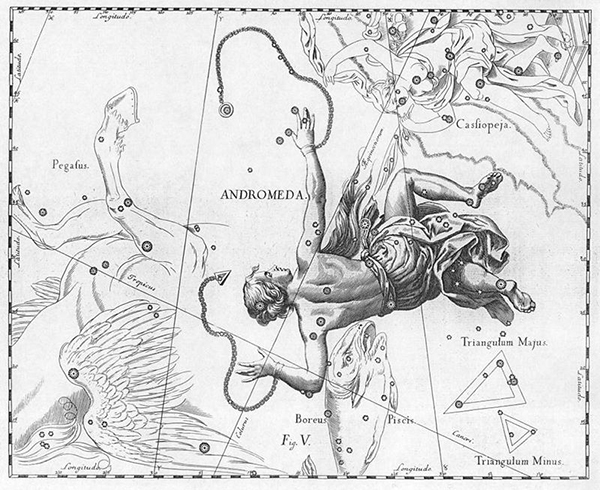
Andromeda is a princess from Greek mythology who, as divine punishment for her mother's bragging, (the Boast of Cassiopeia) was chained to a rock as a sacrifice to a sea monster. She was saved from death by Perseus, her future husband. Her name is the Latinized form of the Greek. The subject has been popular in art since classical times. In the Christian period the subject was converted into the legend of St George and the Dragon, but from the Renaissance interest revived in the original story, typically as derived from Ovid's account.
In Greek mythology, Andromeda was the daughter of Cepheus and Cassiopeia, king and queen of the kingdom Ethiopia.
Her mother Cassiopeia boasted that she was more beautiful than the Nereids, the nymph-daughters of the sea god Nereus and often seen accompanying Poseidon. To punish the Queen for her arrogance, Poseidon, brother to Zeus and god of the sea, sent a sea monster (Cetus) to ravage the coast of Ethiopia including the kingdom of the vain Queen. The desperate King consulted the Oracle of Apollo, who announced that no respite would be found until the king sacrificed his virgin daughter Andromeda to the monster. She was chained naked to a rock on the coast.
Perseus was returning from having slain the Gorgon Medusa, he found Andromeda and slew Cetus by approaching invisible with Hades's helm and slaying him. He set her free, and married her in spite of Andromeda having been previously promised to her uncle Phineus. At the wedding a quarrel took place between the rivals, and Phineus was turned to stone by the sight of the Gorgon's head (Ovid, Metamorphoses v. 1).
Andromeda followed her husband to Tiryns in Argos, and together they became the ancestors of the family of the Perseidae through the line of their son Perses. Perseus and Andromeda had seven sons: Perseides, Perses, Alcaeus, Heleus, Mestor, Sthenelus, and Electryon, and one daughter, Gorgophone. Their descendants ruled Mycenae from Electryon down to Eurystheus, after whom Atreus attained the kingdom, and would also include the great hero Heracles. According to this mythology, Perseus is the ancestor of the Persians.
After her death, Andromeda was placed by Athena amongst the constellations in the northern sky, near Perseus and Cassiopeia. The constellation had been named after her. Read more
Astronomers identify 20 ultraviolet-emitting supernova remnants in the Andromeda Galaxy PhysOrg - February 2, 2023
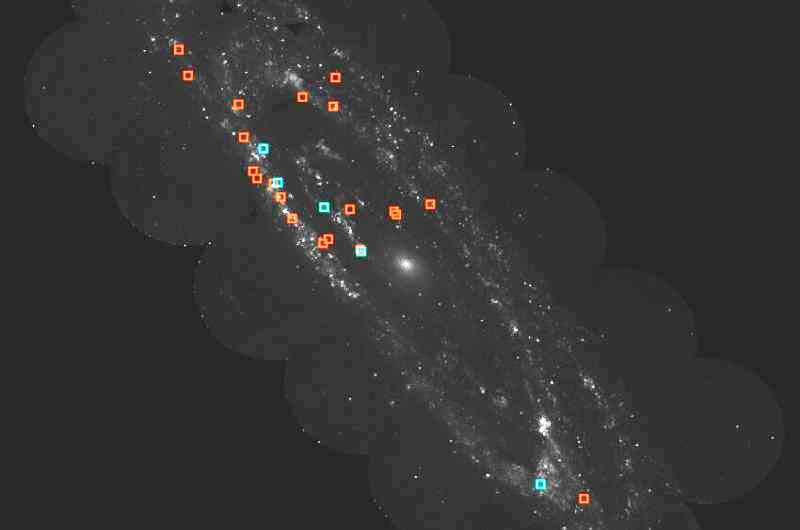

Using the AstroSat satellite, astronomers from the University of Calgary, Canada, have identified 20 supernova remnants (SNRs) in the Andromeda Galaxy, which exhibit diffuse ultraviolet emission.
Hubble maps giant halo around Andromeda Galaxy Science Daily - August 29, 2020

In a landmark study, scientists using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have mapped the immense halo of gas enveloping the Andromeda galaxy, our nearest large galactic neighbor. Scientists were surprised to find that this tenuous, nearly invisible halo of diffuse plasma extends 1.3 million light-years from the galaxy - about halfway to our Milky Way - and as far as 2 million light-years in some directions. This means that Andromeda's halo is already bumping into the halo of our own galaxy. They also found that the halo has a layered structure, with two main nested and distinct shells of gas. This is the most comprehensive study of a halo surrounding a galaxy.
An Andromeda Signal - From No Known Particle or Atom Daily Galaxy - February 9, 2019

Astronomers think they may have detected the first real signal from the 'dark universe.' While studying data collected by the European Space Agency's XMM-Newton spacecraft this past September 2018, a team of researchers observed an odd spike in X-ray emissions that corresponds to no known particle or atom and thus may have been produced by dark matter coming from two different celestial objects: the Andromeda Galaxy a swirling metropolis of a trillion stars, black holes and globular clusters (shown at top and bottom of the page) - and the Perseus Galaxy Cluster.
Andromeda galaxy will deliver a 'glancing blow' to our Milky Way later than expected Mashable - February 9, 2019

Astronomers have long suspected that the colossal Andromeda galaxy would, in billions years, collide with our humble Milky Way.
The collision was forecast to happen in some 3.9 billion years. But after astronomers analyzed new data captured by the European Space Agency's star-surveying satellite Gaia, they now put the imminent date at 4.5 billion years - so 600 million years later than initially expected. The event is characterized as a "swipe" rather than a direct collision. The end result would be a merger of the galaxies into one, monstrous galaxy.
The Milky Way and Andromeda Loom Over a Dutch Sailboat in a Breathtaking Vertical Panorama Space.com - January 25, 2019

Above the boat, you can see two galaxies - our great Milky Way, which stretches across the frame, and the diffuse elliptical shape of the Andromeda galaxy, one of the Milky Way's galactic neighbors. Andromeda appears as a small smudge in the image, located about halfway between the Milky Way and the boat.